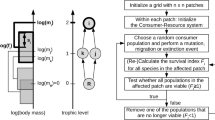
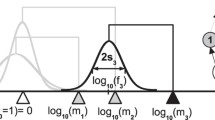
Abstract
Using computer simulations for the population dynamics of systems with many species, we investigate the stability of food webs distributed over several patches that are connected by migration. We evaluate the proportion of persisting species (robustness) and the probability that dynamics reach a fixed point in dependence of food-web complexity, patch arrangement, and migration rule. We find that migration in general increases robustness. This increase is strongest for intermediate migration rates and for star-like patch arrangements. The probability of reaching a fixed point decreases for intermediate migration rate, and has a large peak at larger migration rate for the star topology. We explain these various observations by the rescue effect, by dynamical coexistence of species, and by the buildup of biomass reservoirs in highly connected patches. As the species number becomes larger, differences between different patch arrangements become smaller, and the decrease in the probability of reaching a fixed point vanishes. This means that complex food webs are in some sense dynamically simpler than food webs consisting of less species.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrams PA, Ruokolainen L (2011) How does adaptive consumer movement affect population dynamics in consumer-resource metacommunities with homogeneous patches J Theor Biol 277(1):99–110
Amarasekare P (2008) Spatial Dynamics of Foodwebs. Annu Rev Ecol Evol Syst 39(1):479–500
Bascompte J, Solé RV (1994) Spatially induced bifurcations in single-species population dynamics. J Anim Ecol 63(2):256–264
Berlow EL, Neutel AM, Cohen JE, de Ruiter PC, Ebenman B, Emmerson M, Fox JW, Jansen VAA, Iwan Jones J, Kokkoris GD, Logofet DO, McKane AJ, Montoya JM, Petchey O (2004) Interaction strengths in food webs: issues and opportunities. J Anim Ecol 73(3):585–598
Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2006) Allometric scaling enhances stability in complex food webs. Ecol Lett 9(11):1228–1236
Brose U, Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2003) Comment on foraging adaptation and the relationship between food-web complexity and stability. Science 301(5635):918–918
Brown JH, Kodric-Brown A (1977) Turnover rates in insular biogeography: effect of immigration on extinction. Ecology 58(2):445–449
Brown JH, Gillooly JF, Allen AP, Savage VM, West GB (2004) Toward a metabolic theory of ecology. Ecology 85(7):1771–1789
Calcagno V, Massol F, Mouquet N, Jarne P, David P (2011) Constraints on food chain length arising from regional metacommunity dynamics. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 278(1721):3042–3049
Cooper JK, Li J, Montagnes DJS (2012) Intermediate fragmentation per se provides stable predator-prey metapopulation dynamics. Ecol Lett 15(8):856–863
Gouhier TC, Guichard F, Gonzalez A (2010) Synchrony and stability of food webs in metacommunities. Am Nat 175(2):E16–E34
Gravel D, Canard E, Guichard F, Mouquet N (2011) Persistence increases with diversity and connectance in trophic metacommunities. PLoS One 6(5):e19,374
Gross T, Rudolf L, Levin SA, Dieckmann U (2009) Generalized models reveal stabilizing factors in food webs. Science 325(80):747–750
Haegeman B, Loreau M (2014) General relationships between consumer dispersal, resource dispersal and metacommunity diversity. Ecol Lett 17(2):175–184
Hauzy C, Gauduchon M, Hulot FD, Loreau M (2010) Density-dependent dispersal and relative dispersal affect the stability of predator-prey metacommunities. J Theor Biol 266(3):458–469
Heckmann L, Drossel B, Brose U, Guill C (2012) Interactive effects of body-size structure and adaptive foraging on food-web stability. Ecol Lett 15(3):243–250
Holt RD (2002) Food webs in space: On the interplay of dynamic instability and spatial processes. Ecol Res 17:261–273
Holyoak M, Lawler SP (1996) The role of dispersal in predator-prey metapopulation dynamics. J Anim Ecol 65(5):640–652
Huang Y, Diekmann O (2001) Predator migration in response to prey density: what are the consequences J Math Biol 43:561– 581
Jansen VAA (1995) Regulation of predator-prey systems through spatial interactions: a possible solution to the paradox of enrichment. Oikos 74(3):384–390
Jansen VAA (2001) The dynamics of two diffusively coupled predator-prey populations. Theor Popul Biol 59(2):119–131
Jansen VAA, Lloyd AL (2000) Local stability analysis of spatially homogeneous solutions of multi-patch systems. J Math Biol 41:232–252
Jansen VAA, de Roos AM (2000) The role of space in reducing predator-prey cycles. In: Geom Ecol Interact Simpl Spat Complex, pp 183–201
Kartascheff B, Guill C, Drossel B (2009) Positive complexity-stability relations in food web models without foraging adaptation. J Theor Biol 259(1):12–23
Kartascheff B, Heckmann L, Drossel B, Guill C (2010) Why allometric scaling enhances stability in food web models. Theor Ecol 3(3):195–208
Koelle K, Vandermeer J (2005) Dispersal-induced desynchronization: from metapopulations to metacommunities. Ecol Lett 8(2):167–175
Kondoh M (2003) Foraging adaptation and the relationship between food-web complexity and stability. Science 299(80-):1388–1391
Kondoh M (2006) Does foraging adaptation create the positive complexity stability relationship in realistic food-web structure J Theor Biol 238(3):646–651
Levin SA (1992) The problem of pattern and scale in ecology: the Robert H. MacArthur award lecture. Ecology 73(6):1943–1967
Loreau M, Mouquet N, Gonzalez A (2003) Biodiversity as spatial insurance in heterogeneous landscapes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(22):12,765–12,770
Martinez ND, Williams RJ, Dunne JA (2005) Diversity, complexity, and persistence in large model ecosystems. In: Pascual M, Dunne JA (eds) Ecol Networks Link Struct to Dyn Food Webs, pp 163–185
Maser GL, Guichard F, McCann KS (2007) Weak trophic interactions and the balance of enriched metacommunities. J Theor Biol 2472):337–345
May RM (1972) Will a large complex system be stable Nature 238:413–414
McCann KS (2000) The diversity-stability debate. Nature 405(6783):228–233
McCann KS, Hastings A, Huxel GR (1998) Weak trophic interactions and the balance of nature. Nature 395(6704):794–798
McCann KS, Rasmussen J, Umbanhowar J (2005) The dynamics of spatially coupled food webs. Ecol Lett 8(5):513–523
Mouquet N, Loreau M (2003) Community patterns in sourcesink metacommunities. Am Nat 162(5):544–557
Neutel AM, Heesterbeek JAP, de Ruiter PC (2002) Stability in real food webs: weak links in long loops. Science 296(80-):1120–1123
Plitzko SJ, Drossel B, Guill C (2012) Complexity-stability relations in generalized food-web models with realistic parameters. J Theor Biol 306:7–14
Post DM, Conners ME, Goldberg DS (2000) Prey preference by a top predator and the stability of linked food chains. Ecology 81(1):8–14
de Roos AM, McCauley E, Wilson WG (1998) Pattern formation and the spatial scale of interaction between predators and their prey. Theor Popul Biol 53(2):108–130
Sinha S, Sinha S (2005) Evidence of universality for the May-Wigner stability theorem for random networks with local dynamics. Phys Rev E 71(2):020,902
Tromeur E, Rudolf L , Gross T (2013) Impact of dispersal on the stability of metapopulations. arXiv:1305.2769v1
Uchida S, Drossel B, Brose U (2007) The structure of food webs with adaptive behaviour. Ecol Modell 206(3–4):263–276
Williams RJ, Martinez ND (2000) Simple rules yield complex food webs. Nature 404(6774):180–183
Yodzis P (1981) The stability of real ecosystems. Nature 289(5799):674–676
Yodzis P, Innes S (1992) Body size and consumer-resource dynamics. Am Nat 139(6):1151–1175
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation under contract number Dr300/12-1.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plitzko, S.J., Drossel, B. The effect of dispersal between patches on the stability of large trophic food webs. Theor Ecol 8, 233–244 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12080-014-0247-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12080-014-0247-3