Abstract
Objective
To establish normal reference standards for six minute walk test of children aged between 7–12 y in India.
Methods
Healthy children aged between 7 to 12 y were recruited randomly from the selected schools in India. 400 children were included .Six minute walk test (MWT) was performed according to standardized ATS guidelines. Distance walked in 6 min, Heart rate (HR), Blood pressure (BP), Oxygen saturation, anthropometric measurements and level of dyspnea were taken as outcome measures.
Results
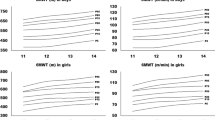
Mean distance walked in 6 min was 609 ± 166 m, with significant difference between boys and girls( p < 0.001). Boys covered more distance than girls. Heart rate increased from a baseline of 82.73 ± 1.63 to a maximum of 104.32 ± 3.11; heart rate recovery occurred at 5 min in both the genders. SBP increased from baseline 109 ± 2.38 to maximum of 121.86 ± 1.75 at the end of the test, with no significant increase in DBP which was 68.51 ± 2.21 and 69 ± 2.78 at the end of the test. No significant change in oxygen saturation and dyspnea was observed during the test. Mean oxygen saturation was 97% at baseline, with an immediate drop of 96%.
Conclusions
In this study, the mean distance covered in 6 min by boys was 670.74 ± 86.21 m and girls were 548.93 ± 44.78 m.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li AM, Yin J, Yu WC, et al. The six—minute walk test in healthy children: reliability and validity. Eur Respir J. 2005;25:1057–60.
Lammers AE, Hislop AA, Flynn Y, Haworth SG. The 6- minute walk test: normal values for children of 4–11 y of age. Arch Dis Child. 2008;93:464–8.
Li AM, Yin J, Au JT, et al. Standard reference for the six-minute-walk test in healthy children aged 7 to 16 y. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:174–80.
Geiger R, Strasak A, Treml B, et al. Six-minute walk test in children and adolescents. J Pediatr 2007;150:395–9.
Solway S, Brooks D, Lacoose Y, Thomas S. A qualitative systemic overview of the measured properties of functional walk tests used in cardio respiratory domain. Chest. 2001;119:256–70.
Noonan V, Dean E. Submaximal exercise testing: clinical application and interpretation. Phys Ther. 2000;80:8.
Downie AP, Anderson JM, Innocenti DM, Jackson SE. Cash text book of chest, heart and vascular disorder for physiotherapists. 4th ed. New Delhi: Jaypee; 1987. p. 336–37.
American Thoracic Society. ATS statement. Guidelines for the six minute walk test. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;166:111–7.
Enright PL. The six minute walk test. Respir Care. 2003;48:783–5.
Deigo S, Kendrick K, Baxi SC, Smith RM. Usefulness of the modified 0–10 Borg scale in assessing the degree of dyspnea in patients with COPD and asthma. J Emerg Nurs. 2000;26:216–22.
Khadilkar VV, Khadilkar AV, Cole TJ, Sayyad MG. Cross-sectional growth curves for height, weight and body mass index for affluent Indian children, 2007. Indian Pediatr. 2009;46:477–89.
Mahon AD, Anderson CS, Hipp MJ, Hunt KA. Heart rate recovery from submaximal exercise in boys and girls. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2003;35:2093–7.
Cole CR, Blackstone EH, Pashkow FJ, et al. Heart-rate recovery immediately after exercise as a predictor of mortality. N Engl J Med 1999;341:1351–7.
Dimpka U. Post –exercise heart rate recovery: an index of cardiovascular fitness. JEP online. 2009;12:16–22.
Singh TP, Rhodes J, Gauvreau W. Determinants of heart rate recovery following exercise in children. Med Sci Sports Exer. 2008;40:601–5.
Turley KR, Wilmore JH. Cardiovascular responses to submaximal exercise in 7- to 9-yr-old boys and girls. Med Sci Sports Exer. 1997;29:824–32.
Bar O, Rowland WT. Paediatric exercise medicine from physiological principles to health care application. 1st ed. USA: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins; 2004. p. 30–2.
Washington RL, Bricker JT, Alpert BS, et al. Guidelines for exercise testing in the pediatric age group from the committee on atherosclerosis and hypertension in children council on cardiovascular disease in the young, AHA. Circulation. 1994;90:2166–79.
Paridon MS, Alpert SB, Boas RS, et al. Clinical stress testing in the pediatric age group A statement from the American heart association council on cardiovascular disease in the young, committee on atherosclerosis, hypertension, and obesity in youth. Circulation. 2006;113:1905–20.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all the teachers and staff of the schools, parents and children for their support, and active participation in this study.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of funding Source
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’silva, C., Vaishali K & Venkatesan, P. Six-Minute Walk Test-Normal Values of School Children Aged 7–12 Y in India: A Cross-Sectional Study. Indian J Pediatr 79, 597–601 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-011-0559-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-011-0559-x