Abstract
Purpose
In the literature, small number of study has addressed time of recurrence in breast cancer. We analyzed clinicopathological factors predicting early or late recurrence in breast cancer patients and also prognostic factors related with recurrence-free survival (RFS) in recurrent patients.
Patients/methods
We evaluated retrospectively 1980 breast cancer patients. Relapsed was defined as early if it was occured first 5 year of follow-up (Group 1) and late if it was occured after 5 years (Group 2). The clinicopathological factors were compared in respect of time of recurrence. The prognostic factors were evaluated using univariate and multivariate analyses.
Results
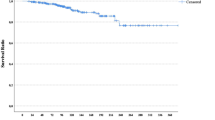
Recurrence wase detected in 141 patient during follow-up. Tumors recurred after 5 years more likely to have lower stage (p = 0.05), tumors without lymphovascular invasion (LVI) (p < 0.001) and perineural invasion (PNI) (p = 0.01), and also HER2 negative (p < 0.001). The median RFS time and 5 years RFS rates were 42.9 months and 31.9 %, respectively. LVI (p = 0.01), PNI (p = 0.03), HER2 (p = 0.003), progesterone receptor (PR) (p = 0.04), the presence of neoadjuvant chemotherapy (p = 0.003), adjuvant hormonotherapy (p = 0.05) were found to be related with RFS. Axillary lymph node metastasis (p = 0.05) and the presence of PNI (p = 0.009) were poor prognostic factors for early recurrent group. PR-positive tumors (p = 0.001) and luminal subtypes (p = 0.03) had instances of late recurrences significantly.
Conclusions
Clinicopathological factors predicting the recurrence time in breast cancer were important to modify adjuvant therapy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carter CL, Allen C, Henson DE. Relation of tumor size, lymph node status, and survival in 24,740 breast cancer cases. Cancer. 1989;63:181–7.
Kennecke H, McArthur H, Olivotto IA, Speers C, Bajdik C, Chia SK, et al. Risk of early recurrence among postmenopausal women with estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer treated with adjuvant tamoxifen. Cancer. 2008;112:1437–44.
Chevallier B, Fumoleau P, Kerbrat P, Dieras V, Roche H, Krakowski I, et al. Docetaxel is a major cytotoxic drug for the treatment of advanced breast cancer: a phase II trial of the Clinical Screening Cooperative Group of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:314–22.
Demicheli R, Abbattista A, Miceli R, Valagussa P, Bonadonna G. Time distribution of the recurrence risk for breast cancer patients undergoing mastectomy: further support about the concept of tumor dormancy. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1996;41:177–85.
Kamby C, Vejborg I, Kristensen B, Olsen LO, Mouridsen HT. Metastatic pattern in recurrent breast cancer. Special reference to intrathoracic recurrences. Cancer. 1988;62:2226–33.
Saphner T, Tormey DC, Gray R. Annual hazard rates of recurrence for breast cancer after primary therapy. J Clin Oncol. 1996;14:2738–46.
Joensuu K, Leidenius M, Kero M, Andersson LC, Horwitz KB, Heikkilä P. ER, PR, HER2, Ki-67 and CK5 in Early and Late Relapsing Breast Cancer-Reduced CK5 Expression in Metastases. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2013;7:23–34.
Song WJ, Kim KI, Park SH, Kwon MS, Lee TH, Park HK, et al. The Risk Factors Influencing between the Early and Late Recurrence in Systemic Recurrent Breast Cancer. J Breast Cancer. 2012;15:218–23.
Hammond ME, Hayes DF, Dowsett M, Allred DC, Hagerty KL, Badve S, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American pathologists guideline recommendations for immunohistochemical testing of estrogen and progesterone receptors in breast cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:907–22.
Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative Group. Effects of radiotherapy and surgery in early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1444–55.
Arriagada R, Lê MG, Guinebretière JM, Dunant A, Rochard F, Tursz T. Late local recurrences in a randomised trial comparing conservative treatment with total mastectomy in early breast cancer patients. Ann Oncol. 2003;14:1617–22.
Kennecke HF, Olivotto IA, Speers C, Norris B, Chia SK, Bryce C, et al. Late risk of relapse and mortality among postmenopausal women with estrogen responsive early breast cancer after 5 years of tamoxifen. Ann Oncol. 2007;18:45–51.
Brewster AM, Hortobagyi GN, Broglio KR, Kau SW, Santa-Maria CA, Arun B, Buzdar AU, et al. Residual risk of breast cancer recurrence 5 years after adjuvant therapy. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:1179–83.
Bosco JL, Lash TL, Prout MN, Buist DS, Geiger AM, Haque R, et al. BOW Investigators. Breast cancer recurrence in older women five to ten years after diagnosis. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:2979–83.
Takeuchi H, Tsuji K, Ueo H. Prediction of early and late recurrence in patients with breast carcinoma. Breast Cancer. 2005;12:161–5.
Vollenweider-Zerargui L, Barrelet L, Wong Y, Lemarchand-Béraud T, Gómez F. The predictive value of estrogen and progesterone receptors’ concentrations on the clinical behaviour of breast cancer in women. Clinical correlation on 547 patients. Cancer. 1986;57:1171–80.
Brollo J, Kneubil MC, Botteri E, Rotmensz N, Duso BA, Fumagalli L, et al. Locoregional recurrence in patients with HER2 positive breast cancer. Breast. 2013;22:856–62.
Ahn SG, Lee HM, Cho SH, Bae SJ, Lee SA, Hwang SH, et al. The difference in prognostic factors between early recurrence and late recurrence in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer: nodal stage differently impacts early and late recurrence. PLoS One. 2013;8(5):e63510.
Nguyen PL, Taghian AG, Katz MS, Niemierko A, Abi Raad RF, Boon WL, et al. Breast cancer subtype approximated by estrogen receptor, progesterone receptor, and HER-2 is associated with local and distant recurrence after breast-conserving therapy. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:2373–8.
Jagsi R, Raad RA, Goldberg S, Sullivan T, Michaelson J, Powell SN, et al. Locoregional recurrence rates and prognostic factors for failure in node-negative patients treated with mastectomy: implications for postmastectomy radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2005;62:1035–9.
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oven Ustaalioglu, B.B., Balvan, O., Bilici, A. et al. The differences of clinicopathological factors for breast cancer in respect to time of recurrence and effect on recurrence-free survival. Clin Transl Oncol 17, 895–902 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1323-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-015-1323-x