Abstract
Objective
To detect subtelomeric copy number variations (deletions and duplications) using Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) technique in children with idiopathic mental retardation.
Methods
All children presenting to the genetics out-patient department for evaluation of mental retardation or developmental delay over a period of two years, for whom no identifiable cause could be found by clinical evaluation, karyotyping, neuroimaging and other relevant investigations.
Results
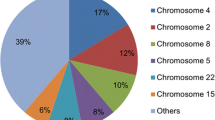
In the present study, two cases deletions and one case of duplication were detected amongst 65 cases with idiopathic mental retardation/ global developmental delay. The overall detection rate is 4.6%. The detection rate is higher (13%) in children with facial dysmorphism.
Conclusion
MLPA for subtelomeric regions is recommended for evaluation of children with idiopathic mental retardation/ global developmental delay were included in the study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rauch A, Hoyer J, Guth S, Zweier C, Kraus C, Becker C. Diagnostic yield of various genetic approaches in patients with unexplained developmental delay or mental retardation. Am J Med Genet A 2006; 140:2063–2074.
Popp S, Schulze B, Granzow M et al. Study of 30 patients with unexplained developmental delay and dysmorphic features or congenital abnormalities using conventional cytogenetics and multiplex FISH telomere (M-TEL) integrity assay. Hum Genet 2002; 111:31–39.
De Vries BBA, Winter R, Schinzel A, van Ravenswaaij-Arts C. Telomeres: a diagnosis at the end of the chromosomes. J Med Genet 2003; 40:385–398.
Koolen DA, Nillesen WM, Versteeg MH et al. Screening for subtelomeric rearrangements in 210 patients with unexplained mental retardation using multiplex ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA). J Med Genet 2004;41:892–899.
Temtamy SA, Kamel AK, Ismail S et al. Phenotypic and cytogenetic spectrum of 9p trisomy. Genet Couns 2007; 18:29–48.
Ruiter EM, Koolen DA, Kleefstra T et al. Pure subtelomeric microduplications as a cause of mental retardation. Clin Genet 2007;72:362–368.
Shevell M, Ashwal S, Donley D et al. Practice parameter: evaluation of the child with global developmental delay—report of the Quality Standards Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology and the Practice Committee of the Child Neurology Society. Neurology 2003;60:367–380.
Moeschler JB, Shevell M. Committee on Genetics. Clinical Genetic Evaluation of the Child With Mental Retardation or Developmental Delays. Pediatrics 2006;117;2304–2316.
Irons M. Use of subtelomeric fluorescence in situ hybridization in cytogenetic diagnosis. Curr Opin Pediatr 2003;15:594–597.
Battaglia A, Filippi T, Carey JC. Update on the clinical features and natural history of Wolf-Hirschhorn (4p-) syndrome: experience with 87 patients and recommendations for routine health supervision. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet 2008;148C:246–251.
Kondoh T, Shimokawa O, Harada N et al. Genotypephenotype correlation of 5p-syndrome: pitfall of diagnosis. J Hum Genet 2005;50:26–29.
Rooms L, Reyniers E, van Luijk R et al. Subtelomeric deletions detected in patients with idiopathic mental retardation using multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA). Hum Mutat 2004;23:17–21.
Rooms L, Reyniers E, Wuyts W et al. Multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification to detect subtelomeric rearrangements in routine diagnostics. Clin Genet 2006; 69:58–64.
Moeschler JB. Medical genetics diagnostic evaluation of the child with global developmental delay or intellectual disability. Curr Opin Neurol 2008;21:117–122
Shao L, Shaw CA, Lu XY, Sahoo T et al. Identification of chromosome abnormalities in subtelomeric regions by microarray analysis: a study of 5,380 cases. Am J Med Genet A 2008;146A:2242–2251
Palomares M, Delicado A, Lapunzina P et al. MLPA vs multiprobe FISH: comparison of two methods for the screening of subtelomeric rearrangements in 50 patients with idiopathic mental retardation. Clin Genet 2006;69:228–233.
Erjavec-Škerget A, Stangler-Herodeğ S, Zagorac A, Zagradišnik B, Kokalj-Vokač N. Subtelomeric Chromosome Rearrangements in Children with Idiopathic Mental Retardation: Applicability of Three Molecular-cytogenetic Methods. Croat Med J 2006; 47:841–850.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mandal, K., Boggula, V.R., Borkar, M. et al. Use of Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) in screening of subtelomeric regions in children with idiopathic mental retardation. Indian J Pediatr 76, 1027–1031 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0218-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-009-0218-7