Abstract
Purpose
This study focuses on investigating the expression correlation of vimentin, survivin and p53 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and the clinical significance.
Methods
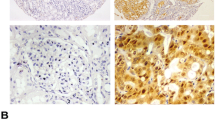
The mRNA and protein expression levels of the vimentin, survivin and p53 were determined in ccRCC and adjacent normal renal tissues, using quantitative real-time-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) and Western blot. We detected the expression and localization of vimentin, survivin and p53 protein in ccRCC by immunohistochemistrical SP method and analyzed the relationships among clinical pathologic parameters and patient prognosis.
Results
The expression of vimentin and survivin was significantly increased in ccRCC compared with adjacent normal renal tissues, which were positively correlated with the pathological grade and clinical stage (P < 0.05). p53 was highly expressed in ccRCC compared with normal tissues (P < 0.05), which was not positively correlated with the pathological grade and clinical stage (P > 0.05). Furthermore, univariate and multivariate analysis showed that high expression levels of vimentin and survivin were independent prognostic indicators for ccRCC. The levels of vimentin and survivin were positively correlated in ccRCC (r = 0.428, P < 0.01).
Conclusions
Reliable basis about biological behavior and prognosis judgments of ccRCC can be provided by combining detection of vimentin and survivin. Foundation and new ideas for gene therapy of ccRCC may be provided by further studying the relationship among vimentin, survivin and p53 in ccRCC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rini BI, Campbell SC, Escudier B. Renal cell carcinoma. Lancet. 2009;373:1119–32.
Klatte T, Pantuck AJ, Kleid MD, Belldegrun AS. Understanding the natural biology of kidney cancer: implications for targeted cancer therapy. Rev Urol. 2007;9:47–56.
Cohen HT, McGovern FJ. Renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2477–90.
Schopferer M, Bär H, Hochstein B, Sharma S, Mücke N, Herrmann H, et al. Desmin and vimentin intermediate filament networks: their viscoelastic properties investigated by mechanical rheometry. J Mol Biol. 2009;388:133–43.
Shirahata A, Sakata M, Sakuraba K, Goto T, Mizukami H, Saito M, et al. Vimentin methylation as a marker for advanced colorectal carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:279–81.
Moustakas A, Heldin CH. Signaling networks guiding epithelial–mesenchymal transitions during embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci. 2007;98:1512–20.
Perlson E, Michaelevski I, Kowalsman N, Ben-Yaakov K, Shaked M, Seger R, et al. Vimentin binding to phosphorylated Erk sterically hinders enzymatic dephosphorylation of the kinase. J Mol Biol. 2006;364:938–44.
Derynck R, Akhurst RJ. Differentiation plasticity regulated by TGF-beta family proteins in development and disease. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:1000–4.
Thiery JP, Sleeman JP. Complex networks orchestrate epithelial–mesenchymal transitions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:131–42.
Chang L, Goldman RD. Intermediate filaments mediate cytoskeletal crosstalk. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2004;5:601–13.
Dean EJ, Ranson M, Blackhall F, Dive C. X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007;11:1459–71.
Oto OA, Paydas S, Tanriverdi K, Seydaoglu G, Yavuz S, Disel U. Survivin and EPR-1 expression in acute leukemias: prognostic significance and review of the literature. Leuk Res. 2007;31:1495–501.
Oren M, Rotter V. Mutant p53 gain-of-function in cancer. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010;2:a001107.
Goldstein I, Marcel V, Olivier M, Oren M, Rotter V, Hainaut P. Understanding wild-type and mutant p53 activities in human cancer: new landmarks on the way to targeted therapies. Cancer Gene Ther. 2011;18:2–11.
Vousden KN, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:275–83.
Yang X, Wang J, Liu C, Grizzle WE, Yu S, Zhang S, et al. Cleavage of p53-vimentin complex enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-mediated apoptosis of rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Am J Pathol. 2005;167:705–19.
Hollstein M, Sidransky D, Vogelstein B, Harris CC. p53 mutation in human cancers. Science. 1991;253:49–53.
Levine AJ, Perry ME, Chang A, Silver A, Dittmer D, Wu M, et al. The 1993 Walter Hubert Lecture: the role of the p53 tumour-suppressor gene in tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 1994;69:409–16.
Mohammed A, Shergill I, Little B. Management of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: current trends. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2009;9:75–83.
Liu T, Zhang X, Shang M, Zhang Y, Xia B, Niu M, et al. Dysregulated expression of Slug, vimentin, and E-cadherin correlates with poor clinical outcome in patients with basal like breast cancer. J Surg Oncol. 2013;107:188–94.
Yao X, Wang X, Wang Z, Dai L, Zhang G, Yan Q, et al. Clinicopathological and prognostic significance of epithelial mesencymal transition-related protein expression in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Onco Targets Ther. 2012;5:255–61.
Al-Saad S, Al-Shibli K, Donnem T, Persson M, Bremnes RM, Busund LT. The prognostic impact of NF-kappaB p105, vimentin, E-cadherin and Par6 expression in epithelial and stromal compartment in non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2008;99:1467–83.
Zhao Y, Yan Q, Long X, Chen X, Wang Y. Vimentin affects the mobility and invasiveness of prostate cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2008;26:571–7.
Hwa JS, Park HJ, Jung JH, Kam SC, Park HC, Kim CW, et al. Identification of proteins differentially exrpressed in the conventional renal cell carcinoma by proteomic analysis. J Korean Med Sci. 2005;20:450–5.
Williams AA, Higgins JP, Zhao H, Ljunberg B, Brooks JD. CD9 and vimentin distinguish clear cell from chromophobe renal cell carcinoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2009;9:9.
Hsu KF, Lin CK, Yu CP, Tzao C, Lee SC, Lee YY, et al. Cortactin, fascin, and survivin expression associated with clinicopathological parameters in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 2009;22:402–8.
Shariat SF, Ashfaq R, Karakiewicz PI, Saeedi O, Sagalowsky AI, Lotan Y. Survivin expression is associated with bladder cancer presence, stage, progression, and mortality. Cancer. 2007;109:1106–13.
Wang GC, Hsieh PS, Hsu HH, Sun GH, Nieh S, Yu CP, et al. Expression of cortactin and survivin in renal cell carcinoma associated with tumor aggressiveness. World J Urol. 2009;27:557–63.
Andersen MH, Svane IM, Becker JC, Straten PT. The universal character of the tumor-associated antigen survivin. Clin Cancer Res. 2007;13:5991–4.
Hernandez JM, Farma JM, Coppola D, Hakam A, Fulp WJ, Chen DT, et al. Expression of the antiapoptotic protein survivin in colon cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 2011;10:188–93.
Hsu YF, Sheu JR, Lin CH, Yang DS, Hsiao G, Ou G, et al. Trichostatin A and sirtinol suppressed survivin expression through AMPK and p38MAPK in HT29 colon cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1820:104–15.
Masuda A, Kamai T, Abe H, Arai K, Yoshida K. Is Stat3 and/or p53 mRNA expression a prognostic marker for renal cell carcinoma? Biomed Res. 2009;30:171–6.
Zubac DP, Bostad L, Kihl B, Seidal T, Wentzel-Larsen T, Haukaas SA. The expression of thrombospondin-1 and p53 in clear cell renal cell carcinoma: its relationship to angiogenesis, cell proliferation and cancer specific survival. J Urol. 2009;182:2144–9.
Mirza A, McGuirk M, Hockenberry TN, Wu Q, Ashar H, Black S, et al. Human survivin is negatively regulated by wild-type p53 and participates in p53-dependent apoptotic pathway. Oncogene. 2002;21:2613–22.
Hoffman WH, Biade S, Zilfou JT, Chen J, Murphy M. Transcriptional repression of the anti-apoptotic survivin gene by wild type p53. J Biol Chem. 2002;277:3247–57.
Lynch CJ, Milner J. Loss of one p53 allele results in four-fold reduction of p53 mRNA and protein: a basis for p53 haplo-insufficiency. Oncogene. 2006;25:3463–70.
Vegran F, Boidot R, Oudin C, Riedinger JM, Lizard-Nacol S. Distinct expression of survivin splice vaiants in breast carcinomas. Int J Oncol. 2005;27:1151–7.
Kar R, Sen S, Singh A, Sharma H, Kumar S, Gupta SD, et al. Role of apoptotic regulators in human epithelial ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007;6:1101–5.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants from Program for Science & Technology Innovation Talents in Universities of Henan Province (#13HASTIT025) to SQL. The authors thank all the members in the laboratory when this work was carried out. The experiments complied with the current laws of China.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, ZG., Li, SQ., Li, ZJ. et al. Expression of vimentin and survivin in clear cell renal cell carcinoma and correlation with p53. Clin Transl Oncol 17, 65–73 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1199-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1199-1