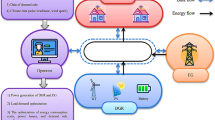
Abstract
One of the major aspects regarding the operation and planning of a power system was to reduce the emission of pollutions and fuel costs in thermal power plants. This issue was resolved as an optimization crisis, where the reduction of emission of pollutions and fuel cost was done and it is known as the combined economic emission dispatch (CEED) problem. Various techniques were introduced for improving the performance of the power plants with respect to algorithm reliability, solution accuracy, global optimality, and convergence speed for resolving the CEED issues. Therefore, this work establishes a CEED approach for the smart grid system and resolves it by exploiting the hybridized concepts of the crow search algorithm (CSA) and differential evolution (DE). The hybridized model of the two well-known schemes is achieved by updating the solutions of both the schemes and merging them with the random searching model. Thus, the new approach is named as hybrid DE and CSA model. The CEED approach is subjected to reduce its cost and therefore, sufficient trade-off between the emission and economic costs could be sustained. The presented hybrid scheme is simulated on 3 diverse bus systems and its performance is evaluated over other state-of-the-art models in terms of CPU time and generation strategy.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CEED:
-
Combined economic emission dispatch
- CSA:
-
Crow search algorithm
- DE:
-
Differential evolution
- hDECSA:
-
Hybrid DE and CSA
- PSO:
-
Particle swarm optimization
- GU:
-
Generating units
- LM:
-
Lagrangian multiplier
- FLC:
-
Fuzzy logic control
- ANN:
-
Artificial neural network
- GA:
-
Genetic algorithm
- BA:
-
Bat algorithm
- HD:
-
High dimensional
- FPA:
-
Flower pollination algorithm
- ELD:
-
Emission load dispatch
- VPE:
-
Valve point effect
- MPSO:
-
Modulated particle swarm optimization
- POZ:
-
Prohibited operating zones
- CPU:
-
Central processing unit
- VPE:
-
Valve point effect
- SOA:
-
Spiral optimization algorithm
- AWL:
-
Avoidance of worst locations
- DEED:
-
Dynamic EED
- AWL:
-
Avoidance of worst locations
- GIDN:
-
Gradually increasing directed neighbourhood
- MARL:
-
Multi-agent reinforcement learning
- CNO:
-
Collective neurodynamic optimization
- PNN:
-
Projection neural network
- MG:
-
Micro grid
- MHS:
-
Modified harmony search
References
Liang H, Liu Y, Li F, Shen Y (2018) A multiobjective hybrid bat algorithm for combined economic/emission dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 101:103–115
Abdelaziz AY, Ali ES, Elazim SMA (2016) Combined economic and emission dispatch solution using flower pollination algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 80:264–274
Abdelaziz AY, Ali ES, Elazim SMA (2016) Implementation of flower pollination algorithm for solving economic load dispatch and combined economic emission dispatch problems in power systems. Energy 101:506–518
Benasla L, Belmadani A, Rahli M (2014) Spiral optimization algorithm for solving combined economic and emission dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 62:163–174
Mason K, Duggan J, Howley E (2017) Multi-objective dynamic economic emission dispatch using particle swarm optimisation variants. Neurocomputing 270:188–197
Wang T, He X, Huang T, Li C, Zhang W (2017) Collective neurodynamic optimization for economic emission dispatch problem considering valve point effect in microgrid. Neural Netw 93:126–136
Basu M (2014) Fuel constrained economic emission dispatch using non dominated sorting genetic algorithm-II. Energy 78:649–664
Elattar EE (2018) Modified harmony search algorithm for combined economic emission dispatch of microgrid incorporating renewable sources. Energy 159:496–507
Ma H, Yang Z, You P, Fei M (2017) Multi-objective biogeography-based optimization for dynamic economic emission load dispatch considering plug-in electric vehicles charging. Energy 135:101–111
Zou D, Li S, Li Z, Kong X (2017) A new global particle swarm optimization for the economic emission dispatch with or without transmission losses. Energy Convers Manag 139:45–70
Modiri-Delshad M, Rahim NA (2016) Multi-objective backtracking search algorithm for economic emission dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput 40:479–494
Goudarzi A, Li Y, Xiang J (2020) A hybrid non-linear time-varying double-weighted particle swarm optimization for solving non-convex combined environmental economic dispatch problem. Appl Soft Comput 86:105894
Shilaja C, Ravi K (2017) Optimization of emission/economic dispatch using euclidean affine flower pollination algorithm (eFPA) and binary FPA (BFPA) in solar photo voltaic generation. Renew Energy 107:550–566
Rajan A, Malakar T (2016) Optimum economic and emission dispatch using exchange market algorithm. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 82:545–560
Jadoun VK, Gupta N, Niazi KR, Swarnkar A (2015) Modulated particle swarm optimization for economic emission dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 73:80–88
Palanichamy C, Babu NS (2008) Analytical solution for combined economic and emissions dispatch. Electr Power Syst Res 78(7):1129–1137
Narimani H, Razavi S-E, Azizivahed A, Naderi E, Narimani MR (2018) A multi-objective framework for multi-area economic emission dispatch. Energy 154:126–142
Sahu BK, Pati S, Panda S (2014) Hybrid differential evolution particle swarm optimisation optimised fuzzy proportional–integral derivative controller for automatic generation control of interconnected power system. IET Gener Transm Distrib 8(11):1789–1800
Shaabani YA, Seifi AR, Kouhanjani MJ (2017) Stochastic multi-objective optimization of combined heat and power economic/emission dispatch. Energy 141:1892–1904
Lokeshgupta B, Sivasubramani S (2018) Multi-objective dynamic economic and emission dispatch with demand side management. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 97:334–343
Ghorbani N, Babaei E, Sadikoglu F (2017) Exchange market algorithm for multi-objective economic emission dispatch and reliability. Proc Comput Sci 120:633–640
Amiri M, Khanmohammadi S, Badamchizadeh MA (2018) Floating search space: a new idea for efficient solving the economic and emission dispatch problem. Energy 158:564–579
Secui DC (2017) Large-scale multi-area economic/emission dispatch based on a new symbiotic organisms search algorithm. Energy Convers Manag 154:203–223
Mason K, Duggan J, Howley E (2018) A multi-objective neural network trained with differential evolution for dynamic economic emission dispatch. Int J Electr Power Energy Syst 100:201–221
Kheshti M, Ding L, Ma S, Zhao B (2018) Double weighted particle swarm optimization to non-convex wind penetrated emission/economic dispatch and multiple fuel option systems. Renew Energy 125:1021–1037
Zhang S, Du P, Chen C, Zhong W, Alphones A (2019) Robust 3D indoor VLP system based on ANN using hybrid RSS/PDOA. IEEE Access 7:47769–47780
Anand H, Ramasubbu R (2018) A real time pricing strategy for remote micro-grid with economic emission dispatch and stochastic renewable energy sources. Renew Energy 127:779–789
Askarzadeh A (2016) A novel metaheuristic method for solving constrained engineering optimization problems: crow search algorithm. Comput Struct 169:1–12
Kulkarni PS, Kothari AG, Kothari DP (2000) Combined economic and emission dispatch using improved back propagation neural network. Int J Electr Mach Power Syst 28:31–44
Güvenç U, Sonmez Y, Duman S, Yorükeren N (2012) Combined economic and emission dispatch solution using gravitational search algorithm. Sci Iran D Comput Sci Eng Electr Eng 19(6):1754–1762
Yadav NK (2019) Hybridization of particle swarm optimization with differential evolution for solving combined economic emission dispatch model for smart grid. J Eng Res 7(3):244–257
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bhargava, G., Yadav, N.K. Solving combined economic emission dispatch model via hybrid differential evaluation and crow search algorithm. Evol. Intel. 15, 1161–1169 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00357-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12065-020-00357-0