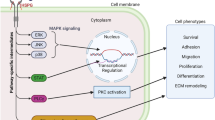
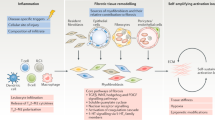
Abstract
There is no treatment for fibrotic disease. TGFβ is known to promote fibrogenesis in vivo and in vitro, however, development of anti-fibrotic strategies targeting the TGFβ axis is problematic owing to the pleitropic nature of TGFβ action. Two recent papers (Kavian et al. 2010; Nyhan et al. 2010) suggest that the jagged/Notch pathway may selectively mediate fibrogenic properties of TGFβ and thus may represent a novel therapeutic approach to fibrosis for scleroderma and kidney fibrosis; these papers are the subject of this commentary.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hay ED (1995) An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat (Basel) 154:8–20
Hills CE, Squires PE (2010) TGF-beta1-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and therapeutic intervention in diabetic nephropathy. Am J Nephrol 31:68–74
Hinz B, Phan SH, Thannickal VJ, Galli A, Bochaton-Piallat ML, Gabbiani G (2007) The myofibroblast: one function, multiple origins. Am J Pathol 170:1807–1816
Humphreys BD, Lin SL, Kobayashi A, Hudson TE, Nowlin BT, Bonventre JV, Valerius MT, McMahon AP, Duffield JS (2010) Fate tracing reveals the pericyte and not epithelial origin of myofibroblasts in kidney fibrosis. Am J Pathol 176:85–97
Kavian N, Servettaz A, Mongaret C, Wang A, Nicco C, Chéreau C, Grange P, Vuiblet V, Birembaut P, Diebold MD, Weill B, Dupin N, Batteux F. (2010) Targeting ADAM17-notch signaling abrogates the development of systemic sclerosis in a murine model. Arthritis Rheum, Jun 25. doi:10.1002/art.27626
Krieg T, Abraham D, Lafyatis R (2007) Fibrosis in connective tissue disease: the role of the myofibroblast and fibroblast-epithelial cell interactions. Arthritis Res Ther 9(Suppl 2):S4
Leask A, Abraham DJ (2004) TGF-beta signaling and the fibrotic response. FASEB J 18:816–827
Liu S, Taghavi R, Leask A (2010) Connective tissue growth factor is induced in bleomycin-induced skin scleroderma. J Cell Commun Signal 4:25–30
Morrissey J, Guo G, Moridaira K, Fitzgerald M, McCracken R, Tolley T, Klahr S (2002) Transforming growth factor-beta induces renal epithelial jagged-1 expression in fibrotic disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1499–1508
Moustakas A, Heldin CH (2007) Signaling networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci 98:1512–1520
Nyhan KC, Faherty N, Murray G, Cooey LB, Godson C, Crean JK, Brazil DP (2010) Jagged/Notch signalling is required for a subset of TGFβ1 responses in human kidney epithelial cells. Biochim Biophys Acta, Sep 15. doi:10.1016/j.bbamcr.2010.09.001
Pinzani M (2008) Welcome to fibrogenesis & tissue repair. Fibrogenesis Tiss Rep 1:1
Rajkumar VS, Sundberg C, Abraham DJ, Rubin K, Black CM (1999) Activation of microvascular pericytes in autoimmune Raynaud’s phenomenon and systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 42:930–941
Rajkumar VS, Howell K, Csiszar K, Denton CP, Black CM, Abraham DJ (2005) Shared expression of phenotypic markers in systemic sclerosis indicates a convergence of pericytes and fibroblasts to a myofibroblast lineage in fibrosis. Arthritis Res Ther 7:R1113–R1123
Shiwen X, Rajkumar V, Denton CP, Leask A, Abraham DJ (2009) Pericytes display increased CCN2 expression upon culturing. J Cell Commun Signal 3:61–64
Zavadil J, Cermak L, Soto-Nieves N, Böttinger EP (2004) Integration of TGF-beta/Smad and Jagged1/Notch signalling in epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. EMBO J 23:1155–1165
Zeisberg M, Duffield JS (2010) Resolved: EMT produces fibroblasts in the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1247–1253
Zeisberg M, Kalluri R (2008) Fibroblasts emerge via epithelial-mesenchymal transition in chronic kidney fibrosis. Front Biosci 13:6991–6998
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Leask, A. Targeting the jagged/notch pathway: a new treatment for fibrosis?. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 4, 197–198 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0101-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-010-0101-3