Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy and safety of Bifilacℳ on reducing the episodes (frequency) and duration of diarrhea induced by rotaviral infection and to evaluate the efficacy of Bifilacℳ to ameliorate the associated symptoms like dehydration and duration of rotaviral shedding in faeces.
Methods
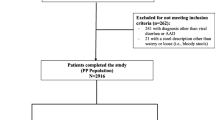
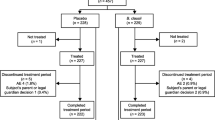
80 children aged between 3 months and 3 years were enrolled and divided into 2 groups, one group received standard therapy + placebo, the other group received standard therapy + probiotic (Bifilac) randomly. Children assessed for frequency and duration of diarrhea. Degree of dehydration, duration and volume of oral rehydration salt [ORS] therapy, duration and volume of Intra venous fluids and duration of rotaviral shedding.
Results
When compared to the placebo, Bifilac showed clinical as well as statistically significant reduction in Number of episodes (frequency) of diarrhea in a day, mean duration of diarrhea (in days) degree of dehydration, duration and volume of oral rehydration salt [ORS] therapy, duration and volume of intravenous fluid [IVF] therapy, duration of rotaviral shedding (P<0.01).
Conclusion
The synbiotic, bifilac, appears to be a safe and very effective adjuvant in the management of acute rotaviral diarrhea.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Perdigon G, Alvarez S, Rachid M, Agüero G, Gobbato N. Immune stimulation by probiotics. J Dairy Sci 1995; 78: 1597–1606.[Abstract/Free Full Text]
Duffy LC, Zielezny MA, Riepenhoff-Talty M et al. Reduction of virus shedding by B. bifidum in experimentally induced MRV infection. Dig Dis Sci 1994; 39: 2334–2340.[Medline]
Isolauri E, Juntunen M, Rautanen T, Sillanaukee P, Koivula T. A human Lactobacillus strain (Lactobacillus casei sp strain GG) promotes recovery from acute diarrhea in children. Pediatrics 1991; 88: 90–97.[Abstract]
Isolauri E, Kaila M, Mykkanen H, Ling WH, Salminen S. Oral bacteriotherapy for viral gastroenteritis. Dig Dis Sci 1994; 39: 2595–2600.[Medline]
Kaila M, Isolauri E, Saxelin M, Arvilommi H, Vesikari T. Viable versus inactivated lactobacillus strain GG in acute rotavirus diarrhoea. Arch Dis Child 1995; 72: 51–53.[Abstract]
Kaila M, Isolauri E, Virtanen E, Laine S, Arvilommi H. Enhancement of the circulating antibody secreting cell response in human diarrhea by a human Lactobacillus strain. Pediatr Res 1992; 32: 141–144.[Abstract]
Majamaa M, Isolauri E, Saxelin M, Vesikari T. Lactic acid bacteria in the treatment of acute rotavirus gastroenteritis. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1995; 20: 333–338.[Medline]
Shornikova A-V, Isolauri E, Burnakova L, Lukovnikova S, Vesikari T. A trial in the Karelian Republic of oral rehydration and Lactobacillus GG for treatment of acute diarrhoea. Acta Paediatr 1997; 86: 460–465.[Medline]
Pant AR, Graham SM, Allen SJ et al. Lactobacillus GG and acute diarrhea in young children in the tropics. J Trop Pediatr 1996; 42: 162–165.[Medline]
Guarino A, Canani RB, Spagnuolo MI, Albano F, Di Benedetto L. Oral bacterial therapy reduces the duration of symptoms and of viral excretion in children with mild diarrhea. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr 1997; 25: 516–519.[Medline]
Isolauri E, Joensuu J, Suomalainen H, Luomala M, Vesikari T. Improved immunogenicity of oral D × RRV reassortant rotavirus vaccine by Lactobacillus casei GG. Vaccine 1995; 13: 310–312.[Medline]
Saavedra JM, Bauman NA, Oung I, Perman JA, Yolken RH. Feeding of Bifidobacterium bifidum and Streptococcus thermophilus to infants in hospital for prevention of diarrhea and shedding of rotavirus. Lancet 1994; 344: 1046–1049.[Medline].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayanappa, D. Randomized double blinded controlled trial to evaluate the efficacy and safety of Bifilac in patients with acute viral diarrhea. Indian J Pediatr 75, 709–713 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0134-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12098-008-0134-2