Abstract
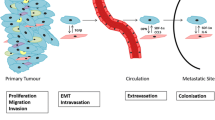
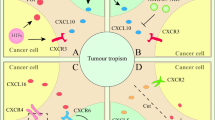
Over the last decade, genetic and cell biology studies have indicated that tumour growth is not only determined by malignant cancer cells themselves, but also by the tumour microenvironment. Cells present in the tumour microenvironment include fibroblasts, vascular, smooth muscle, adipocytes, immune cells and mesenchymal stem cells (MSC). The nature of the relationship between MSC and tumour cells appears dual and whether MSC are proor anti-tumorigenic is a subject of controversial reports. This review is focused on the role of MSC and bone marrow (BM) niches in cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hutchinson GE (1957) Concluding remarks. Cold Spring Harbor Symp Quant Biol 22:415–427
Witz IP (2008) Yin-yang activities and vicious cycles in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res 68:9
Kalluri R, Zeisberg M (2006) Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 6:392–401
Li H, Fan X, Houghton JM (2007) Tumor microenvironment: the role of the tumor stroma in cancer. J Cell Biochem 101:805–815
Mundy GR (2002) Metastasis: metastasis to bone: causes, consequences and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cancer 2:584–593
Ehninger A, Trumpp A (2011) The bone marrow stem cell niche grows up: mesenchymal stem cells and macrophages move in. J Exp Med 208: 421
Yin T, Li L (2006) The stem cell niches in bone. J Clin Invest 116:1195
Voog J, Jones DL (2010) Stem cells and the niche: a dynamic duo. Cell Stem Cell 6:103–115
Méndez-Ferrer S, Michurina TV, Ferraro F et al (2010) Mesenchymal and haematopoietic stem cells form a unique bone marrow niche. Nature 466:829–834
Bergfeld SA, DeClerck YA (2010) Bone marrowderived mesenchymal stem cells and the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Metastasis Rev 29: 249–261
Moore KA, Lemischka IR (2006) Stem cells and their niches. Science 311:1880
Li L, Neaves WB (2006) Normal stem cells and cancer stem cells: the niche matters. Cancer Res 66:4553
Scadden DT (2006) The stem-cell niche as an entity of action. Nature 441:1075–1079
Shiozawa Y, Havens AM, Pienta KJ, Taichman RS (2008) The bone marrow niche: habitat to hematopoietic and mesenchymal stem cells, and unwitting host to molecular parasites. Leukemia 22:941–950
Mohseny AB, Hogendoorn PCW (2011) Concise review: mesenchymal tumors: when stem cells go mad. Stem Cells 29:397–403
Tang N, Song WX, Luo J et al (2008) Osteosarcoma development and stem cell differentiation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2114–2130
Lin PP, Wang Y, Lozano G (2011) Mesenchymal stem cells and the origin of Ewing's sarcoma. Sarcoma doi.10.1155/2011/276463
Garrett RW, Emerson SG (2009) Bone and blood vessels: the hard and the soft of hematopoietic stem cell niches. Cell Stem Cell 4:503–506
Horowitz MC, Bothwell ALM, Hesslein DGT et al (2005) B cells and osteoblast and osteoclast development. Immunol Rev 208:141–153
Raaijmakers M (2011) Niche contributions to oncogenesis: emerging concepts and implications for the hematopoietic system. Haematologica 96: 1041–1048
Carlesso N, Cardoso AA (2010) Stem cell regulatory niches and their role in normal and malignant hematopoiesis. Curr Opin Hematol 17:281–286
Perry JM, Li L (2007) Disrupting the stem cell niche: good seeds in bad soil. Cell 129:1045–1047
Lindemann RK (2008) Stroma-initiated hedgehog signaling takes center stage in B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res 68:961
Scupoli MT, Donadelli M, Cioffi F et al (2008) Bone marrow stromal cells and the upregulation of interleukin-8 production in human T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia through the CXCL12/CXCR4 axis and the NF-κ B and JNK/AP-1 pathways. Haematologica 93:524
Kurtova AV, Tamayo AT, Ford RJ, Burger JA (2009) Mantle cell lymphoma cells express high levels of CXCR4, CXCR5, and VLA-4 (CD49d): importance for interactions with the stromal microenvironment and specific targeting. Blood 113: 4604
Ayala F, Dewar R, Kieran M, Kalluri R (2009) Contribution of bone microenvironment to leukemogenesis and leukemia progression. Leukemia 23:2233–2241
Colmone A, Amorim M, Pontier AL et al (2008) Leukemic cells create bone marrow niches that disrupt the behavior of normal hematopoietic progenitor cells. Science 322:1861
Cook G, Dumbar M, Franklin IM (1997) The role of adhesion molecules in multiple myeloma. Acta Haematol 97:81–89
Faid L, Riet I, Waele M et al (1996) Adhesive interactions between tumour cells and bone marrow stromal elements in human multiple myeloma. Eur J Haematol 57:349–358
Thomas X, Anglaret B, Magaud JP et al (1998) Interdependence between cytokines and cell adhesion molecules to induce interleukin-6 production by stromal cells in myeloma. Leuk Lymphoma 32:107–119
Michigami T, Shimizu N, Williams PJ et al (2000) Cell-cell contact between marrow stromal cells and myeloma cells via VCAM-1 and α4β1-integrin enhances production of osteoclast-stimulating activity. Blood 96:1953–1960
Damiano JS, Cress AE, Hazlehurst LA et al (1999) Cell adhesion mediated drug resistance (CAM-DR): role of integrins and resistance to apoptosis in human myeloma cell lines. Blood 93: 1658–1667
Walkley CR, Olsen GH, Dworkin S et al (2007) A microenvironment-induced myeloproliferative syndrome caused by retinoic acid receptor [gamma] deficiency. Cell 129:1097–1110
Walkley CR, Shea JM, Sims NA et al (2007) Rb regulates interactions between hematopoietic stem cells and their bone marrow microenvironment. Cell 129:1081–1095
Walkley CR, Shea JM, Sims NA et al (2007) pRb extrinsically regulates hematopoietic stem cells via myeloid cell-bone marrow microenvironment interactions. Cell 129:1081
Stavroulaki E, Kastrinaki MC, Pontikoglou CG et al (2011) Mesenchymal stem cells contribute to the abnormal bone marrow microenvironment in patients with chronic idiopathic neutropenia by overproduction of transforming growth factor-β1. Stem Cells Dev doi: 10.1089/scd.2010.0425
Raaijmakers MH, Mukherjee S, Guo S et al (2010) Bone progenitor dysfunction induces myelodysplasia and secondary leukaemia. Nature 464:852–857
Flores-Figueroa E, Arana-Trejo RM, Gutiérrez-Espíndola G et al (2005) Mesenchymal stem cells in myelodysplastic syndromes: phenotypic and cytogenetic characterization. Leuk Res 29:215–224
Garayoa M, Garcia JL, Santamaria C et al (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells from multiple myeloma patients display distinct genomic profile as compared with those from normal donors. Leukemia 23:1515–1527
Corre J, Mahtouk K, Attal M et al (2007) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells are abnormal in multiple myeloma. Leukemia 21:1079–1088
Streubel B, Chott A, Huber D, Exner M (2004) Lymphoma-specific genetic aberrations in microvascular endothelial cells in B-cell lymphomas. N Engl J Med 351:250–259
Menendez P, Catalina P, Rodríguez R et al (2009) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells from infants with MLL-AF4 acute leukemia harbor and express the MLL-AF4 fusion gene. J Exp Med 206:3131–3141
Sung SY, Hsieh CL, Law A et al (2008) Coevolution of prostate cancer and bone stroma in three-dimensional coculture: implications for cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Res 68:9996–10003
Cogle CR, Theise ND, Fu DT et al (2007) Bone marrow contributes to epithelial cancers in mice and humans as developmental mimicry. Stem Cells 25:1881–1887
Quante M, Tu SP, Tomita H et al (2011) Bone marrow-derived myofibroblasts contribute to the mesenchymal stem cell niche and promote tumor growth. Cancer Cell 19:257–272
Patenaude A, Parker J, Karsan A (2010) Involvement of endothelial progenitor cells in tumor vascularization. Microvasc Res 79:217–223
Mishra PJ, Mishra PJ, Glod JW, Banerjee D (2009) Mesenchymal stem cells: flip side of the coin. Cancer Res 69:1255
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Fang S, Salven P (2010) Stem cells in tumor angiogenesis. J Mol Cell Cardiol 50:290–295
Butler JM, Kobayashi H, Rafii S (2010) Instructive role of the vascular niche in promoting tumour growth and tissue repair by angiocrine factors. Nat Rev Cancer 10:138–146
Liu S, Ginestier C, Ou SJ et al (2011) Breast cancer stem cells are regulated by mesenchymal stem cells through cytokine networks. Cancer Res 71:614–624
McLean K, Gong Y, Choi Y et al (2011) Human ovarian carcinoma-associated mesenchymal stem cells regulate cancer stem cells and tumorigenesis via altered BMP production. J Clin Invest DOI 10.1172/JCI45273
Catena R, Luis-Ravelo D, Antón I et al (2011) PDGFR signaling blockade in marrow stroma impairs lung cancer bone metastasis. Cancer Res 71:164–174
Sohara Y, Shimada H, Minkin C et al (2005) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells provide an alternate pathway of osteoclast activation and bone destruction by cancer cells. Cancer Res 65: 1129–1135
Chantrain CF, Feron O, Marbaix E, DeClerck YA (2008) Bone marrow microenvironment and tumor progression. Cancer Microenviron 1:23–35
Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA (2011) A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science 331:1559–1564
Karnoub AE, Dash AB, Vo AP et al (2007) Mesenchymal stem cells within tumour stroma promote breast cancer metastasis. Nature 449:557–563
Shinagawa K, Kitadai Y, Tanaka M et al (2010) Mesenchymal stem cells enhance growth and metastasis of colon cancer. Int J Cancer 127:2323–2333
Meads MB, Hazlehurst LA, Dalton WS (2008) The bone marrow microenvironment as a tumor sanctuary and contributor to drug resistance. Clin Cancer Res 14:2519–2526
Sneddon JB, Werb Z (2007) Location, location, location: the cancer stem cell niche. Cell Stem Cell 1:607–611
LaBarge MA (2010) The difficulty of targeting cancer stem cell niches. Clin Cancer Res 16:3121–3129
Frassanito MA, Cusmai A, Iodice G, Dammacco F (2001) Autocrine interleukin-6 production and highly malignant multiple myeloma: relation with resistance to drug-induced apoptosis. Blood 97:483–489
Voorhees PM, Chen Q, Kuhn DJ et al (2007) Inhibition of interleukin-6 signaling with CNTO 328 enhances the activity of bortezomib in preclinical models of multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 13: 6469–6478
Duan Z, Foster R, Bell DA et al (2006) Signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 pathway activation in drug-resistant ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:5055–5063
Alsayed Y, Ngo H, Runnels J et al (2007) Mechanisms of regulation of CXCR4/SDF-1 (CXCL12)-dependent migration and homing in multiple myeloma. Blood 109:2708–2717
Juarez J, Pena AD, Baraz R et al (2007) CXCR4 antagonists mobilize childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells into the peripheral blood and inhibit engraftment. Leukemia 21:1249–1257
Spiegel A, Kollet O, Peled A et al (2004) Unique SDF-1-induced activation of human precursor-B ALL cells as a result of altered CXCR4 expression and signaling. Blood 103:2900–2907
Ratajczak MZ, Zuba-Surma E, Kucia M et al (2006) The pleiotropic effects of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis in organogenesis, regeneration and tumorigenesis. Leukemia 20:1915–1924
Yoon Y, Liang Z, Zhang X et al (2007) CXC chemokine receptor-4 antagonist blocks both growth of primary tumor and metastasis of head and neck cancer in xenograft mouse models. Cancer Res 67:7518–7524
Tavor S, Petit I, Porozov S et al (2004) CXCR4 regulates migration and development of human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells in transplanted NOD/SCID mice. Cancer Res 64:2817–2824
Sanz-RodrÍguez F, Hidalgo A, Teixidó J (2001) Chemokine stromal cell-derived factor-1α modulates VLA-4 integrin-mediated multiple myeloma cell adhesion to CS-1/fibronectin and VCAM-1. Blood 97:346–351
Stupp R, Ruegg C (2007) Integrin inhibitors reaching the clinic. J Clin Oncol 25:1637–1638
Miller DH, Khan OA, Sheremata WA et al (2003) A controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 348:15–23
Iwamoto S, Mihara K, Downing JR et al (2007) Mesenchymal cells regulate the response of acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells to asparaginase. J Clin Invest 117:1049–1057
Garrido SM, Appelbaum FR, Willman CL, Banker DE (2001) Acute myeloid leukemia cells are protected from spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis by direct contact with a human bone marrow stromal cell line (HS-5). Exp Hematol 29: 448–457
Kurtova AV, Balakrishnan K, Chen R et al (2009) Diverse marrow stromal cells protect CLL cells from spontaneous and drug-induced apoptosis: development of a reliable and reproducible system to assess stromal cell adhesion-mediated drug resistance. Blood 114:4441–4450
Balakrishnan K, Burger JA, Quiroga MP et al (2010) Influence of bone marrow stromal microenvironment on forodesine-induced responses in CLL primary cells. Blood 116:1083–1091
Ishikawa F, Yoshida S, Saito Y et al (2007) Chemotherapy-resistant human AML stem cells home to and engraft within the bone-marrow endosteal region. Nat Biotechnol 25:1315–1321
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All authors contribute equally to this work
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abarrategi, A., Mariñas-Pardo, L., Mirones, I. et al. Mesenchymal niches of bone marrow in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 13, 611–616 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0706-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12094-011-0706-x