Abstract
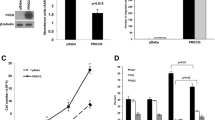
Breast cancers and most malignant tumors are composed of heterogeneous tumor cells both at genetic and morphological levels; intra-tumor heterogeneity can be one underlying cause of therapeutic resistance. Classical studies have focused on analyses of the relationship between primary tumors and metastatic dissemination, and on subclone evolution. However, it should be noted that tumor heterogeneity at the level of protein expression (proteomics) has not been yet studied in depth. The differences in protein expression also can play an important role in elucidating the relationship between intra-tumor heterogeneity and resistance to systemic therapy. In fact, in human tumors there is not always a homogeneous expression of many of the crucial factors involved in cell signaling, such as pMAPK, pAKt, pMTOR, even with constitutive oncogenic alterations upstream, such as HER2, PI3 K. Conversely, two of these factors, peIF4E and p4E-BP1, which are downstream, and control protein translation, show a diffuse and strong protein expression. In summary, most of cell signaling factors show a heterogeneous expression, regardless of oncogenic alterations. Tissue heterogeneity could be driven by local factors, including hypoxia. The fact that the phosphorylation of crucial proteins such as 4E-BP1 and eIF4E is observed homogeneously throughout most tumors and are druggable opens the chance to get real potential targets in cancer therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 4E-BP1:
-
4E-binding protein 1
- AKT:
-
V-aktmurinethymoma viral oncogene homolog
- eIF4E:
-
Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase
- FISH:
-
Fluorescence in situ hybridization
- MAPK/ERK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- mTOR:
-
Mammalian target of rapamycin
- PI3K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- p:
-
Phosphorylated
- S6:
-
Ribosomal protein S6
References
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB, van de Rijn M, Jeffrey SS, Rees CA, et al. Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature. 2000;406(6797):747–52.
Turner NC, Reis-Filho JS. Genetic heterogeneity and cancer drug resistance. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(4):e178–85.
Gerlinger M, Rowan AJ, Horswell S, Larkin J, Endesfelder D, Gronroos E, et al. Intra-tumor heterogeneity and branched evolution revealed by multi region sequencing. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(10):883–92.
Shah SP, Roth A, Goya R, Oloumi A, Ha G, Zhao Y, et al. The clonal and mutational evolution spectrum of primary triple-negative breast cancers. Nature. 2012;486(7403):395–9.
Swanton C. Intratumor heterogeneity: evolution through space and time. Cancer Res. 2012;72(19):4875–82.
Newburger DE, Kashef-Haghighi D, Weng Z, Salari R, Sweeney RT, Brunner AL, et al. Genome evolution during progression to breast cancer. Genome Res. 2013;23(7):1097–108.
De Mattos-Arruda L, Cortes J, Santarpia L, Vivancos A, Tabernero J, Reis-Filho JS, et al. Circulating tumour cells and cell-free DNA as tools for managing breast cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2013;10(7):377–89.
Navin N, Kendall J, Troge J, Andrews P, Rodgers L, McIndoo J, et al. Tumour evolution inferred by single-cell sequencing. Nature. 2011;472(7341):90–4.
Nik-Zainal S, Van Loo P, Wedge DC, Alexandrov LB, Greenman CD, Lau KW, et al. The life history of 21 breast cancers. Cell. 2012;149(5):994–1007.
Miller TW, Rexer BN, Garrett JT, Arteaga CL. Mutations in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway: role in tumor progression and therapeutic implications in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2011;13(6):224.
Wolff AC, Hammond ME, Schwartz JN, Hagerty KL, Allred DC, Cote RJ, et al. American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guideline recommendations for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 testing in breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(1):118–45.
Rojo F, Najera L, Lirola J, Jimenez J, Guzman M, Sabadell MD, et al. 4E-binding protein 1, a cell signaling hallmark in breast cancer that correlates with pathologic grade and prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13(1):81–9.
Armengol G, Rojo F, Castellvi J, Iglesias C, Cuatrecasas M, Pons B, et al. 4E-binding protein 1: a key molecular “funnel factor” in human cancer with clinical implications. Cancer Res. 2007;67(16):7551–5.
Alain T, Morita M, Fonseca BD, Yanagiya A, Siddiqui N, Bhat M, et al. eIF4E/4E-BP ratio predicts the efficacy of mTOR targeted therapies. Cancer Res. 2012;72(24):6468–76.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
S. Ramon y Cajal and L. De Mattos-Arruda contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12094_2014_1203_MOESM1_ESM.jpg
Supplementary Figure S1. Heterogeneity of cell signaling factors in breast carcinomas: focal vs diffuse cellular expression (JPEG 38 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramon y Cajal, S., De Mattos-Arruda, L., Sonenberg, N. et al. The intra-tumor heterogeneity of cell signaling factors in breast cancer: p4E-BP1 and peIF4E are diffusely expressed and are real potential targets. Clin Transl Oncol 16, 937–941 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1203-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1203-9