Abstract
Objective
To assess the association of nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) and complications of Kawasaki disease (KD) in Chinese children.
Methods
Based on color Doppler examination results, 86 affected children in the KD group were divided into two groups: 39 cases in coronary artery lesion group (CALs subgroup) and 47 cases in non-coronary artery lesion group (Non-CALs subgroup). Infection control group consisted of 65 cases of hospitalized infected children with fever, having same age as the affected children. Healthy control group consisted of 102 cases of healthy children of the same age, visiting the hospital for physical examination. Western blot was used to detect the expression of NF-кBp65 and IкBα proteins in periphery blood mononuclear cells (PBMC); reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was used to detect the expression of TNF-α and MCP-1 mRNA.
Results
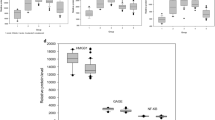
The value of NF-kBp65 (optical density) in the PBMC cell nuclei in the KD group was significantly higher than that in the two control groups (p < 0.01). The value of NF-κBp65 in the CALs subgroup was significantly higher than that in the Non-CALs subgroup (p < 0.05). The value of NF-κBp65 inhibitor IκBα in the KD group was significantly lower than that in the infection control group and the healthy control group (p < 0.01). There was a positive correlation between the ratio nucleus NF-κBP65/ IκBα and the severity degree of CALs(r = 0.536, p < 0.05). The value of TNF-α mRNA (O.D ratio) in the KD group was significantly higher than that in the two control groups (P < 0.01), and the value of TNF-α mRNA in the CALs subgroup was significantly higher than that in the Non-CALs subgroup (P < 0.05). The value of MCP-1 mRNA in the KD group was significantly higher than that in the two control groups (P < 0.01), and the value of MCP-1 mRNA in the CALs subgroup was significantly higher than that in the Non-CALs subgroup (P < 0.05).
Conclusions
NF-κBp65 participates in the pathogenesis of vasculitis of KD in acute stage, and may aggravate the vasculitis in KD and plays a part in the formation of CALs.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rowley AH, Shulman ST. Kawasaki disease. In: Behrman RE, Kliegma RM, Arivin AM, Jenson HB, editors. Nelson textbook of pediatrics. 16th ed. Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders; 2000. p. 725–7.
Newburger JW, Fulton DR. Kawasaki disease. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2004;16:508–14.
Ichiyama T, Yoshitomi T, Nishikawa M, et al. NF-kappaB activation in peripheral blood monocytes/macrophages and T cells during acute Kawasaki disease. Clin Immunol. 2001;99:373–7.
Whiteside ST, Israel A. IκB proteins: structure, function and regulation. Semin Cancer Biol. 1997;8:75–82.
Collart MA, Baeuerle PA, Vassalli P. Regulation of tumor necrosis factor alpha transcription in macrophages: involvement of four κB-like motifs and of constitutive and inducible forms of NF-κB. Mol Cell Biol. 1990;10:1498–507.
Vincenti MP, Burrell TA, Taffet SM. Regulation of NF-κB activity in murine macrophages: effect of bacterial lipopolysaccharide and phorbolester. J Cell Physiol. 1992;150:204–15.
Ahn SY, Jang GC, Shin JS, et al. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels and promoter polymorphism in patients with Kawasaki disease in Korea. Yonsei Med J. 2003;44:1021–6.
Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, et al. Use of laboratory data to identify risk factors of giant coronary aneurysms due to Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Int. 2004;46:33–8.
Okopien B, Haberka M, Cwalina L, et al. Plasma cytokines as predictors of coronary heart disease. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol. 2002;112:5–15.
Terai M, Jibiki T, Harada A, et al. Dramatic decrease of circulating levels of monocyte chemoattractant Protein-1 in Kawasaki disease after gamma globulin treatment. J Leukoc Biol. 1999;65:566–72.
Noursadeghi M, Pepys MB, Gallimore R, et al. Relationship of granulocyte colony stimulating factor with other acute phase reactants in man. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;140:97–100.
Sha WC. Regulation of immune responses by NF-κB/Rel transcription factors. J Exp Med. 1998;187:143–6.
Krause I, Shoenfeld Y. Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment for fibrosis, atherosclerosis, and malignant conditions. Methods Mol Med. 2005;109:403–8.
Kagoshima M, Ito K, Cosio B, et al. Glucocorticoid suppression of nuclear factor-kappa B: a role for histone modifications. Biochem Soc Trans. 2003;31:60–5.
Picado C, Bioque G, Roca-Frrer J, et al. Nuclear factor-kappaB activity is down-regulated in nasal polyps from aspirin-sensitive asthmatics. Allergy. 2003;58:122–6.
Ziegelbauer K, Gantner F, Lukacs NW, et al. A selective novel low- molecular- weight inhibitor of IkappaB kinase-beta (IKK-beta) prevents pulmonary inflammation and shows broad anti-inflammatory activity. Br J Pharmacol. 2005;170:736–42.
Contributions
YW; in charge of experiment design, case collection and essay writing, WX; involved in statistical analysis and data process, DY; involved in case collection and RT-PCR, PH; in charge of western blot and RT-PCR, L Ya-li; in charge of experiment director, W R-g, Y Ya- ling, X Jun-hui, K Shi-xiu; involved in case collection.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Role of Funding Source
This study was supported by a grant from the Wuhan Science and technology committee.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, W., Wang, X., Ding, Y. et al. Expression of Nuclear Factor -κBp65 in Mononuclear Cells in Kawasaki Disease and its Relation to Coronary Artery Lesions. Indian J Pediatr 78, 1378–1382 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-011-0478-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-011-0478-x