Abstract
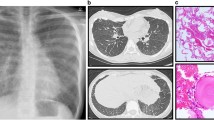
Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis (PAM) is an autosomal recessive disorder with distinctive deposition of calcium phosphate microliths in the lungs. Mutation of the SLC34A2 gene was proved to be responsible for PAM. Here, we report the study of a family affected by PAM in China. Two daughters of an inbred family whose parents are cousins and are affected by PAM. Mutation analysis of the SLC34A2 gene by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification and direct sequencing in both patients revealed that exon 5 was deleted on both alleles. Both parents of the patients are proved to be carriers of the mutated allele. Gap-PCR was performed to determine the breakpoints and a homologous deletion of 1152 bp encompassing exon 5 of the SLC34A2 gene (c.IVS4+1452_IVS5+660del) was confirmed. A 4-bp fragment of TGGG was located on the edge of both upstream and downstream breakpoints. The upstream breakpoint lies in the same region as the breakpoint of a fused gene SLC34A2–ROS1, which encodes a constitutive kinase in the lung cancer cell line HCC78 and nonsmall-cell lung cancer (NSCLC), suggesting that the deletion in this family is a hot spot for recombination, not only in cancer samples with somatic mutation, but also in PAM patients with germline genetic defects of SLC34A2.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castellana G., Castellana G., Gentile M., Castellana R. and Resta O. 2015 Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: review of the 1022 cases reported worldwide. Eur. Respir. Rev. 24, 607–620.
Castellana G., Gentile M., Castellana R., Fiorente P. and Lamorgese V. 2002 Pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: clinical features, evolution of the phenotype, and review of the literature. Am. J. Med. Genet. 111, 220–224.
Corut A., Senyigit A., Ugur S. A., Altin S., Ozcelik U., Calisir H. et al. 2006 Mutations in SLC34A2 cause pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis and are possibly associated with testicular microlithiasis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 79, 650–656.
Davies K. D., Le A. T., Theodoro M. F., Skokan M. C., Aisner D. L., Berge E. M. et al. 2012 Identifying and targeting ROS1 gene fusions in non-small cell lung cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 4570–4579.
Emiralioglu N., Beken B., Ozcan H. N., Yalcin E., Dogru D., Ozcelik U. et al. 2016 Diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Pediatr. Int. 58, 805–807.
Francisco F. A., Rodrigues R. S., Barreto M. M., Escuissato D. L., Araujo Neto C. A., Silva J. L. et al. 2015 Can chest high-resolution computed tomography findings diagnose pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis? Radiol. Bras. 48, 205–210.
Hashimoto M., Wang D. Y., Kamo T., Zhu Y., Tsujiuchi T., Konishi Y. et al. 2000 Isolation and localization of type IIb Na/Pi cotransporter in the developing rat lung. Am. J. Pathol. 157, 21–27.
Huqun, Izumi S., Miyazawa H., Ishii K., Uchiyama B., Ishida T. et al. 2007 Mutations in the SLC34A2 gene are associated with pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 175, 263–268.
Lee J., Lee S. E., Kang S. Y., Do I. G., Lee S., Ha S. Y. et al. 2013 Identification of ROS1 rearrangement in gastric adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 119, 1627–1635.
Ratcliffe S., Jugdaohsingh R., Vivancos J., Marron A., Deshmukh R., Ma J. F. et al. 2017 Identification of a mammalian silicon transporter. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Physiol. 312, C550–C561.
Rikova K., Guo A., Zeng Q., Possemato A., Yu J., Haack H. et al. 2007 Global survey of phosphotyrosine signaling identifies oncogenic kinases in lung cancer. Cell 131, 1190–1203.
Vismara M. F., Colao E., Fabiani F., Bombardiere F., Tamburrini O., Alessio C. et al. 2015 The sodium-phosphate co-transporter SLC34A2, and pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: presentation of an inbred family and a novel truncating mutation in exon 3. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 16, 77–80.
Wang H., Yin X., Wu D. and Jiang X. 2014 SLC34A2 gene compound heterozygous mutation identification in a patient with pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis and computational 3D protein structure prediction. Meta Gene. 2, 557–564.
Wagner C. A., Hernando N., Forster I. C. and Biber J. 2014 The SLC34 family of sodium-dependent phosphate transporters. Pflugers Arch. 466, 139–153.
Yin X., Wang H., Wu D., Zhao G., Shao J. and Dai Y. 2013 SLC34A2 gene mutation of pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: report of four cases and review of literatures. Respir. Med. 107, 217–222.
Acknowledgements
We thank the patients and their families for consenting to participate in this study. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China to Dandan Shang (grant number 81100242).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Kunal Ray
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dandan, S., Yuqin, C., Wei, L. et al. Novel deletion of SLC34A2 in Chinese patients of PAM shares mutation hot spot with fusion gene SLC34A2–ROS1 in lung cancer. J Genet 97, 939–944 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-0977-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-018-0977-x