Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the accuracy of preoperative 3T multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (3TmMRI) for local staging of prostate cancer and its influence on the decision to change the clinical target volume (CTV), total dose and hormonal therapy when treating prostate cancer patients with radiotherapy.
Methods
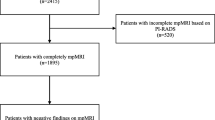
From 2009 to 2013, 150 patients, who had confirmed prostate cancer and underwent a 3TmMRI before treatment with radical prostatectomy or radical radiation therapy, were included. Radiation therapy treatment (CTV, total dose and hormonal therapy) was initially determined on the basis of the clinical information, and radiation therapy plan was reevaluated after 3TmMRI review. The value of preoperative 3TmMRI in local staging and in the decision of radiotherapy treatment according to NCCN risk classification was analyzed.
Results
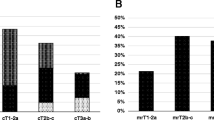
3TmMRI performed correct, over- and under staging in 78.7 % (37/47), 6.3 % (3/47), 14.8 % patients (7/47), respectively. 3TmMRI identified 6 cT2a, 7 cT2b, 28 cT2c, 3 cT3a, 3 cT3b tumors. At final pathology, 5 tumors were classified as pT2a, 5 as pT2b, 30 as pT2c, 4 as pT3a, 3 as pT3b. After reviewing the MRI reports, the initial radiotherapy and hormonal therapy plan was changed in 33.9 % patients (35/103).
Conclusions
In our group of patients, 3TmMRI has been a reliable technique providing an optimal staging for prostate cancer. Its routine use could induce important changes in radiation therapy treatments in a significant number of such patients. However, more additional studies are needed to clarify this issue.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R1, Ma J, Zou Z, Jemal A (2014) Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin 64:9–29.
Edge S, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG, Greene FL, Trotti A. American Join Committee on Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed. New York: Springer; 2010.
Freedland SJ. Screening, risk assessment, and the approach to therapy in patients with prostate cancer. Cancer. 2011;117:1123–35.
Bostwick DG. Staging prostate cancer 1997: current methods and limitations. Eur Urol. 1997;32:2–14.
Spiegelman SS, McNeal JE, Freiha FS, Stamey TA. Rectal examination in volume determination of carcinoma of the prostate: clinical and anatomical correlations. J Urol. 1986;136:1228–30.
Smith JA Jr, Scardino PT, Resnick MI, Hernandez AD, Rose SC, Egger MJ. Transrectal ultrasound versus digital rectal examination for the staging of carcinoma of the prostate: results of a prospective multi-institutional trial. J Urol. 1997;157:902–6.
Boonsirikamchai P, Choi S, Frank SJ, Ma J, Elsayes KM, Kaur H, et al. MR imaging of prostate cancer in radiation oncology: what radiologists need to know. Radiographics. 2013;33:741–76.
Mullerad M, Hricak H, Kuroiwa K, Pucar D, Chen HN, Kattan MW, et al. Comparison of endorectal magnetic resonance imaging, guided prostate biopsy and digital rectal examination in the preoperative anatomical localization of prostate cancer. J Urol. 2005;174:2158–63.
Sala E, Akin O, Moskowitz CS, Eisenberg HF, Kuroiwa K, Ishill NM, et al. Endorectal MR imaging in the evaluation of seminal vesicle invasion: diagnostic accuracy and multivariate feature analysis. Radiology. 2006;238:929–37.
Wang L, Mullerad M, Chen HN, Eberhardt SC, Kattan MW, Scardino PT, et al. Prostate cancer: incremental value of endorectal MRI findings for prediction of extracapsular extension. Radiology. 2004;232:133–9.
Mullins JK1, Bonekamp D, Landis P, Begum H, Partin AW, Epstein JI et al (2013) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging findings in men with low-risk prostate cancer followed using active surveillance. BJU Int 111:1037–1045.
Dickinson L, Ahmed HU, Allen C, Barentsz JO, Carey B, Futterer JJ, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging for the detection, localisation, and characterisation of prostate cancer: recommendations from a European Consensus Meeting. Eur Urol. 2011;59:477–94.
Barentsz OJ, Richenberg J, Clements R, Choyke P, Verma S, Villeirs G, et al. Esur prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:746–57.
Fütterer JJ, Heijmink SW, Scheenen TW, Jager GJ, Hulsbergen-Van de Kaa CA, Witjes JA, et al. Prostate cancer: local staging at 3-T endorectal MR imaging-early experience. Radiology. 2006;238:184–91.
Augustin H, Fritz GA, Ehammer T, Auprich M, Pummer K. Accuracy of 3-Tesla magnetic resonance imaging for the staging of prostate cancer in comparison to the Partin tables. Acta Radiol. 2009;50:562–9.
Heijmink SW, Fütterer JJ, Hambrock T, Takahashi S, Scheenen TW, Huisman HJ, et al. Prostate cancer: body-array versus endorectal coil MR imaging at 3T-comparison of image quality, localization, and staging performance. Radiology. 2007;244:184–95.
Torricelli P, Barberini A, Cinquantini F, Sighinolfi M, Casinaro AM. 3-T MRI with phased-array coil in local staging of prostatic cancer. Acad Radiol. 2008;15:1118–25.
Beyersdorff D, Taymoorian K, Knösel T, Schnorr D, Felix R, Hamm B, et al. MRI of prostate cancer at 1.5 and 3.0: comparison of image quality in tumor detection and staging. AJR. 2005;185:1214–20.
Park BK, Kim B, Kim CK, Lee HM, Kwon GY. Comparison of phased-array 3.0-T and endorectal 1.5-T magnetic resonance imaging in the evaluation of local staging accuracy for prostate cancer. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2007;31:534–8.
Sciarra A, Barentsz J, Bjartell A, Eastham J, Hricak H, Panebianco V, et al. Advances in magnetic resonance imaging: how they are changing the management of prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 2011;59:962–77.
Mohler JL, Kantoff PW, Armstrong AJ, Bahnson RR, Cohen M, D’Amico AV, et al. Prostate cancer, version 1.2014. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 2013;11:1471–9.
Heidenreich A, Bastian PJ, Bellmunt J, Bolla M, Joniau S, van der Kwast T, et al. EAU Guidelines on prostate cancer. Part 1: screening, diagnosis, and local treatment with curative intent-update 2013. Eur Urol. 2014;65:124–37.
Boehmer D, Maingon P, Poortmans P, Baron MH, Miralbell R, Remouchamps V, et al. Guidelines for primary radiotherapy of patients with prostate cancer. Radiother Oncol. 2006;79:259–69.
Chao KK, Goldstein NS, Yan D, Vargas CE, Ghilezan MI, Korman HJ, et al. Clinicopathologic analysis of extracapsular extension in prostate cancer: should the clinical target volume be expanded posterolaterally to account for microscopic extension? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2006;65:999–1007.
Tamada T, Sone T, Jo Y, Yamamoto A, Yamashita T, Egashira N, et al. Prostate cancer: relationships between post biopsy hemorrhage and tumor detectability at MR diagnosis. Radiology. 2008;248:531–9.
Walsh PC. Anatomic radical prostatectomy: evolution of the surgical technique. J Urol. 1998;160:2418–24.
Hedge JV, Chen MH, Mulken RV, Fennessy FM, D’Amico AV, Tempany CM. Preoperative 3-Tesla multiparametric endorectal magnetic resonance imaging findings and the odds of upgrading and upstaging at radical prostatectomy in men with clinically localized prostate cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;85:101–7.
Cerantola Y, Valerio M, Kawkabani Marchini A, Meuwly JY, Jichlinski P. Can 3T multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging accurately detect prostate cancer extracapsular extension? Can Urol Assoc J. 2013;7:699–703.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank María Mateo for her contribution to this study like Research and Department Manager of Hospital Universitario Quirón Madrid.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Couñago, F., Recio, M., del Cerro, E. et al. Role of 3.0 T multiparametric MRI in local staging in prostate cancer and clinical implications for radiation oncology. Clin Transl Oncol 16, 993–999 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1186-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-014-1186-6