Abstract
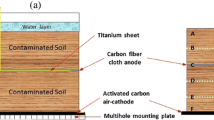
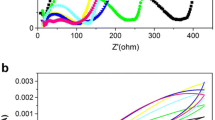
To investigate soil microbial community dynamics in sediment microbial fuel cells (MFCs), this study applied nonhydric (D) and hydric (S) soils to single-chamber and mediator-free MFCs. Glucose was also used to enrich microorganisms in the soils. The voltage outputs of both the D and S sediment MFCs increased over time but differed from each other. The initial open circuit potentials were 345 and 264 mV for the D and S MFCs. The voltage output reached a maximum of 503 and 604 mV for D and S on days 125 and 131, respectively. The maximum power densities of the D and S MFCs were 2.74 and 2.12 mW m−2, analyzed on day 50. Clustering results revealed that the two groups did not cluster after glucose supplementation and 126 days of MFC function. The change in Geobacter abundance was consistent with the voltage output, indicating that these bacteria may act as the main exoelectrogens on the anode. Spearman correlation analysis demonstrated that, in the D soils, Geobacter was positively correlated with Dialister and negatively correlated with Bradyrhizobium, Kaistobacter, Pedomicrobium, and Phascolarctobacterium; in the S soils, Geobacter was positively correlated with Shewanella and negatively correlated with Blautia. The results suggested that different soil sources in the MFCs and the addition of glucose as a nutrient produced diverse microbial communities with varying voltage output efficiencies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Slate AJ, Whitehead KA, Brownson DA, Banks CE (2019) Microbial fuel cells: an overview of current technology. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 101:22
Sallam ER, Khairy HM, Elnouby MS, Fetouh HA (2021) Sustainable electricity production from seawater using Spirulina platensis microbial fuel cell catalyzed by silver nanoparticles-activated carbon composite prepared by a new modified photolysis method. Biomass Bioenergy 148:106038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2021.106038
Matsumoto A, Nagoya M, Tsuchiya M, Suga K, Inohana Y, Hirose A, Yamada S, Hirano S, Ito Y, Tanaka S, Kouzuma A, Watanabe K (2020) Enhanced electricity generation in rice paddy-field microbial fuel cells supplemented with iron powders. Bioelectrochemistry 136:107625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2020.107625
Logan BE (2009) Exoelectrogenic bacteria that power microbial fuel cells. Nat Rev Microbiol 7:375–381. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2113
Shi L, Dong H, Reguera G, Beyenal H, Lu A, Liu J, Yu HQ, Fredrickson JK (2016) Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals. Nat Rev Microbiol 14:651–662. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro.2016.93
Kondaveeti S, Mohanakrishna G, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2019) Methane as a substrate for energy generation using microbial fuel cells. Indian J Microbiol 59:121–124
Bond DR, Holmes DE, Tender LM, Lovley DR (2002) Electrode-reducing microorganisms that harvest energy from marine sediments. Science 295:483–485. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1066771
Holmes DE, Bond DR, O’Neil RA, Reimers CE, Tender LR, Lovley DR (2004) Microbial communities associated with electrodes harvesting electricity from a variety of aquatic sediments. Microb Ecol 48:178–190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-003-0004-4
Kouzuma A, Kasai T, Nakagawa G, Yamamuro A, Abe T, Watanabe K (2013) Comparative metagenomics of anode-associated microbiomes developed in rice paddy-field microbial fuel cells. PLoS ONE 8:e77443. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0077443
Yamamuro A, Kouzuma A, Abe T, Watanabe K (2014) Metagenomic analyses reveal the involvement of syntrophic consortia in methanol/electricity conversion in microbial fuel cells. PLoS ONE 9:e98425. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098425
Sun Y, Zuo J, Cui L, Deng Q, Dang Y (2010) Diversity of microbes and potential exoelectrogenic bacteria on anode surface in microbial fuel cells. J Gen Appl Microbiol 56:19–29. https://doi.org/10.2323/jgam.56.19
Beecroft NJ, Zhao F, Varcoe JR, Slade RC, Thumser AE, Avignone-Rossa C (2012) Dynamic changes in the microbial community composition in microbial fuel cells fed with sucrose. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:423–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3590-y
Zhang H, Chen X, Braithwaite D, He Z (2014) Phylogenetic and metagenomic analyses of substrate-dependent bacterial temporal dynamics in microbial fuel cells. PLOS ONE 9:e107460. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0107460
Ishii S, Suzuki S, Norden-Krichmar TM, Phan T, Wanger G, Nealson KH, Sekiguchi Y, Gorby YA, Bretschger O (2014) Microbial population and functional dynamics associated with surface potential and carbon metabolism. ISME J 8:963–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/ismej.2013.217
Inglett PW, Reddy KR, Corstanje R (2005) Anaerobic soils. In: Hillel D (eds) Encyclopedia of soils in the environment. Elsevier, pp 72–78
Yang SF, Huang HD, Fan WL, Jong YJ, Chen MK, Huang CN, Chuang CY, Kuo YL, Chung WH, Su SC (2018) Compositional and functional variations of oral microbiota associated with the mutational changes in oral cancer. Oral Oncol 77:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oraloncology.2017.12.005
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:5069–5072. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.03006-05
Wang Q, Garrity GM, Tiedje JM, Cole JR (2007) Naive Bayesian classifier for rapid assignment of rRNA sequences into the new bacterial taxonomy. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:5261–5267. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00062-07
Gu Z, Eils R, Schlesner M (2016) Complex heatmaps reveal patterns and correlations in multidimensional genomic data. Bioinformatics 32:2847–2849. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btw313
R Core Team (2017) R: A language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria
Timmers RA, Strik DP, Hamelers HV, Buisman CJ (2010) Long-term performance of a plant microbial fuel cell with Spartina anglica. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 86:973–981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2440-7
Kondaveeti S, Mohanakrishna G, Kumar A, Lai C, Lee J-K, Kalia VC (2019) Exploitation of citrus peel extract as a feedstock for power generation in microbial fuel cell (MFC). Indian J Microbiol 59:476–481. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-019-00829-7
Kondaveeti S, Mohanakrishna G, Pagolu R, Kim I-W, Kalia VC, Lee J-K (2019) Bioelectrogenesis from raw algal biomass through microbial fuel cells: effect of acetate as co-substrate. Indian J Microbiol 59:22–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-018-0769-2
Choo YF, Lee J, Chang IS, Kim BH (2006) Bacterial communities in microbial fuel cells enriched with high concenrations of glucose and glutamate. J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:4
Jung S, Regan JM (2007) Comparison of anode bacterial communities and performance in microbial fuel cells with different electron donors. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 77:393–402. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-007-1162-y
Arcand MM, Levy-Booth DJ, Helgason BL (2017) Resource legacies of organic and conventional management differentiate soil microbial carbon use. Front Microbiol 8:2293. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02293
Wu Y, Cai P, Jing X, Niu X, Ji D, Ashry NM, Gao C, Huang Q (2019) Soil biofilm formation enhances microbial community diversity and metabolic activity. Environ Int 132:105116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2019.105116
Song N, Jiang H, Yan Z (2019) Contrasting effects of sediment microbial fuel cells (SMFCs) on the degradation of macrophyte litter in sediments from different areas of a shallow eutrophic lake. Appl Sci 9:13
Yang J, Cheng S (2019) Effects of using anode biofilm and cathode biofilm bacteria as inoculum on the start-up, electricity generation, and microbial community of air-cathode single-chamber microbial fuel cells. Pol J Environ Stud 28:8
Li X, Li Y, Zhang X, Zhao X, Chen X, Li Y (2020) The metolachlor degradation kinetics and bacterial community evolution in the soil bioelectrochemical remediation. Chemosphere 248:125915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.125915
Li X, Wang X, Wan L, Zhang Y, Li N, Li D, Zhou Q (2016) Enhanced biodegradation of aged petroleum hydrocarbons in soils by glucose addition in microbial fuel cells. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 91:9
Jumas-Bilak E, Jean-Pierre H, Carlier JP, Teyssier C, Bernard K, Gay B, Campos J, Morio F, Marchandin H (2005) Dialister micraerophilus sp. nov. and dialister propionicifaciens sp. nov., isolated from human clinical samples. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:2471–2478. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.63715-0
Gan Y, Qiu Q, Liu P, Rui J, Lu Y (2012) Syntrophic oxidation of propionate in rice field soil at 15 and 30 °C under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol 78:4923–4932. https://doi.org/10.1128/AEM.00688-12
Harris HW, Sanchez-Andrea I, McLean JS, Salas EC, Tran W, El-Naggar MY, Nealson KH (2017) Redox sensing within the genus Shewanella. Front Microbiol 8:2568. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02568
Carvalhais LC, Dennis PG, Tyson GW, Schenk PM (2012) Application of metatranscriptomics to soil environments. J Microbiol Methods 91:246–251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mimet.2012.08.011
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Mr. Cheng-Yu Lin for his hard work and Mrs. Glory Chen (C.-H.L.’s wife) for her correction on English writing. This manuscript was edited by Wallace Academic Editing. This research was supported partly by Grant ORD-104074 from Da-Yeh University to C.-H. L.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuo, J., Liu, D., Wang, SH. et al. Dynamic Changes in Soil Microbial Communities with Glucose Enrichment in Sediment Microbial Fuel Cells. Indian J Microbiol 61, 497–505 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00959-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-021-00959-x