Abstract
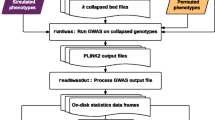
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) examine the entire human genome with the goal of identifying genetic variants (usually single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs)) that are associated with phenotypic traits such as disease status and drug response. The discordance of significantly associated SNPs for the same disease identified from different GWAS indicates that false associations exist in such results. In addition to the possible sources of spurious associations that have been investigated and discussed intensively, such as sample size and population stratification, an accurate and reproducible genotype calling algorithm is required for concordant GWAS results from different studies. However, variations of genotype calling of an algorithm and their effects on significantly associated SNPs identified in downstream association analyses have not been systematically investigated. In this paper, the variations of genotype calling using the Bayesian Robust Linear Model with Mahalanobis distance classifier (BRLMM) algorithm and the resulting influence on the lists of significantly associated SNPs were evaluated using the raw data of 270 HapMap samples analysed with the Affymetrix Human Mapping 500K Array Set (Affy500K) by changing algorithmic parameters. Modified were the Dynamic Model (DM) call confidence threshold (threshold) and the number of randomly selected SNPs (size). Comparative analysis of the calling results and the corresponding lists of significantly associated SNPs identified through association analysis revealed that algorithmic parameters used in BRLMM affected the genotype calls and the significantly associated SNPs. Both the threshold and the size affected the called genotypes and the lists of significantly associated SNPs in association analysis. The effect of the threshold was much larger than the effect of the size. Moreover, the heterozygous calls had lower consistency compared to the homozygous calls.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Affymetrix 2006 BRLMM: an improved genotype calling method for the GeneChip Human Mapping 500K array set, Revision version 1.0. April 14, 2006. URL: http://www.affymetrix.com/support/technical/whitepapers/brlmm whitepaper.pdf
Arking D. E., Cutler D. J., Brune C. W., Teslovich T. M., West K., Ikeda M. et al. 2008 A common genetic variant in the neurexin superfamily member CNTNAP2 increases familial risk of autism. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 160–164.
Benjamini Y. and Hochberg Y. 1995 Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Statist. Soc. B. 57, 289–300.
Buch S., Schafmayer C., Völzke H., Becker C., Franke A., von Eller-Eberstein H. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association scan identifies the hepatic cholesterol transporter ABCG8 as a susceptibility factor for human gallstone disease. Nature Genet. 39, 995–999.
Butcher L. M., Davis O. S., Craig I. W. and Plomin R. 2008 Genome-wide quantitative trait locus association scan of general cognitive ability using pooled DNA and 500K single nucleotide polymorphism microarrays. Genes Brain Behav. 7, 435–446.
Cargill M., Schrodi S. J., Chang M., Garcia V. E., Brandon R., Callis K. P. et al. 2007 A large-scale genetic association study confirms IL12B and leads to the identification of IL23R as psoriasis-risk genes. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 273–290.
Chanock S. J., Manolio T., Boehnke M., Boerwinkle E., Hunter D. J., Thomas G. et al. (NCI-NHGRI working group on replication in association studies) 2007 Replicating genotype-phenotype associations. Nature 447, 655–660.
Di X., Matsuzaki H., Webster T. A., Hubbell E., Liu G., Dong S. et al. 2005 Dynamic model based algorithms for screening and genotyping over 100K SNPs on oligonucleotide microarrays. Bioinformatics 21, 1958–1963.
Duerr R. H., Taylor K.D., Brant S. R., Rioux J. D., Silverberg M. S., Daly M. J. et al. 2006 A genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory bowel disease gene. Science 314, 1461–1463.
Easton D. F., Pooley K. A., Dunning A. M., Pharoah P. D., Thompson D., Ballinger D. G. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study identifies novel breast cancer susceptibility loci. Nature 447, 1087–1093.
Frayling T. M., Timpson N. J., Weedon M. N., Zeggini E., Freathy R. M., Lindgren C. M. et al. 2007 A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity. Science 316, 889–894.
Fu W., Wang Y., Wang Y., Li R., Lin R. and Jin L. 2009 Missing call bias in high-throughput genotyping. BMC Genomics 10, 106.
Gold B., Kirchhoff T., Stefanov S., Lautenberger J., Viale A., Garber J. et al. 2008 A genome-wide association study provides evidence for a breast cancer risk at 6q22.33. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 4340–4345.
Grupe A., Abraham R,, Li Y., Rowland C., Hollingworth P., Morgan A. et al. 2007 Evidence for novel susceptibility genes for lateonset Alzheimers disease from a genome-wide association study of putative functional variants. Hum. Mol. Genet. 16, 865–873.
Gudmundsson J., Sulem P., Manolescu A., Amundadottir L. T., Gudbjartsson D., Helgason A. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study identifies a second breast cancer susceptibility variant at 8q24. Nature Genet. 39, 631–637.
Hampe J., Franke A., Rosenstiel P., Till A., Teuber M., Huse K. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association scan of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for Crohn disease in ATG16L1. Nature Genet. 39, 207–211.
Hong H., Su Z., Ge W., Shi L., Perkins R., Fang H. et al. 2008 Assessing batch effects of genotype calling algorithm BRLMM for the Affymetrix GeneChip human mapping 500K Array Set using 270 HapMap samples. BMC Bioinformatics 9, S17.
Hunter D. J., Kraft P., Jacobs K. B., Cox D. G., Yeager M., Hankinson S. E. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer. Nature Genet. 39, 870–874.
Kayser M., Liu F., Janssens A. C., Rivadeneira F., Lao O., van Duijn K. et al. 2008 Three genome-wide association studies and a linkage analysis identify HERC2 as a human iris color gene. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 82, 411–423.
Klein R. J., Zeiss C., Chew E. Y., Tsai J. Y., Sackler R. S., Haynes C. et al. 2005 Complement factor H polymorphism in age-related macular degeneration. Science 308, 385–389.
Moore A. F., Jablonski K. A., McAteer J. B., Saxena R., Pollin T. I., Franks P. W. et al. 2008 Extension of type 2 diabetes genomewide association scan results in the Diabetes Prevention Program. Diabetes 57, 2503–2510.
Moskvina V., Craddock N., Holmans P., Owen M. J. and O’Donovan M. C. 2006 Effects of differential genotyping error rate on the type I error probability of case-control studies. Hum. Hered. 61, 55–64.
Raelson J. V., Little R. D., Ruether A., Fournier H., Paquin B., Eerdewegh P. V. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study for Crohn’s disease in the Quebec Founder Population identifies multiple validated disease loci. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 14747–14752.
Rioux J. D., Xavier R. J., Taylor K. D., Silverberg M. S., Goyette P., Huett A. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study identifies new susceptibility loci for Crohn’s disease and implicates autophagy in disease pathogenesis. Nature Genet. 39, 596–604.
Saxena R., Voight B. F., Lyssenko V., Burtt N. P., de Bakker P. I., Chen H. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association analysis identifies loci for type 2 diabetes and triglyceride level. Science 316, 1331–1336.
Scott L., Mohlke K. L., Bonnycastle L. L., Willer C. J., Li Y., Duren W. L. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association study of type 2 diabetes in Finns detects multiple susceptibility variants. Science 316, 1341–1345.
Sladek R., Rocheleau G., Rung J., Dina C., Shen L., Serre D. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association study identifies novel risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Nature 445, 881–885.
Smyth D. J., Cooper J. D., Bailey R., Field S., Burren O., Smink L. J. et al. 2006 A genome-wide association study of nonsynonymous SNPs identifies a type 1 diabetes locus in the interferoninduced helicase (IFIH1) region. Nature Genet. 38, 617–619.
Steinthorsdottir V., Thorleifsson G., Reynisdottir I., Benediktsson R., Jonsdottir T., Walters G. B. et al. 2007 A variant in CDKAL1 influences insulin response and risk of type 2 diabetes. Nature Genet. 39, 770–775.
Teo Y. Y. 2008 Common statistical issues in genome-wide association studies: a review on power, data quality control, genotype calling and population structure. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 19, 133–143.
The International HapMap Consortium 2005 A haplotype map of the human genome. Nature 437, 1299–1320.
The International HapMap Consortium 2007 A second generation human haplotype map of over 3.1 million SNPs. Nature 449, 851–862.
Todd A. J., Walker N. M., Cooper J. D., Smyth D. J., Downes K., Plagnol V. et al. 2007 Robust associations of four new chromosome regions from genome-wide analyses of type 1 diabetes. Nature Genet. 39, 857–864.
Tomlinson I., Webb E., Carvajal-Carmona L., Broderick P., Kemp Z., Spain S. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nature Genet. 39, 984–988.
Uda M., Galanello R., Sanna S., Lettre G., Sankaran V. G., Chen W. et al. 2008 Genome-wide association study shows BCL11A associated with persistent fetal hemoglobin and amelioration of the phenotype of β-thalassemia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 1620–1625.
van Heel D. A., Franke L., Hunt K. A., Gwilliam R., Zhernakova A., Inouye M. et al. 2007 A genome-wide association study for celiac disease identifies risk variants in the region harbouring IL2 and IL21. Nature Genet. 39, 827–829.
Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2007 Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 447, 661–678.
Winkelmann J., Schormair B., Lichtner P., Ripke S., Xiong L., Jalilzadeh S. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study of restless legs syndrome identifies common variants in three genomic regions. Nature Genet. 39, 1000–1006.
Yang H. H., Hu N., Taylor P. R. and Lee M. P. 2008 Whole genomewide association study using Affymetrix snp chip: a two-stage sequential selection method to identify genes that increase the risk of developing complex diseases. Clin. Bioinform. 141, 23–35.
Yeager M., Orr N., Hayes R. B., Jacobs K. B., Kraft P., Wacholder S. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association study of breast cancer identifies a second risk locus at 8q24. Nature Genet. 39, 645–649.
Zanke B. W., Greenwood C. M., Rangrej J., Kustra R., Tenesa A., Farrington S. M. et al. 2007 Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 8q24. Nature Genet. 39, 989–994.
Zeggini E., Weedon M. N., Lindgren C. M., Frayling T. M., Elliott K. S., Lango H. et al. 2007 Replication of genome-wide association signals in UK samples reveals risk loci for type 2 diabetes. Science 316, 1336–1341.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The views presented in this article do not necessarily reflect those of the US Food and Drug Administration.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, H., Su, Z., Ge, W. et al. Evaluating variations of genotype calling: a potential source of spurious associations in genome-wide association studies. J Genet 89, 55–64 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-010-0011-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-010-0011-4