Abstract
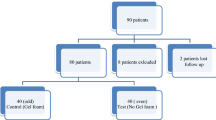
The objective of this study was to compare graft uptake and hearing improvement in active and inactive mucosal chronic otitis media patients after endoscopic myringoplasty. This is prospective study conducted at a government medical college and hospital from February 2014 to August 2015. A total of 40 active (wet) ears with mucoid discharge and 40 inactive (dry) ears (at least 6 weeks dry before surgery) with mucosal chronic otitis media were operated on by endoscopic myringoplasty by transcanal approach. Graft uptake and hearing gain rates 3 months after surgery were compared for both groups. Endoscopic myringoplasty using temporal fascia graft via transcanal approach was used. The graft take rate was 77.5% for the active ear group and 85% for the inactive ear group. The hearing gain rate was 82.5% for the inactive ear group and 72.5% for the active ear group. Differences were found to be statistically insignificant for both graft uptake and hearing gain. The success of endoscopic myringoplasty is not adversely affected by the presence of mucoid ear discharge at the time of surgery, and outcomes are comparable to those of the operation done for inactive ear.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gulya AJ (2010) Pathology and clinical course of the inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. Glasscock–Shambaugh surgery of the ear, 6th edn. People’s Medical House, Shelton, pp 427–428
Rourke T, Snelling JD, Aldren C (2010) Cartilage graft butterfly myringoplasty: how we do it. Clin Otolaryngol 35:135–138
Berthold E (1878) Ueber myringoplastik. Wier Med Bull 1:627
Wullstein H (1956) Theory and practice of myringoplasty. Laryngoscope 66:1076–1093
Zollner F (1955) The principles of plastic surgery of the sound-conducting apparatus. J Laryngol Otol 69:637–652
Harugop AS, Mudhol RS, Godhi RA (2008) A comparative study of endoscope assisted myringoplasty and micrsoscope assisted myringoplasty. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 60:298–302
Thomassin JM, Duchon-Doris JM, Emram B, Rud C, Conciatori J, Vilcoq P (1990) Endoscopic ear surgery. Initial evaluation. Ann Otolaryngol Chir Cervicofac 107:564–570
El-Guindy A (1992) Endoscopic transcanal myringoplasty. J Laryngol Otol 106:493–495
Vartiainen E, Nuutinen J (1993) Success and pitfalls in myringoplasty: follow-up study of 404 cases. Am J Otol 14(3):301–305
Westerberg J, Harder H, Magnuson B, Westerberg L, Hyden D (2011) Ten year myringoplasty series: does the cause of perforation affect the success rate? J Laryngol Otol 125:126–132
Mills R, Thiel G, Mills N (2013) Results of myringoplasty operations in active and inactive ears in adults. Laryngoscope 123:2245–2249
Umapathy N, Dekker PJ (2003) Myringoplasty: is it worth performing in children? Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:1053–1055
Vrabec JT, Deskin RW, Grady JJ (1999) Meta-analysis of pediatric tympanoplasty. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 125:530–534
Nagle SK, Jagade MV, Gandhi SR, Pawar PV (2009) Comparative study of outcome of type I tympanoplasty in dry and wet ear. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 61:138–140
Gersdorff M, Garin P, Decat M (1995) Myringoplasty: long term results in adults and children. Am J Otol 16:532–535
Pignataro L, Grillo Della Berta L, Capaccio P, Zaghis A (2001) Myringoplaty in children: anatomical and functional results. J Laryngol Otol 115:369–373
Noh H, Lee DH (2012) Vascularisation of myringo-tympanoplastic grafts in active and inactive chronic mucosal otitis media: a prospective cohort study. Clin Otolaryngol 37:355–361
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights Statement
All procedures performed in the study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tasleem, M., Rahman, A. & Aslam, M. Comparative Study of Outcome of Endoscopic Myringoplasty in Active and Inactive Mucosal Chronic Otitis Media Patients. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 69, 319–322 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1121-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-017-1121-6