Abstract
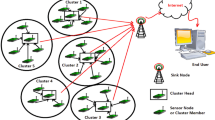
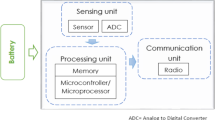
Wireless sensor network (WSN) is composed of high density spatially dispersed and dedicated autonomous sensors for monitoring or recording the physical conditions of the environment. Still, the sensor nodes are battery-powered with limited energy supply; moreover, in many of the applications, sensor nodes are deployed in harsh natural environment or vast space so that the continuous energy supplement is impossible. Many authors focused to achieve trade-offs in terms of energy, and delay for such data collection tasks; few of them are concerned with sleep scheduling. In this paper, we propose energy efficient and delay aware routing using multi-objective clustering and a sleep schedules scheme for WSN (E2DR-MCS). The first contribution of this paper is to propose a multi-objective wolf optimization algorithm for clustering. Additionally, a sleep scheduling scheme is utilized to save power and increase the lifetime of the entire network. The second contribution is that the efficient data collection is achieved by a selective track search algorithm, which provides a suitable path between the source-destination pairs. The simulation results show that E2DR-MCS approach greatly contributes to minimizing energy consumption, delay, and overhead; maximize the network lifetime and delivery ratio.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pu F, Wang Z, Chen N, Zhang W, Du C (2016) Semantic integration of wireless sensor networks into open geospatial consortium sensor observation service to access and share environmental monitoring systems. IET Softw 10(2):45–53. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-sen.2014.0141
More A, Wagh S, Joshi K (2015) A test-bed for habitat monitoring system using Wi-Fi in Wireless Sensor Networks. 2015 IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Computing Research (ICCIC). https://doi.org/10.1109/iccic.2015.7435758
Wan L, Han G, Shu L, Feng N, Zhu C, Lloret J (2015) Distributed parameter estimation for Mobile wireless sensor network based on cloud computing in battlefield surveillance system. IEEE Access 3:1729–1739. https://doi.org/10.1109/access.2015.2482981
Chen J, Klein J, Wu Y et al (2016) A thermoelectric energy harvesting system for powering wireless sensors in nuclear power plants. IEEE Trans Nucl Sci 63(5):2738–2746. https://doi.org/10.1109/tns.2016.2606090
Mendis C, Skvortsov A, Gunatilaka A, Karunasekera S (2012) Performance of wireless chemical sensor network with dynamic collaboration. IEEE Sensors J 12(8):2630–2637. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2012.2198349
Hao W, Yuqing Z (2014) AraTRM: attack resistible ant-based trust and reputation model. 2014 IEEE Int Conf Comput Inform Technol. https://doi.org/10.1109/cit.2014.78
Dilhac J, Bafleur M (2014) Energy harvesting in aeronautics for battery-free wireless sensor networks. IEEE Aerosp Electron Syst Mag 29(8):18–22. https://doi.org/10.1109/maes.2014.130002
Huang J, Wang H, Qian Y, Wang C (2013) Priority-based traffic scheduling and utility optimization for cognitive radio communication infrastructure-based smart grid. IEEE Trans Smart Grid 4(1):78–86. https://doi.org/10.1109/tsg.2012.2227282
Balapuwaduge I, Jiao L, Pla V, Li F (2014) Channel assembling with priority-based queues in cognitive radio networks: strategies and performance evaluation. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 13(2):630–645. https://doi.org/10.1109/twc.2013.120713.121948
Xiong Z, Wang B, Wang Z (2015) Priority-based greedy scheduling for confident information coverage in energy harvesting wireless sensor networks. 2015 11th International Conference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Networks (MSN). doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/msn.2015.20
Darbha S, Agrawal D (1994) A task duplication based optimal scheduling algorithm for variable execution time tasks. 1994 Int Conf Parallel Process (ICPP'94). https://doi.org/10.1109/icpp.1994.47
Mei J, Li K (2012) Multi-copy deleting approach for duplication based scheduling on heterogeneous computing systems. 2012 41st Int Conf Parallel Process Workshops. https://doi.org/10.1109/icppw.2012.93
Peng M, Xiao Y, Wang P (2009) Error analysis and kernel density approach of scheduling sleeping nodes in cluster-based wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 58(9):5105–5114. https://doi.org/10.1109/tvt.2009.2027908
Hsieh M (2011) Data aggregation model using energy-efficient delay scheduling in multi-hop hierarchical wireless sensor networks. IET Commun 5(18):2703–2711. https://doi.org/10.1049/iet-com.2011.0140
Chae S, Kang K, Cho Y (2013) A scalable joint routing and scheduling scheme for large-scale wireless sensor networks. Ad Hoc Netw 11(1):427–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adhoc.2012.07.004
WU X, LI Y, JI H (2014) Clustering and scheduling methods based on SLNR in downlink CoMP system. J Chin Univ Posts Telecommun 21(1):74–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1005-8885(14)60271-5
Sun Q, Zhuge Q, Hu J, Yi J, Sha E (2014) Efficient grouping-based mapping and scheduling on heterogeneous cluster architectures. Comput Electr Eng 40(5):1604–1620. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compeleceng.2014.03.009
Wang L, Wei R, Tian Z (2011) Cluster based node scheduling method for wireless sensor networks. Scientia Sinica Informationis: 1013–1023
Indra Gandhi K, Narayanasamy P (2010) A cluster-based quad-tree partitioning for scheduling the mobile element in wireless sensor networks. Int J Wireless Inf Networks 18(1):50–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10776-010-0119-8
Severino R, Pereira N, Tovar E (2014) Dynamic cluster scheduling for cluster-tree WSNs. SpringerPlus. 3(1):493. https://doi.org/10.1186/2193-1801-3-493
Wu B, Feng Y, Zheng H, Chen X (2016) Dynamic cluster members scheduling for target tracking in sensor networks. IEEE Sensors J 16(19):7242–7249. https://doi.org/10.1109/jsen.2016.2597544
Lersteau C, Rossi A, Sevaux M (2016) Robust scheduling of wireless sensor networks for target tracking under uncertainty. Eur J Oper Res 252(2):407–417. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejor.2016.01.018
Izadi D, Ghanavati S, Abawajy J, Herawan T (2016) An alternative data collection scheduling scheme in wireless sensor networks. Computing. 98(12):1287–1304. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00607-016-0484-y
Gentz R, Scaglione A, Ferrari L, Hong Y (2016) PulseSS: a pulse-coupled synchronization and scheduling protocol for clustered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Internet Things J 3(6):1222–1234. https://doi.org/10.1109/jiot.2016.2576923
Yang C, Lu J, Yang W, Shi H (2017) Sensor scheduling for lifetime maximization in centralized state estimation. Neurocomputing. 270:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neucom.2016.12.107
Palaniappan S, Periasamy P (2017) Proposed energy efficient multi attribute time slot scheduling algorithm for quality of Service in Wireless Sensor Network. Wirel Pers Commun 97(4):5951–5968. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11277-017-4821-z
Li J, Peng M, Cheng A, Yu Y, Wang C (2017) Resource allocation optimization for delay-sensitive traffic in fronthaul constrained cloud radio access networks. IEEE Syst J 11(4):2267–2278. https://doi.org/10.1109/JSYST.2014.2364252
Peng M, Yu Y, Xiang H, Poor HV (2016) Energy-efficient resource allocation optimization for multimedia heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. IEEE Trans Multimed 18(5):879–892. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMM.2016.2535722
Li J, Peng M, Yu Y, Ding Z (2016) Energy-efficient joint congestion control and resource optimization in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 65(12):9873–9887. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2016.2531184
Peng M, Zhang K, Jiang J, Wang J, Wang W (2015) Energy-efficient resource assignment and power allocation in heterogeneous cloud radio access networks. IEEE Trans Veh Technol 64(11):5275–5287. https://doi.org/10.1109/TVT.2014.2379922
Li J, Wu J, Peng M, Zhang P (2016) Queue-aware energy-efficient joint remote radio head activation and beamforming in cloud radio access networks. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 15(6):3880–3894. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2016.2530711
Chen H, Lou W, Wang Z, Xia F (2018) On achieving asynchronous energy-efficient neighbour discovery for mobile sensor networks. IEEE Trans Emerg Top Comput 6(5):553–565. https://doi.org/10.1109/TETC.2016.2586192
Caleffi M, Trianni V, Cacciapuoti AS (2018) Self-organizing strategy design for heterogeneous coexistence in the sub-6 GHZ. IEEE Trans Wirel Commun 17(11):7128–7143. https://doi.org/10.1109/TWC.2018.2864734
Ashrafi S (2018) Inventor; NxGen partners IP LLC, assignee. Sdn-based channel estimation for multiplexing between los mmwaves, nlos sub-6 ghz and fso. United States patent application US 15/689,782
Naqvi SA, Pervaiz H, Hassan SA, Musavian L, Ni Q, Imran MA, Ge X, Tafazolli R (2018) Energy-aware radio resource management in D2D-enabled multi-tier hetnets. IEEE Access 6:16610–16622. https://doi.org/10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2817189
Neamatollahi P, Naghibzadeh M, Abrishami S, Yaghmaee M (2017) Distributed clustering-task scheduling for wireless sensor networks using dynamic hyper round policy. IEEE Trans Mob Comput :1–1. doi:https://doi.org/10.1109/tmc.2017.2710050
Mirjalili S, Mirjalili S, Lewis A (2014) Grey wolf optimizer. Adv Eng Softw 69:46–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.advengsoft.2013.12.007
Bai G, Tian Z, Zuo M (2016) An improved algorithm for finding all minimal paths in a network. Reliab Eng Syst Saf 150:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ress.2016.01.011
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guruprakash, B., Balasubramanian, C. & Sukumar, R. An approach by adopting multi-objective clustering and data collection along with node sleep scheduling for energy efficient and delay aware WSN. Peer-to-Peer Netw. Appl. 13, 304–319 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00779-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12083-019-00779-3