Abstract
Aim
The aim of this study was to compare the effects and mechanisms of action of metformin on estrogen receptor (ER)-positive and ER-negative breast cancer cell lines.
Methods
The anti-proliferative effects of metformin, and of the direct activator of adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK), A-769662, on MCF-7 (ER-positive) and MDA-MB-231 (ER-negative) breast cancer cell lines were evaluated by MTT (3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide, a yellow tetrazole) assays. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting was also used to examine the effect of metformin on the cell cycle. Finally, phosphorylation of the metformin target AMPK, and of its potential downstream targets including acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), p53, p70-S6K and Raptor, was examined using immunoblotting.
Results
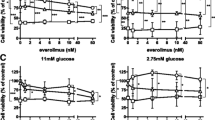
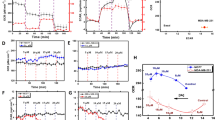
Metformin and A-769662 caused significant, concentration-dependent suppression of cell proliferation with G1 cell cycle arrest in both MCF-7 and MDA-MB-231 cells. The proliferation suppression effect was more profound in MCF-7 cells. A concentration-dependent phosphorylation of AMPK was detected following metformin treatment, as was phosphorylation of ACC in both cell lines, but not p53, p70-S6k or Raptor.
Conclusion
Metformin acts as a growth inhibitor in both ER-positive and ER-negative breast cancer cells in vitro, and arrests cells in G1 phase, particularly in the ER-positive MCF-7 cells. The effect is likely to be mediated by AMPK activation, in part by inhibition of fatty acid synthesis via ACC phosphorylation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans JM, Donnelly LA, Emslie-Smith AM, Alessi DR, Morris AD. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ. 2005;330(7503):1304–5 (Epub 2005/04/26).
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM. New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(9):1620–5 (Epub 2009/07/01).
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA. The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52(9):1766–77 (Epub 2009/07/03).
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B. Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Philadelphia). 2010;3(11):1451–61 (Epub 2010/10/16).
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin: response to Farooki and Schneider. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(8):1990–1 (Epub 2006/07/29).
Bayraktar S, Hernadez-Aya LF, Lei X, Meric-Bernstam F, Litton JK, Hsu L, et al. Effect of metformin on survival outcomes in diabetic patients with triple receptor-negative breast cancer. Cancer. 2012;118(5):1202–11 (Epub 2011/07/30).
Bo S, Ciccone G, Rosato R, Villois P, Appendino G, Ghigo E, et al. Cancer mortality reduction and metformin: a retrospective cohort study in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2012;14(1):23–9 (Epub 2011/08/05).
Hadad S, Iwamoto T, Jordan L, Purdie C, Bray S, Baker L, et al. Evidence for biological effects of metformin in operable breast cancer: a pre-operative, window-of-opportunity, randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;128(3):783–94 (Epub 2011/06/10).
Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes Dev. 2011;25(18):1895–908 (Epub 2011/09/23).
Owen MR, Doran E, Halestrap AP. Evidence that metformin exerts its anti-diabetic effects through inhibition of complex 1 of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Biochem J. 2000;348(Pt 3):607–14 (Epub 2000/06/07).
Hawley SA, Ross FA, Chevtzoff C, Green KA, Evans A, Fogarty S, et al. Use of cells expressing gamma subunit variants to identify diverse mechanisms of AMPK activation. Cell Metab. 2010;11(6):554–65 (Epub 2010/06/04).
Hawley SA, Boudeau J, Reid JL, Mustard KJ, Udd L, Makela TP, et al. Complexes between the LKB1 tumor suppressor, STRAD alpha/beta and MO25 alpha/beta are upstream kinases in the AMP-activated protein kinase cascade. J Biol. 2003;2(4):28 (Epub 2003/09/27).
Xiao B, Sanders MJ, Underwood E, Heath R, Mayer FV, Carmena D, et al. Structure of mammalian AMPK and its regulation by ADP. Nature. 2011;472(7342):230–3 (Epub 2011/03/15).
Lochhead PA, Salt IP, Walker KS, Hardie DG, Sutherland C. 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide riboside mimics the effects of insulin on the expression of the 2 key gluconeogenic genes PEPCK and glucose-6-phosphatase. Diabetes. 2000;49(6):896–903 (Epub 2000/06/24).
Hardie DG, Ross FA, Hawley SA. AMPK: a nutrient and energy sensor that maintains energy homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13(4):251–62 (Epub 2012/03/23).
Foretz M, Hebrard S, Leclerc J, Zarrinpashneh E, Soty M, Mithieux G, et al. Metformin inhibits hepatic gluconeogenesis in mice independently of the LKB1/AMPK pathway via a decrease in hepatic energy state. J Clin Investig. 2010;120(7):2355–69 (Epub 2010/06/26).
Fullerton MD, Galic S, Marcinko K, Sikkema S, Pulinilkunnil T, Chen ZP, et al. Single phosphorylation sites in ACC1 and ACC2 regulate lipid homeostasis and the insulin-sensitizing effects of metformin. Nat Med. 2013 (Epub 2013/11/05).
Pollak M. Metformin and other biguanides in oncology: advancing the research agenda. Cancer Prev Res (Philadelphia). 2010;3(9):1060–5 (Epub 2010/09/03).
Jones RG, Plas DR, Kubek S, Buzzai M, Mu J, Xu Y, et al. AMP-activated protein kinase induces a p53-dependent metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell. 2005;18(3):283–93 (Epub 2005/05/04).
Hadad SM, Baker L, Quinlan PR, Robertson KE, Bray SE, Thomson G, et al. Histological evaluation of AMPK signalling in primary breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2009;9:307 (Epub 2009/09/03).
Wingo SN, Gallardo TD, Akbay EA, Liang MC, Contreras CM, Boren T, et al. Somatic LKB1 mutations promote cervical cancer progression. PloS One. 2009;4(4):e5137 (Epub 2009/04/03).
Zheng B, Jeong JH, Asara JM, Yuan YY, Granter SR, Chin L, et al. Oncogenic B-RAF negatively regulates the tumor suppressor LKB1 to promote melanoma cell proliferation. Mol Cell. 2009;33(2):237–47 (Epub 2009/02/04).
Algire C, Amrein L, Bazile M, David S, Zakikhani M, Pollak M. Diet and tumor LKB1 expression interact to determine sensitivity to anti-neoplastic effects of metformin in vivo. Oncogene. 2011;30(10):1174–82 (Epub 2010/11/26).
Goransson O, McBride A, Hawley SA, Ross FA, Shpiro N, Foretz M, et al. Mechanism of action of A-769662, a valuable tool for activation of AMP-activated protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(45):32549–60 (Epub 2007/09/15).
Zakikhani M, Dowling R, Fantus IG, Sonenberg N, Pollak M. Metformin is an AMP kinase-dependent growth inhibitor for breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006;66(21):10269–73 (Epub 2006/10/26).
Segal ED, Yasmeen A, Beauchamp MC, Rosenblatt J, Pollak M, Gotlieb WH. Relevance of the OCT1 transporter to the antineoplastic effect of biguanides. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;414(4):694–9 (Epub 2011/10/12).
Dowling RJ, Niraula S, Stambolic V, Goodwin PJ. Metformin in cancer: translational challenges. J Mol Endocrinol. 2012;48(3):R31–43 (Epub 2012/02/23).
Imamura K, Ogura T, Kishimoto A, Kaminishi M, Esumi H. Cell cycle regulation via p53 phosphorylation by a 5′-AMP activated protein kinase activator, 5-aminoimidazole- 4-carboxamide-1-beta-D-ribofuranoside, in a human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;287(2):562–7 (Epub 2001/09/14).
Cool B, Zinker B, Chiou W, Kifle L, Cao N, Perham M, et al. Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metab. 2006;3(6):403–16.
Sanders MJ, Ali ZS, Hegarty BD, Heath R, Snowden MA, Carling D. Defining the mechanism of activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by the small molecule A-769662, a member of the thienopyridone family. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(45):32539–48.
Huang X, Wullschleger S, Shpiro N, McGuire VA, Sakamoto K, Woods YL, et al. Important role of the LKB1–AMPK pathway in suppressing tumorigenesis in PTEN-deficient mice. Biochem J. 2008;412(2):211–21 (Epub 2008/04/05).
Gwinn DM, Shackelford DB, Egan DF, Mihaylova MM, Mery A, Vasquez DS, et al. AMPK phosphorylation of raptor mediates a metabolic checkpoint. Mol Cell. 2008;30(2):214–26 (Epub 2008/04/29).
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan KL. TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell. 2003;115(5):577–90 (Epub 2003/12/04).
Liang J, Shao SH, Xu ZX, Hennessy B, Ding Z, Larrea M, et al. The energy sensing LKB1–AMPK pathway regulates p27(kip1) phosphorylation mediating the decision to enter autophagy or apoptosis. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(2):218–24 (Epub 2007/01/24).
Stevens RJ, Ali R, Bankhead CR, Bethel MA, Cairns BJ, Camisasca RP, et al. Cancer outcomes and all-cause mortality in adults allocated to metformin: systematic review and collaborative meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. Diabetologia. 2012;55(10):2593–603 (Epub 2012/08/10).
Acknowledgments
All authors acknowledge help and contributions from: AMT group, in particular Ms Karen Murray. DGH group, in particular Dr. Jamie Sampayo, Dr. Sarah Fogarty, Dr. Simon Hawley, Dr. Mhairi Towler, Dr. Fiona Ross and Mr. Kevin Green. Breast Cancer Research Scotland for funding the project.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadad, S.M., Hardie, D.G., Appleyard, V. et al. Effects of metformin on breast cancer cell proliferation, the AMPK pathway and the cell cycle. Clin Transl Oncol 16, 746–752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1144-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-013-1144-8