Abstract
Purpose
Several angiogenic prognostic markers are under investigation because of their potential clinical utility, aiming to improve patient outcomes. We hypothesized that genetic variant in the VEGF pathway could be used as prognostic markers of survival in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing pulmonary resection.
Methods
We evaluated the relationship between genetic variants in the VEGF pathway and relapse-free survival (RFS, main endpoint) and overall survival (OS, secondary endpoint) among 131 patients with stage I–III NSCLC treated with surgical resection from 2009 to 2013. Clinical, pathological and surgical data were prospectively collected. Twenty-five variants in sixteen relevant genes were selected and genotyped in tumor samples by real time PCR. The Kaplan–Meier method with the log-rank test and Cox’s regression models were used for RFS and OS analyses.
Results
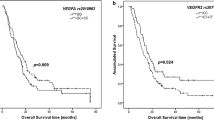
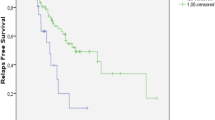
With a median follow-up of 36 (min = 2.8; max = 67.4) months, there were 31 (24%) relapses and 31 (24%) deaths. Overall, median RFS was not reached and median OS was 65 [95% confidence interval (CI) 56–75] months. The KRAS rs1137282 and PIK3C2A rs4356203 variants were significantly associated with RFS. For KRAS rs1137282, the 3-year RFS was 76% [95% CI 64–84%] in patients harboring an A/A genotype compared to 53% [95% CI 37–69%] in patients harboring an A/G or G/G genotype (p = 0.02). For PIK3C2A rs4356203, patients with an A/A or an A/G genotype had a 3-year RFS of 72% [95% CI 58–76%], whereas in patients with a G/G genotype was 49% [95% CI 28–70%] (p = 0.02). These associations remained statistically significant after adjusting for all the relevant clinical parameters in the multivariable analysis.
Conclusion
Genetic variants in VEGF pathway may be associated with recurrence in stage I–III NSCLC. Specifically, the KRAS rs1137282 could be considered as a prognostic factor for recurrence in resectable NSCLC patients. Although PIK3C2A rs4356203 was associated with RFS, further analyses are necessary to confirm these data.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86.
Chansky K, Sculier J-P, Crowley JJ, Giroux D, Van Meerbeeck J, Goldstraw P, et al. The international association for the study of lung cancer staging project: prognostic factors and pathologic TNM stage in surgically managed non-small cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:792–801.
Visbal AL, Leighl NB, Feld R, Shepherd FA. Adjuvant chemotherapy for early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2005;128:2933–43.
Burdett S, Pignon JP, Tierney J, Tribodet H, Stewart L, Le Pechoux C, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for resected early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD011430.
Folkman J, Shing Y. Angiogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:10931–4.
Carmeliet P, Jain RK. Angiogenesis in cancer and other diseases. Nature. 2000;407:249–57.
Carmeliet P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat Med. 2003;9:653–60.
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell. 2011;144:646–74.
Stefanou D, Goussia AC, Arkoumani E, Agnantis NJ. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and the adhesion molecule E-cadherin in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2003;23:4715–20.
Zhan P, Wang J, Lv X, Wang Q, Qiu L, Lin X, et al. Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J Thorac Oncol. 2009;4:1094–103.
FDA. Approves new combination therapy for lung cancer. http://www.fda.gov/NewsEvents/Newsroom/PressAnnouncements/2006/ucm108766.htm. Accessed 12 Oct 2006.
European Medicines Agency-Find medicine-Avastin. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medicines/000582/human_med_000663.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058001d124. Accessed 24 Aug 2007.
European Medicines Agency-Find medicine-Vargatef. http://www.ema.europa.eu/ema/index.jsp?curl=pages/medicines/human/medicines/002569/human_med_001822.jsp&mid=WC0b01ac058001d124. Accessed 21 Nov 2014.
Guyot M, Pagès G. VEGF splicing and the role of VEGF splice variants: from physiological-pathological conditions to specific pre-mRNA splicing. Methods Mol Biol Clifton NJ. 2015;1332:3–23.
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM. Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:1011–27.
Lohela M, Bry M, Tammela T, Alitalo K. VEGFs and receptors involved in angiogenesis versus lymphangiogenesis. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2009;21:154–65.
Koch S, Claesson-Welsh L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2012;2:a006502.
Jain L, Vargo CA, Danesi R, Sissung TM, Price DK, Venzon D, et al. The role of vascular endothelial growth factor SNPs as predictive and prognostic markers for major solid tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 2009;8:2496–508.
Maeda A, Nakata M, Yasuda K, Yukawa T, Saisho S, Okita R, et al. Influence of vascular endothelial growth factor single nucleotide polymorphisms on non-small cell lung cancer tumor angiogenesis. Oncol Rep. 2013;29:39–44.
Koukourakis MI, Papazoglou D, Giatromanolaki A, Bougioukas G, Maltezos E, Sivridis E, et al. VEGF gene sequence variation defines VEGF gene expression status and angiogenic activity in non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2004;46:293–8.
Stevens A, Soden J, Brenchley PE, Ralph S, Ray DW. Haplotype analysis of the polymorphic human vascular endothelial growth factor gene promoter. Cancer Res. 2003;63:812–6.
Gerger A, El-Khoueiry A, Zhang W, Yang D, Singh H, Bohanes P, et al. Pharmacogenetic angiogenesis profiling for first-line Bevacizumab plus oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5783–92.
Masago K, Fujita S, Kim YH, Hatachi Y, Fukuhara A, Nagai H, et al. Effect of vascular endothelial growth factor polymorphisms on survival in advanced-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2009;100:1917–22.
Guan X, Yin M, Wei Q, Zhao H, Liu Z, Wang L-E, et al. Genotypes and haplotypes of the VEGF gene and survival in locally advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy. BMC Cancer. 2010;10:431.
Yu W, Jiang X, Bai T, Lv X, Chang F. Association between +936 C > T gene polymorphism of vascular endothelial growth factor and lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Cancer Biomark. 2014;14:483–92.
de Mello RA, Ferreira M, Soares-Pires F, Costa S, Cunha J, Oliveira P, et al. The impact of polymorphic variations in the 5p15, 6p12, 6p21 and 15q25 Loci on the risk and prognosis of portuguese patients with non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS One. 2013;8:e72373.
Heist RS, Zhai R, Liu G, Zhou W, Lin X, Su L, et al. VEGF polymorphisms and survival in early-stage non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:856–62.
Edge SB. In: American Joint Committee on Cancer, editors. AJCC cancer staging manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010.
Paré-Brunet L, Glubb D, Evans P, Berenguer-Llergo A, Etheridge AS, Skol AD, et al. Discovery and functional assessment of gene variants in the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway. Hum Mutat. 2014;35:227–35.
FastSNP. http://bioinformatics.ca/links_directory/tool/10250/fastsnp.
SNP Function Prediction (FuncPred). https://snpinfo.niehs.nih.gov/snpinfo/snpfunc.php.
Sebio A, Paré L, Páez D, Salazar J, González A, Sala N, et al. The LCS6 polymorphism in the binding site of let-7 microRNA to the KRAS 3′-untranslated region: its role in the efficacy of anti-EGFR-based therapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Pharmacogenet Genom. 2013;23:142–7.
Loupakis F, Ruzzo A, Salvatore L, Cremolini C, Masi G, Frumento P, et al. Retrospective exploratory analysis of VEGF polymorphisms in the prediction of benefit from first-line FOLFIRI plus bevacizumab in metastatic colorectal cancer. BMC Cancer. 2011;11:247.
Glubb DM, Cerri E, Giese A, Zhang W, Mirza O, Thompson EE, et al. Novel functional germline variants in the VEGF receptor 2 gene and their effect on gene expression and microvessel density in lung cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:5257–67.
Dong G, Guo X, Fu X, Wan S, Zhou F, Myers RE, et al. Potentially functional genetic variants in KDR gene as prognostic markers in patients with resected colorectal cancer. Cancer Sci. 2012;103:561–8.
Glubb DM, Paré-Brunet L, Jantus-Lewintre E, Jiang C, Crona D, Etheridge AS, et al. Functional FLT1 genetic variation is a prognostic factor for recurrence in stage I–III non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2015;10:1067–75.
Schemper M, Smith TL. A note on quantifying follow-up in studies of failure time. Control Clin Trials. 1996;17:343–6.
Dong J, Dai J, Shu Y, Pan S, Xu L, Chen W, et al. Polymorphisms in EGFR and VEGF contribute to non-small-cell lung cancer survival in a Chinese population. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1080–6.
Eng L, Azad AK, Habbous S, Pang V, Xu W, Maitland-van der Zee AH, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor pathway polymorphisms as prognostic and pharmacogenetic factors in cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Cancer Res. 2012;18:4526–37.
Eng L, Liu G. VEGF pathway polymorphisms as prognostic and pharmacogenetic factors in cancer: a 2013 update. Pharmacogenomics. 2013;14:1659–67.
Bos JL. Ras oncogenes in human cancer: a review. Cancer Res. 1989;49:4682–9.
Vojtek AB, Der CJ. Increasing complexity of the Ras signaling pathway. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:19925–8.
Rodenhuis S, van de Wetering ML, Mooi WJ, Evers SG, van Zandwijk N, Bos JL. Mutational activation of the K-ras oncogene. A possible pathogenetic factor in adenocarcinoma of the lung. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:929–35.
Prior IA, Lewis PD, Mattos C. A comprehensive survey of Ras mutations in cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:2457–67.
Shepherd FA, Domerg C, Hainaut P, Jänne PA, Pignon J-P, Graziano S, et al. Pooled analysis of the prognostic and predictive effects of KRAS mutation status and KRAS mutation subtype in early-stage resected non-small-cell lung cancer in four trials of adjuvant chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol. 2013;31:2173–81.
Wood K, Hensing T, Malik R, Salgia R. Prognostic and predictive value in KRAS in non-small-cell lung cancer: a review. JAMA Oncol. 2016;2:805–12.
Wang W-Y, Chien Y-C, Wong Y-K, Lin Y-L, Lin J-C. Effects of KRAS mutation and polymorphism on the risk and prognosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck. 2012;34:663–6.
Yuan P, Liu D, Deng M, Liu J, Wang J, Zhang L, et al. Identification of differently expressed genes with specific SNP loci for breast cancer by the integration of SNP and gene expression profiling analyses. Pathol Oncol Res. 2015;21:469–75.
Acknowledgements
Ivana Sullivan has a Rio Hortega contract (CM13/00117) from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Madrid, Spain. This work was performed within the framework of the Doctorate of Medicine at the Autonomous University of Barcelona. The authors thank Carolyn Newey for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional ethics committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments.
Funding
No funding received for this study.
Informed consent
Written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
I. Sullivan and J. Salazar contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sullivan, I., Salazar, J., Arqueros, C. et al. KRAS genetic variant as a prognostic factor for recurrence in resectable non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 19, 884–890 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-017-1620-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-017-1620-7