Abstract
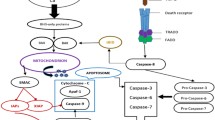
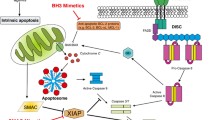
Apoptosis serves to remove excess or damaged cells and its dysregulation may lead to a number of pathological disorders including cancer. Studies during the last 20 years have unravelled much of the molecular mechanisms that control apoptosis. Whether a cell dies in response to diverse apoptotic stimuli, including DNA-damaging agents, is determined largely by interactions between proteins of the Bcl-2 family. A death signal is transmitted through the BH3-only proteins to Bax and Bak which in turn permeabilise the outer mitochondrial membrane allowing the release of apoptogenic factors, which triggers activation of cell-death-promoting caspases. These proteolytic enzymes are tightly controlled by members of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) family. Activation of the caspase cascade via cell death receptors also represents a key apoptotic pathway in both normal and tumour cells. Basic knowledge of these apoptosis regulators provides the basis for novel therapeutic strategies aimed at promoting tumour cell death or enhancing susceptibility to apoptotic inducers. This review focuses on these strategies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meier P, Finch A, Evan G (2000) Apoptosis in development. Nature 407:796–801
Hutchins JB, Barger SW (1998) Why neurons die: cell death in the nervous system. Anat Rec 253:79–90
Fadeel B, Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B (1999) Apoptosis in human disease: a new skin for the old ceremony? Biochem Biophys Res Commun 266:699–717
Saraste A, Pulkki K (2000) Morphologic and biochemical hallmarks of apoptosis. Cardiovasc Res 45:528–537
Hengartner MO, Horvitz HR (1994) The ins and outs of programmed cell death during C. elegans development. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 345:243–246
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH, Currie AR (1972) Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer 26:239–257
Vaux DL, Cory S, Adams JM (1988) Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature 335:440–442
Reed JC, Cuddy M, Slabiak T et al (1988) Oncogenic potential of bcl-2 demonstrated by gene transfer. Nature 336:259–261
McDonnell TJ, Deane N, Platt FM et al (1989) bcl-2-immunoglobulin transgenic mice demonstrate extended B cell survival and follicular lymphoproliferation. Cell 57:79–88
Yuan J, Shaham S, Ledoux S et al (1993) The C. elegans cell death gene ced-3 encodes a protein similar to mammalian interleukin-1 beta-converting enzyme. Cell 75:641–652
Liu X, Kim CN, Yang J et al (1996) Induction of apoptotic program in cell-free extracts: requirement for dATP and cytochrome c. Cell 86:147–157
Inohara N, Ding L, Chen S et al (1997) harakiri, a novel regulator of cell death, encodes a protein that activates apoptosis and interacts selectively with survival-promoting proteins Bcl-2 and Bcl-X(L). EMBO J 16:1686–1694
Yang E, Zha J, Jockel J et al (1995) Bad, a het-erodimeric partner for Bcl-XL and Bcl-2, displaces Bax and promotes cell death. Cell 80:285–291
Wang K, Yin XM, Chao DT et al (1996) BID: a novel BH3 domain-only death agonist. Genes Dev 10:2859–2869
Yin XM, Wang K, Gross A et al (1999) Bid-deficient mice are resistant to Fas-induced hepatocellular apoptosis. Nature 400:886–891
Bouillet P, Metcalf D, Huang DC et al (1999) Proapoptotic Bcl-2 relative Bim required for certain apoptotic responses, leukocyte homeostasis, and to preclude autoimmunity. Science 286:1735–1738
Uren AG, Pakusch M, Hawkins CJ et al (1996) Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologs that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93: 4974–4978
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW et al (1996) A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus iap gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J 15:2685–2694
Muchmore SW, Sattler M, Liang H et al (1996) X-ray and NMR structure of human Bcl-xL, an inhibitor of programmed cell death. Nature 381:335–341
Wang JL, Liu D, Zhang ZJ et al (2000) Structure-based discovery of an organic compound that binds Bcl-2 protein and induces apoptosis of tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:7124–7129
Oltersdorf T, Elmore SW, Shoemaker AR et al (2005) An inhibitor of Bcl-2 family proteins induces regression of solid tumours. Nature 435:677–681
Letai A, Bassik MC, Walensky LD et al (2002) Distinct BH3 domains either sensitize or activate mitochondrial apoptosis, serving as prototype cancer therapeutics. Cancer Cell 2:183–192
Willis SN, Chen L, Dewson G et al (2005) Proapoptotic Bak is sequestered by Mcl-1 and Bcl-xL, but not Bcl-2, until displaced by BH3-only proteins. Genes Dev 19:1294–1305
Kim H, Rafiuddin-Shah M, Tu HC et al (2006) Hierarchical regulation of mitochondrion-dependent apoptosis by BCL-2 subfamilies. Nat Cell Biol 8:1348–1358
Nunez G, Benedict M, Hu Y et al (1998) Caspases: the proteases of the apoptotic pathway. Oncogene 17:3237–3245
Morishima N, Nakanishi K, Takenouchi H et al (2002) An endoplasmic reticulum stress-specific caspase cascade in apoptosis. Cytochrome c-independent activation of caspase-9 by caspase-12. J Biol Chem 277:34287–34294
Boatright KM, Renatus M, Scott FL et al (2003) A unified model for apical caspase activation. Mol Cell 11:529–541
Pop C, Timmer J, Sperandio S et al (2006) The apoptosome activates caspase-9 by dimerization. Mol Cell 22:269–275
Vaux DL, Silke J (2005) IAPs, RINGs and ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:287–297
Gelinas C, White E (2005) BH3-only proteins in control: specificity regulates MCL-1 and BAK-mediated apoptosis. Genes Dev 19:1263–1268
Bredesen DE, Rao RV, Mehlen P (2006) Cell death in the nervous system. Nature 443:796–802
Imaizumi K, Benito A, Kiryu-Seo S et al (2004) Critical role for DP5/Harakiri, a Bcl-2 homology domain 3-only Bcl-2 family member, in axotomy-induced neuronal cell death. J Neurosci 24:3721–3725
Coultas L, Bouillet P, Stanley EG et al (2004) Proapoptotic BH3-only Bcl-2 family member Bik/Blk/Nbk is expressed in hemopoietic and endothelial cells but is redundant for their programmed death. Mol Cell Biol 24:1570–1581
Zinkel SS, Ong CC, Ferguson DO et al (2003) Proapoptotic BID is required for myeloid homeostasis and tumor suppression. Genes Dev 17:229–239
Ranger AM, Zha J, Harada H et al (2003) Bad-deficient mice develop diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:9324–9329
Villunger A, Michalak EM, Coultas L et al (2003) p53-and drug-induced apoptotic responses mediated by BH3-only proteins puma and noxa. Science 302:1036–1038
Tagawa H, Karnan S, Suzuki R et al (2005) Genome-wide array-based CGH for mantle cell lymphoma: identification of homozygous deletions of the proapoptotic gene BIM. Oncogene 24:1348–1358
Mestre-Escorihuela C, Rubio-Moscardo F, Richter JA et al (2007) Homozygous deletions localize novel tumor suppressor genes in B-cell lymphomas. Blood 109:271–280
Puthalakath H, Strasser A (2002) Keeping killers on a tight leash: transcriptional and post-translational control of the pro-apoptotic activity of BH3-only proteins. Cell Death Differ 9:505–512
Sanz C, Mellstrom B, Link W et al (2001) Interleukin 3-dependent activation of DREAM is involved in transcriptional silencing of the apoptotic Hrk gene in hematopoietic progenitor cells. EMBO J 20:2286–2292
Klasa RJ, Gillum AM, Klem RE et al (2002) Oblimersen Bcl-2 antisense: facilitating apoptosis in anticancer treatment. Antisense Nucleic Acid Drug Dev 12:193–213
Reed JC (2006) Drug insight: cancer therapy strategies based on restoration of endogenous cell death mechanisms. Nat Clin Pract Oncol 3:388–398
Tzung SP, Kim KM, Basanez G et al (2001) Antimycin A mimics a cell-death-inducing Bcl-2 homology domains 3. Nat Cell Biol 3:183–191
Real PJ, Cao Y, Wang R et al (2004) Breast cancer cells can evade apoptosis-mediated selective killing by a novel small molecule inhibitor of Bcl-2. Cancer Res 64:7947–7953
Kitada S, Leone M, Sareth S et al (2003) Discovery, characterization, and structure-activity relationships studies of proapoptotic polyphenols targeting B-cell lymphocyte/leukemia-2 proteins. J Med Chem 46:4259–4264
Trauth BC, Klas C, Peters AM et al (1989) Monoclonal antibody-mediated tumor regression by induction of apoptosis. Science 245:301–305
Cretney E, Takeda K, Yagita H et al (2002) Increased susceptibility to tumor initiation and metastasis in TNF-related apoptosis-inducing lig-and-deficient mice. J Immunol 168:1356–1361
Walczak H, Miller RE, Ariail K et al (1999) Tumoricidal activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand in vivo. Nat Med 5:157–163
Hao C, Song JH, Hsi B et al (2004) TRAIL inhibits tumor growth but is nontoxic to human hepatocytes in chimeric mice. Cancer Res 64:8502–8506
Tolcher AW, Mita M, Meropol NJ et al (2007) Phase I pharmacokinetic and biologic correlative study of mapatumumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody with agonist activity to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand receptor-1. J Clin Oncol 25:1390–1395
Schimmer AD, Welsh K, Pinilla C et al (2004) Small-molecule antagonists of apoptosis suppressor XIAP exhibit broad antitumor activity. Cancer Cell 5:25–35
Li L, Thomas RM, Suzuki H et al (2004) A small molecule Smac mimic potentiates TRAIL-and TNFalpha-mediated cell death. Science 305:1471–1474
Jiang X, Kim HE, Shu H et al (2003) Distinctive roles of PHAP proteins and prothymosin-alpha in a death regulatory pathway. Science 299:223–226
Zhang HZ, Kasibhatla S, Wang Y et al (2004) Discovery, characterization and SAR of gambogic acid as a potent apoptosis inducer by a HTS assay. Bioorg Med Chem 12:309–317
Putt KS, Chen GW, Pearson JM et al (2006) Small-molecule activation of procaspase-3 to caspase-3 as a personalized anticancer strategy. Nat Chem Biol 2:543–550
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supported by an unrestricted educational grant from Pfizer.