Abstract
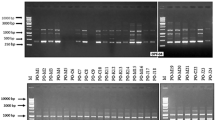
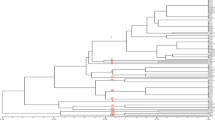
Xanthomonas axonopodis pv manihotis is the causal agent of cassava bacterial blight (CBB) worldwide. CBB disease is a major constraint to cassava cultivation, and losses can be extremely severe in regions where highly susceptible cultivars are grown. To develop an efficient disease management policy, the genetic diversity of the pathogens population must be known. There is dearth of information on the genetic diversity of X. axonopodis pv manihotis population in Nigeria. We used RAPD (random amplified polymorphic DNA) and AFLP (amplified fragment length polymorphism), a PCR-based technique, to characterize the X. axonopodis pv manihotis isolates from the western States of Nigeria. Thirteen strains Xam and 2 reference strains were tested with eight primers combination of AFLP and 4 RAPD primers. RAPD amplified DNA fragment data showed four major clusters at 80 % similarity coefficient level and two strains were not clustered by this analysis. Strains Kwa76A and Ond48A were also separated in the principal component analysis of the same data. Numerical analysis differentiated the AFLP patterns into four distinct clusters and grouped two strains separately at 66 % similarity. PCA assembly grouped the bacterial strains into 4 and one of the strains was singled out from the others. The two DNA analyses techniques seem to be complimentary to one another and informative on the genomic structure of Xam population in Western Nigeria. The genetic analysis presented here contributes to understanding of the Xam population structure in Western Nigeria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nilmanee S (1986) Disease of Cassava. In: Review of Tropical Plant Pathology (Eds. Raychaudhuri SP, Verma JP) 3: 213–247
Lozano JC (1986) Cassava Bacterial Blight: A manageable disease. Plant Disease 70:1089–1093
Verdier V, Dongo P and Boher B (1993) Assessment of genetic diversity among strains of Xanthomonas campestris pv manihotis. J Gen Microbiol 139: 2591–2601
Verdier V, Restrepo S, Mosquera G, Duque MC, Gerstl A and Laberry R (1998) Genetic and pathogenic variation of Xanthomonas axonopodis p v. manihotis in Venezuela. Plant Pathology 47:601–608
Restrepo S and Verdier V (1997) Geographical differentiation of the population of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:4427–4434
Restrepo S, Duque MC, Tohme J and Verdier V (1999) AFLP fingerprinting: an efficient technique for detecting genetic variation of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis. Microbiology 145:107–114
Restrepo S, Velez CM, Duque MC and Verdier V (2004) Genetic structure and population dynamics of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. manihotis in Colombia from 1995 to 1999. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 70:255–261
Assigbetsé K, Verdier V, Wydra K, Rudolph K and Geiger JP (1998) Genetic variation of the cassava bacterial blight pathogen, Xanthomonas campestris pv. manihotis, originating from different ecoregions in Africa, p. 223–229. In IX International Conference on Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, Madras, India
Ogunjobi AA, Fagade OE and Dixon AGO (2006) Molecular variation in population structure of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv manihotis in the south eastern Nigeria. African Journal Biotechnology 5(20):1868–1872
Dixon AGO, Ngeve JM and Nukenine EN (2002) Genotype x environment effects on severity of cassava bacterial blight disease caused by Xanthomonas axonopodis pv manihotis. European Journal of Plant Pathology 108:763–770
FAO (2000) Championing the cause of cassava. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) News and Highlights, www.fao.org/news/2000 (April 2002)
Ogunjobi AA, Fagade OE, Dixon AGO and Amusa N (2007a) Pathological Variation in Cassava Bacterial Blight (CBB) isolates in Nigeria. World Applied Sciences Journal 2(6):587–593
Ogunjobi AA, Fagade OE and Dixon AGO (2007b) Physiological studies on Xanthomonas axonopodis pv manihotis (Xam) strains isolated in Nigeria. Electronic Journal of Environmental Agricultural and Food Chemistry 6(10): 2482–2489
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF and Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning a laboratory manual Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, USA
Rolf FJ (1994) NTSYS-PC: Numerical Taxonomy and multivariate analysis Syst, Version 2.0. New York: Exeter Software
SAS Institute (1998) SAS/IML software: Usage and Reference, Version 8.0 1st edn. Cary, NC: SAS Institute
Verdier, V, Boher B, Maraite H and Geiger JP (1994) Pathological and molecular characterization of Xanthomonas campestris isolates causing diseases of cassava (Manihot esculenta). Applied Environmental Microbiology 60: 4478–4486
Janssen P, Coopman R, Huys G, Swings J, Bleeker M, Vos P, Zabeau M and Kersters K (1996) Evaluation of the DNA fingerprinting method AFLP as a new tool in bacterial taxonomy. Microbiology 142:1881–1893
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ogunjobi, A.A., Fagade, O.E. & Dixon, A.G.O. Comparative analysis of genetic variation among Xanthomonas axonopodis pv manihotis isolated from the western states of Nigeria using RAPD and AFLP. Indian J Microbiol 50, 132–138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-010-0037-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12088-010-0037-6