Abstract
Objective
To study the renal function in term newborns with perinatal asphyxia including urinary excretion of β2 microglobulin (β2M).
Methods
This case control study included 50 term newborn babies with perinatal asphyxia and 50 normal babies as matched controls. In all cases, asphyxia grading (using Apgar score) and Hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) staging (Sarnat and Sarnat) were done. Blood and urinary parameters (including β2M) for renal function were done in all and Fractional excretion of sodium (FENa) and Renal failure index (RFI) were calculated. The renal parameters were compared within subgroups as well as controls using analysis of variance test and the independent samples t test.
Results
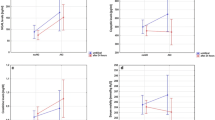
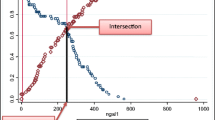
Acute kidney Injury (AKI) was noted in 56 % of cases (24 % prerenal and 32 % intrinsic type). All 9 babies who died had AKI. Serum parameters like urea, creatinine, sodium and potassium had better correlation with the renal function as compared to urine parameters. All individual urine parameters except β2M showed wide variations. FENa, RFI and urinary β2M increased with increasing severity of asphyxia and HIE staging.
Conclusion
AKI is common in term babies with perinatal asphyxia. FENa and RFI are useful parameters for assessing the renal function and urinary β2M is a good biomarker for diagnosis and prognosis of acute tubular injury in term babies with perinatal asphyxia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perlman JM, Tack ED, Martin T, Shackelford G, Amon E. Acute systemic organ injury in term infants after asphyxia. Am J Dis Child. 1989;143:617–20.
Durkan AM, Alexander RT. Acute kidney injury post neonatal asphyxia. J Pediatr. 2011;158:e29–33.
el-Mauhoub M, Kishan J, Jaiswal OP, Asbali AA, el houni N. Urinary beta 2-microglobulin as an indicator of proximal renal tubular dysfunction in asphyxiated full-term newborns. Pediatr Nephrol. 1994;8:787.
Kaur S, Jain S, Saha A, Chawla D, Parmar VR, Basu S, et al. Evaluation of glomerular and tubular renal function in neonates with birth asphyxia. Ann Trop Paediatr. 2011;31:129–34.
Jayashree G, Dutta AK, Sarna MS, Saili A. Acute renal failure in asphyxiated newborns. Indian Pediatr. 1991;28:19–23.
Misra PK, Kumar A, Natu SM, Kapoor RK, Srivastava KL, Das K. Renal failure in symptomatic perinatal asphyxia. Indian Pediatr. 1991;28:1147–51.
Ashraf M, Ahmed N, Chowdhary J, Saif RU. Acute renal failure: Nephrosonographic findings in asphyxiated neonates. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2011;22:1187–92.
Mondal N, Bhat BV, Banupriya C, Koner BC. Oxidative stress in perinatal asphyxia in relation to outcome. Indian J Pediatr. 2010;77:515–7.
Espinel CH. The FENa test. Use in the differential diagnosis of acute renal failure. JAMA. 1976;236:579–81.
McGuire W. Perinatal asphyxia. Clin Evid (Online) 2007;2007. pii: 0320.
Perlman JM, Tack ED. Renal injury in the asphyxiated newborn infant: Relationship to neurologic outcome. J Pediatr. 1988;113:875–9.
Nouri S, Mahdhaoui N, Beizig S, Zakhama R, Salem N, Ben Dhafer S, et al. Acute renal failure in full term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Prospective study of 87 cases. Arch Pediatr. 2008;5:229–35.
Agras PI, Tarcan A, Baskin E, Cengiz N, Gürakan B, Saatci U. Acute renal failure in the neonatal period. Ren Fail. 2004;26:305–9.
Aggarwal A, Kumar P, Chowdhary G, Majumdar S, Narang A. Evaluation of renal functions in asphyxiated newborns. J Trop Pediatr. 2005;51:295–9.
Gupta BD, Sharma P, Bagla J, Parakh M, Soni JP. Renal failure in asphyxiated neonates. Indian Pediatr. 2005;42:928–34.
Askenazi DJ, Ambalavanan N, Goldstein SL. Acute kidney injury in critically ill newborns: What do we know? What do we need to learn? Pediatr Nephrol. 2009;24:265–74.
Aldana VC, Romaro MS, Vargas OA, Hernández AJ. Acute complications in full term neonates with severe neonatal asphyxia. Ginecol Obstet Mex. 1995;63:123–7.
Goodwin TM, Belai I, Hernandez P, Durand M, Paul RH. Asphyxial complications in the term newborn with severe umbilical acidemia. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1992;167:1506–12.
Karlowicz MG, Adelman RD. Nonoliguric and oliguric acute renal failure in asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995;9:718–22.
Mathew OP, Jones AS, James E, Bland H, Groshong T. Neonatal renal failure: Usefulness of diagnostic indices. Pediatrics. 1980;65:57–60.
Coca SG, Yalavarthy R, Concato J, Parikh CR. Biomarkers for the diagnosis and risk stratification of acute kidney injury: A systematic review. Kidney Int. 2008;73:1008–16.
Askenazi DJ, Koralkar R, Hundley HE, Montesanti A, Parwar P, Sonjara S, et al. Urine biomarkers predict acute kidney injury in newborns. J Pediatr. 2012;161:270–5.
Sarafidis K, Tsepkentzi E, Agakidou E, Diamanti E, Taparkou A, Soubasi V, et al. Serum and urine acute kidney injury biomarkers in asphyxiated neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27:1575–82.
Fernandez F, Barrio V, Guzman J, Huertas MD, Zapatero M, de Miguel MD, et al. Beta-2-microglobulin in the assessment of renal function in full term newborns following perinatal asphyxia. J Perinat Med. 1989;17:453–9.
Martin AA, Garcia AA, Gaya F, Cabanas F, Burgueros M, Quero J. Multiple organ involvement in perinatal asphyxia. J Pediatr. 1995;127:786–93.
Contributions
JK collected and analyzed data; BVB designed and supervised the study; BCK helped with the biochemical investigations and BA drafted manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karlo, J., Bhat, B.V., Koner, B.C. et al. Evaluation of Renal Function in Term Babies with Perinatal Asphyxia. Indian J Pediatr 81, 243–247 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1068-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-013-1068-x