Abstract
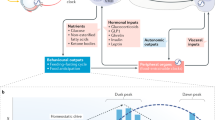
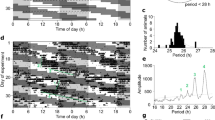
An essential component of energy homeostasis lies in an organism’s ability to coordinate daily patterns in activity, feeding, energy utilization and energy storage across the daily 24-h cycle. Most tissues of the body contain the molecular clock machinery required for circadian oscillation and rhythmic gene expression. Under normal circumstances, behavioural and physiological rhythms are orchestrated and synchronized by the suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) of the hypothalamus, considered to be the master circadian clock. However, metabolic processes are easily decoupled from the primarily light-driven SCN when food intake is desynchronized from normal diurnal patterns of activity. This dissociation from SCN based timing demonstrates that the circadian system is responsive to changes in energy supply and metabolic status. There has long been evidence for the existence of an anatomically distinct and autonomous food-entrainable oscillator (FEO) that can govern behavioural rhythms, when feeding becomes the dominant entraining stimulus. But now rapidly growing evidence suggests that core circadian clock genes are involved in reciprocal transcriptional feedback with genetic regulators of metabolism, and are directly responsive to cellular energy supply. This close interaction is likely to be critical for normal circadian regulation of metabolism, and may also underlie the disruption of proper metabolic rhythms observed in metabolic disorders, such as obesity and type-II diabetes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M., Herzog E. D., Yamazaki S., Straume M., Tei H., Sakaki Y. et al. 2002 Circadian rhythms in isolated brain regions. J. Neurosci. 22, 350–356.
Adelmant G., Begue A., Stehelin D. and Laudet V. 1996 A functional Rev-erb alpha responsive element located in the human Rev-erb alpha promoter mediates a repressing activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 3553–3558.
Akhtar R. A., Reddy A. B., Maywood E. S., Clayton J. D., King V. M., Smith A. G. et al. 2002 Circadian cycling of the mouse liver transcriptome, as revealed by cDNA microarray, is driven by the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Curr. Biol. 12, 540–550.
Ando H., Yanagihara H., Hayashi Y., Obi Y., Tsuruoka S., Takamura T. et al. 2005 Rhythmic messenger ribonucleic acid expression of clock genes and adipocytokines in mouse visceral adipose tissue. Endocrinology 146, 5631–5636.
Angeles-Castellanos M., Aguilar-Roblero R. and Escobar C. 2004 c-Fos expression in hypothalamic nuclei of food-entrained rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 286, R158–R165.
Asher G., Gatfield D., Stratmann M., Reinke H., Dibner C., Kreppel F. et al. 2008 SIRT1 regulates circadian clock gene expression through PER2 deacetylation. Cell 134, 317–328.
Balsalobre A., Brown S. A., Marcacci L., Tronche F., Kellendonk C., Reichardt H. M. et al. 2000 Resetting of circadian time in peripheral tissues by glucocorticoid signaling. Science 289, 2344–2347.
Bando H., Nishio T., van der Horst G. T., Masubuchi S., Hisa Y. and Okamura H. 2007 Vagal regulation of respiratory clocks in mice. J. Neurosci. 27, 4359–4365.
Bartness T. J., Song C. K. and Demas G. E. 2001 SCN efferents to peripheral tissues: implications for biological rhythms. J. Biol. Rhythms 16, 196–204.
Baur J. A., Pearson K. J., Price N. L., Jamieson H. A., Lerin C., Kalra A. et al. 2006 Resveratrol improves health and survival of mice on a high-calorie diet. Nature 444, 337–342.
Bechtold D. A., Brown T. M., Luckman S. M. and Piggins H. D. 2008 Metabolic rhythm abnormalities in mice lacking VIPVPAC2 signaling. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 294, R344–R351.
Berthoud H. R. 2002 Multiple neural systems controlling food intake and body weight. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 26, 393–428.
Blundell J. E. and Gillett A. 2001 Control of food intake in the obese. Obes. Res. 9,suppl. 4, 263S–270S.
Boden G., Chen X. and Polansky M. 1999 Disruption of circadian insulin secretion is associated with reduced glucose uptake in first-degree relatives of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes 48, 2182–2188.
Bordone L., Motta M. C., Picard F., Robinson A., Jhala U. S., Apfeld J. et al. 2006 Sirt1 regulates insulin secretion by repressing UCP2 in pancreatic beta cells. PLoS Biol. 4, e31.
Boulos Z. and Terman M. 1980 Food availability and daily biological rhythms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 4, 119–131.
Brunet A., Sweeney L. B., Sturgill J. F., Chua K. F., Greer P. L., Lin Y. et al. 2004 Stress-dependent regulation of FOXO transcription factors by the SIRT1 deacetylase. Science 303, 2011–2015.
Buijs R. M. and Kreier F. 2006 The metabolic syndrome: a brain disease? J. Neuroendocrinol. 18, 715–716.
Cailotto C., van Heijningen C., van der Vliet J., van der Plasse G., Habold C., Kalsbeek A. et al. 2008 Daily rhythms in metabolic liver enzymes and plasma glucose require a balance in the autonomic output to the liver. Endocrinology 149, 1914–1925.
Calvani M., Scarfone A., Granato L., Mora E. V., Nanni G., Castagneto M. et al. 2004 Restoration of adiponectin pulsatility in severely obese subjects after weight loss. Diabetes 53, 939–947.
Canaple L., Rambaud J., Dkhissi-Benyahya O., Rayet B., Tan N. S., Michalik L. et al. 2006 Reciprocal regulation of brain and muscle Arnt-like protein 1 and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha defines a novel positive feedback loop in the rodent liver circadian clock. Mol. Endocrinol. 20, 1715–1727.
Carling D. 2007 The role of the AMP-activated protein kinase in the regulation of energy homeostasis. Novartis Found. Symp. 286, 72–81; discussion 81–85.
Cermakian N. and Sassone-Corsi P. 2002 Environmental stimulus perception and control of circadian clocks. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 12, 359–365.
Chaput J. P., Brunet M. and Tremblay A. 2006 Relationship between short sleeping hours and childhood overweight/obesity: results from the ‘Quebec en Forme’ Project. Int. J. Obes. (London) 30, 1080–1085.
Chawla A. and Lazar M. A. 1993 Induction of Rev-ErbA alpha, an orphan receptor encoded on the opposite strand of the alphathyroid hormone receptor gene, during adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 16265–16269.
Chen M. P., Chung F. M., Chang D. M., Tsai J. C., Huang H. F., Shin S. J. and Lee Y. J. 2006 Elevated plasma level of visfatin/pre-B cell colony-enhancing factor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91, 295–299.
Comperatore C. A. and Stephan F. K. 1990 Effects of vagotomy on entrainment of activity rhythms to food access. Physiol. Behav. 47, 671–678.
Cone R. D., Cowley M. A., Butler A. A., Fan W., Marks D. L. and Low M. J. 2001 The arcuate nucleus as a conduit for diverse signals relevant to energy homeostasis. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 25,suppl. 5, S63–S67.
Curtis A. M., Seo S. B., Westgate E. J., Rudic R. D., Smyth E. M., Chakravarti D. et al. 2004 Histone acetyltransferase-dependent chromatin remodeling and the vascular clock. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 7091–7097.
Dali-Youcef N., Lagouge M., Froelich S., Koehl C., Schoonjans K. and Auwerx J. 2007 Sirtuins: the ‘magnificent seven’, function, metabolism and longevity. Ann. Med. 39, 335–345.
Damiola F., Le Minh N., Preitner N., Kornmann B., Fleury-Olela F. and Schibler U. 2000 Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes Dev. 14, 2950–2961.
Dasgupta B. and Milbrandt J. 2007 Resveratrol stimulates AMP kinase activity in neurons. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 7217–7222.
Davidson A. J. and Stephan F. K. 1998 Circadian food anticipation persists in capsaicin deafferented rats. J. Biol. Rhythms 13, 422–429.
Davidson A. J., Cappendijk S. L. and Stephan F. K. 2000 Feedingentrained circadian rhythms are attenuated by lesions of the parabrachial region in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 278, R1296–R1304.
Davidson A. J., Aragona B. J., Houpt T. A. and Stephan F. K. 2001a Persistence of meal-entrained circadian rhythms following area postrema lesions in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 74, 349–354.
Davidson A. J., Aragona B. J., Werner R. M., Schroeder E., Smith J. C. and Stephan F. K. 2001b Food-anticipatory activity persists after olfactory bulb ablation in the rat. Physiol. Behav. 72, 231–235.
Davidson A. J., Poole A. S., Yamazaki S. and Menaker M. 2003 Is the food-entrainable circadian oscillator in the digestive system? Genes Brain Behav. 2, 32–39.
Desvergne B. and Wahli W. 1999 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 20, 649–688.
Doi M., Hirayama J. and Sassone-Corsi P. 2006 Circadian regulator CLOCK is a histone acetyltransferase. Cell 125, 497–508.
Dudley C. A., Erbel-Sieler C., Estill S. J., Reick M., Franken P., Pitts S. and McKnight S. L. 2003 Altered patterns of sleep and behavioral adaptability in NPAS2-deficient mice. Science 301, 379–383.
Duffield G. E., Best J. D., Meurers B. H., Bittner A., Loros J. J. and Dunlap J. C. 2002 Circadian programs of transcriptional activation, signaling, and protein turnover revealed by microarray analysis of mammalian cells. Curr. Biol. 12, 551–557.
Duez H. and Staels B. 2008 The nuclear receptors Rev-erbs and RORs integrate circadian rhythms and metabolism. Diab. Vasc. Dis. Res. 5, 82–88.
Dupré S. M., Burt D. W., Talbot R., Downing A., Mouzaki D., Waddington D. et al. 2008 Identification of melatonin-regulated genes in the ovine pituitary pars tuberalis, a target site for seasonal hormone control. Endocrinol. 149, 5527–5539.
Emery P. and Reppert S. M. 2004 A rhythmic Ror. Neuron 43, 443–446.
Etchegaray J. P., Lee C., Wade P. A. and Reppert S. M. 2003 Rhythmic histone acetylation underlies transcription in the mammalian circadian clock. Nature 421, 177–182.
Feillet C. A., Ripperger J. A., Magnone M. C., Dulloo A., Albrecht U. and Challet E. 2006 Lack of food anticipation in Per2 mutant mice. Curr. Biol. 16, 2016–2022.
Fontaine C., Dubois G., Duguay Y., Helledie T., Vu-Dac N., Gervois P. et al. 2003 The orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erbalpha is a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma target gene and promotes PPARgamma-induced adipocyte differentiation. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 37672–37680.
Fulco M., Cen Y., Zhao P., Hoffman E. P., McBurney M. W., Sauve A. A. and Sartorelli V. 2008 Glucose restriction inhibits skeletal myoblast differentiation by activating SIRT1 through AMPK-mediated regulation of Nampt. Dev. Cell 14, 661–673.
Fuller P.M., Lu J. and Saper C. B. 2008 Differential rescue of lightand food-entrainable circadian rhythms. Science 320, 1074–1077.
Gallego M. and Virshup D. M. 2007 Post-translational modifications regulate the ticking of the circadian clock. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 8, 139–148.
Gallou-Kabani C., Vige A. and Junien C. 2007 Lifelong circadian and epigenetic drifts in metabolic syndrome. Epigenetics 2, 137–146.
Gangwisch J. E., Malaspina D., Boden-Albala B. and Heymsfield S. B. 2005 Inadequate sleep as a risk factor for obesity: analyses of the NHANES I. Sleep 28, 1289–1296.
Gervois P., Chopin-Delannoy S., Fadel A., Dubois G., Kosykh V., Fruchart J. C. et al. 1999 Fibrates increase human REV-ERBalpha expression in liver via a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor response element. Mol. Endocrinol. 13, 400–409.
Gooley J. J., Schomer A. and Saper C. B. 2006 The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus is critical for the expression of food-entrainable circadian rhythms. Nat. Neurosci. 9, 398–407.
Granados-Fuentes D., Prolo L. M., Abraham U. and Herzog E. D. 2004 The suprachiasmatic nucleus entrains, but does not sustain, circadian rhythmicity in the olfactory bulb. J. Neurosci. 24, 615–619.
Guo H., Brewer J. M., Lehman M. N. and Bittman E. L. 2006 Suprachiasmatic regulation of circadian rhythms of gene expression in hamster peripheral organs: effects of transplanting the pacemaker. J. Neurosci. 26, 6406–6412.
Hirayama J., Sahar S., Grimaldi B., Tamaru T., Takamatsu K., Nakahata Y. and Sassone-Corsi P. 2007 CLOCK-mediated acetylation of BMAL1 controls circadian function. Nature 450, 1086–1090.
Hirota T., Okano T., Kokame K., Shirotani-Ikejima H., Miyata T. and Fukada Y. 2002 Glucose down-regulates Per1 and Per2 mRNA levels and induces circadian gene expression in cultured Rat-1 fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 44244–44251.
Iijima M., Yamaguchi S., van der Horst G. T., Bonnefont X., Okamura H. and Shibata S. 2005 Altered food-anticipatory activity rhythm in Cryptochrome-deficient mice. Neurosci. Res. 52, 166–173.
Inoue I., Shinoda Y., Ikeda M., Hayashi K., Kanazawa K., Nomura M. et al. 2005 CLOCK/BMAL1 is involved in lipid metabolism via transactivation of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) response element. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 12, 169–174.
Ishida A., Mutoh T., Ueyama T., Bando H., Masubuchi S., Nakahara D. et al. 2005 Light activates the adrenal gland: timing of gene expression and glucocorticoid release. Cell Metab. 2, 297–307.
Kaasik K. and Lee C. C. 2004 Reciprocal regulation of haem biosynthesis and the circadian clock in mammals. Nature 430, 467–471.
Kahn B. B., Alquier T., Carling D. and Hardie D. G. 2005 AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 1, 15–25.
Kalsbeek A., Kreier F., Fliers E., Sauerwein H. P., Romijn J. A. and Buijs R. M. 2007 Minireview: Circadian control of metabolism by the suprachiasmatic nuclei. Endocrinol. 148, 5635–5639.
Karlsson B., Knutsson A. and Lindahl B. 2001 Is there an association between shift work and having a metabolic syndrome? Results from a population based study of 27,485 people. Occup. Environ. Med. 58, 747–752.
Kersten S., Seydoux J., Peters J. M., Gonzalez F. J., Desvergne B. and Wahli W. 1999 Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha mediates the adaptive response to fasting. J. Clin. Invest. 103, 1489–1498.
Kohsaka A. and Bass J. 2007 A sense of time: how molecular clocks organize metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 18, 4–11.
Kornmann B., Schaad O., Bujard H., Takahashi J. S. and Schibler U. 2007 System-driven and oscillator-dependent circadian transcription in mice with a conditionally active liver clock. PLoS Biol. 5, e34.
Krieger D. T. 1972 Circadian corticosteroid periodicity: critical period for abolition by neonatal injection of corticosteroid. Science 178, 1205–1207.
Kudo T., Kawashima M., Tamagawa T. and Shibata S. 2008 Clock mutation facilitates accumulation of cholesterol in the liver of mice fed a cholesterol and/or cholic acid diet. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 294, E120–E130.
Laitinen S., Fontaine C., Fruchart J. C. and Staels B. 2005 The role of the orphan nuclear receptor Rev-Erb alpha in adipocyte differentiation and function. Biochimie 87, 21–25.
Lamia K. A., Storch K. F. and Weitz C. J. 2008 Physiological significance of a peripheral tissue circadian clock. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 15172–15177.
Lamont E. W., Robinson B., Stewart J. and Amir S. 2005 The central and basolateral nuclei of the amygdala exhibit opposite diurnal rhythms of expression of the clock protein Period2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 4180–4184.
Landry G. J. and Mistlberger R. E. 2007 Food entrainment: methodological issues. J. Biol. Rhythms 22, 484–487.
Landry G. J., Simon M. M., Webb I. C. and Mistlberger R. E. 2006 Persistence of a behavioral food-anticipatory circadian rhythm following dorsomedial hypothalamic ablation in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 290, R1527–R1534.
Landry G. J., Yamakawa G. R., Webb I. C., Mear R. J. and Mistlberger R. E. 2007 The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus is not necessary for the expression of circadian food-anticipatory activity in rats. J. Biol. Rhythms 22, 467–478.
Laposky A. D., Bass J., Kohsaka A. and Turek F.W. 2008 Sleep and circadian rhythms: key components in the regulation of energy metabolism. FEBS Lett. 582, 142–151.
Le Minh N., Damiola F., Tronche F., Schutz G. and Schibler U. 2001 Glucocorticoid hormones inhibit food-induced phase-shifting of peripheral circadian oscillators. EMBO J. 20, 7128–7136.
Lemberger T., Saladin R., Vazquez M., Assimacopoulos F., Staels B., Desvergne B. et al. 1996 Expression of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha gene is stimulated by stress and follows a diurnal rhythm. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 1764–1769.
Leone T. C., Lehman J. J., Finck B. N., Schaeffer P. J., Wende A. R., Boudina S. et al. 2005 PGC-1alpha deficiency causes multisystem energy metabolic derangements: muscle dysfunction, abnormal weight control and hepatic steatosis. PLoS Biol. 3, e101.
Li X., Zhang S., Blander G., Tse J. G., Krieger M. and Guarente L. 2007 SIRT1 deacetylates and positively regulates the nuclear receptor LXR. Mol. Cell 28, 91–106.
Liang H. and Ward W. F. 2006 PGC-1alpha: a key regulator of energy metabolism. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 30, 145–151.
Lin J., Handschin C. and Spiegelman B. M. 2005a Metabolic control through the PGC-1 family of transcription coactivators. Cell. Metab. 1, 361–370.
Lin J., Yang R., Tarr P. T., Wu P. H., Handschin C., Li S. et al. 2005b Hyperlipidemic effects of dietary saturated fats mediated through PGC-1beta coactivation of SREBP. Cell 120, 261–273.
Liu C., Li S., Liu T., Borjigin J. and Lin J. D. 2007 Transcriptional coactivator PGC-1alpha integrates the mammalian clock and energy metabolism. Nature 447, 477–481.
Loudon A. S., Meng Q. J., Maywood E. S., Bechtold D. A., Boot-Handford R. P. and Hastings M. H. 2007 The biology of the circadian Ck1epsilon tau mutation in mice and Syrian hamsters: a tale of two species. Cold. Spr. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 72, 261–271.
Lowrey P. L. and Takahashi J. S. 2004 Mammalian circadian biology: elucidating genome-wide levels of temporal organization. Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet. 5, 407–441.
McCarthy J. J., Andrews J. L., McDearmon E. L., Campbell K. S., Barber B. K., Miller B. H. et al. 2007 Identification of the circadian transcriptome in adult mouse skeletal muscle. Physiol. Genomics 31, 86–95.
McNamara P., Seo S. P., Rudic R. D., Sehgal A., Chakravarti D. and FitzGerald G. A. 2001 Regulation of CLOCK and MOP4 by nuclear hormone receptors in the vasculature: a humoral mechanism to reset a peripheral clock. Cell 105, 877–889.
Meng Q. J., Logunova L., Maywood E. S., Gallego M., Lebiecki J., Brown T. M. et al. 2008 Setting clock speed in mammals: the CK1 epsilon tau mutation in mice accelerates circadian pacemakers by selectively destabilizing PERIOD proteins. Neuron 58, 78–88.
Meyer-Bernstein E. L., Jetton A. E., Matsumoto S. I., Markuns J. F., Lehman M. N. and Bittman E. L. 1999 Effects of suprachiasmatic transplants on circadian rhythms of neuroendocrine function in golden hamsters. Endocrinology 140, 207–218.
Michan S. and Sinclair D. 2007 Sirtuins in mammals: insights into their biological function. Biochem. J. 404, 1–13.
Mieda M., Williams S. C., Richardson J. A., Tanaka K. and Yanagisawa M. 2006 The dorsomedial hypothalamic nucleus as a putative food-entrainable circadian pacemaker. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 12150–12155.
Miller B. H., McDearmon E. L., Panda S., Hayes K. R., Zhang J., Andrews J. L. et al. 2007 Circadian and CLOCK-controlled regulation of the mouse transcriptome and cell proliferation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 3342–3347.
Mistlberger R. E. 1994 Circadian food-anticipatory activity: formal models and physiological mechanisms. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 18, 171–195.
Mistlberger R. E. and Marchant E. G. 1995 Computational and entrainment models of circadian food-anticipatory activity: evidence from non-24-hr feeding schedules. Behav. Neurosci. 109, 790–798.
Mistlberger R. E. and Mumby D. G. 1992 The limbic system and food-anticipatory circadian rhythms in the rat: ablation and dopamine blocking studies. Behav. Brain. Res. 47, 159–168.
Mistlberger R. E. and Rechtschaffen A. 1984 Recovery of anticipatory activity to restricted feeding in rats with ventromedial hypothalamic lesions. Physiol. Behav. 33, 227–235.
Mistlberger R. E. and Rusak B. 1988 Food-anticipatory circadian rhythms in rats with paraventricular and lateral hypothalamic ablations. J. Biol. Rhythms. 3, 277–291.
Motta M. C., Divecha N., Lemieux M., Kamel C., Chen D., Gu W. et al. 2004 Mammalian SIRT1 represses forkhead transcription factors. Cell 116, 551–563.
Nakahata Y., Grimaldi B., Sahar S., Hirayama J. and Sassone-Corsi P. 2007 Signaling to the circadian clock: plasticity by chromatin remodeling. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 19, 230–237.
Nakahata Y., Kaluzova M., Grimaldi B., Sahar S., Hirayama J., Chen D. et al. 2008 The NAD+-dependent deacetylase SIRT1 modulates CLOCK-mediated chromatin remodeling and circadian control. Cell 134, 329–340.
Naruse Y., Oh-hashi K., Iijima N., Naruse M., Yoshioka H. and Tanaka M. 2004 Circadian and light-induced transcription of clock gene Per1 depends on histone acetylation and deacetylation. Mol. Cell Biol. 24, 6278–6287.
Oishi K., Miyazaki K., Kadota K., Kikuno R., Nagase T., Atsumi G. et al. 2003 Genome-wide expression analysis of mouse liver reveals CLOCK-regulated circadian output genes. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 41519–41527.
Oishi K., Amagai N., Shirai H., Kadota K., Ohkura N. and Ishida N. 2005a Genome-wide expression analysis reveals 100 adrenal gland-dependent circadian genes in the mouse liver. DNA Res. 12, 191–202.
Oishi K., Shirai H. and Ishida N. 2005b CLOCK is involved in the circadian transactivation of peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPARalpha) in mice. Biochem. J. 386, 575–581.
Oishi K., Atsumi G., Sugiyama S., Kodomari I., Kasamatsu M., Machida K. and Ishida N. 2006 Disrupted fat absorption attenuates obesity induced by a high-fat diet in Clock mutant mice. FEBS Lett. 580, 127–130.
Panda S., Antoch M. P., Miller B. H., Su A. I., Schook A. B., Straume M. et al. 2002 Coordinated transcription of key pathways in the mouse by the circadian clock. Cell 109, 307–320.
Pitts S., Perone E. and Silver R. 2003 Food-entrained circadian rhythms are sustained in arrhythmic Clk/Clk mutant mice. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 285, R57–R67.
Preitner N., Damiola F., Lopez-Molina L., Zakany J., Duboule D., Albrecht U. and Schibler U. 2002 The orphan nuclear receptor REV-ERBalpha controls circadian transcription within the positive limb of the mammalian circadian oscillator. Cell 110, 251–260.
Ralph M. R., Foster R. G., Davis F. C. and Menaker M. 1990 Transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus determines circadian period. Science 247, 975–978.
Ramsey K. M., Marcheva B., Kohsaka A. and Bass J. 2007 The clockwork of metabolism. Annu. Rev. Nutr. 27, 219–240.
Raspe E., Duez H., Gervois P., Fievet C., Fruchart J. C., Besnard S. et al. 2001 Transcriptional regulation of apolipoprotein CIII gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor RORalpha. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 2865–2871.
Raspe E., Duez H., Mansen A., Fontaine C., Fievet C., Fruchart J. C. et al. 2002a Identification of Rev-erbalpha as a physiological repressor of apoC-III gene transcription. J. Lipid Res. 43, 2172–2179.
Raspe E., Mautino G., Duval C., Fontaine C., Duez H., Barbier O. et al. 2002b Transcriptional regulation of human Rev-erbalpha gene expression by the orphan nuclear receptor retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 49275–49281.
Reick M., Garcia J. A., Dudley C. and McKnight S. L. 2001 NPAS2: an analog of clock operative in the mammalian forebrain. Science 293, 506–509.
Reppert S. M. and Weaver D. R. 2002 Coordination of circadian timing in mammals. Nature 418, 935–941.
Retnakaran R., Youn B. S., Liu Y., Hanley A. J., Lee N. S., Park J. W. et al. 2008 Correlation of circulating full-length visfatin (PBEF/Nampt) with metabolic parameters in subjects with and without diabetes: a cross-sectional study. Clin. Endocrinol. (Oxf.) (in press).
Revollo J. R., Grimm A. A. and Imai S. 2004 The NAD biosynthesis pathway mediated by nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase regulates Sir2 activity in mammalian cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 50754–50763.
Revollo J. R., Korner A., Mills K. F., Satoh A., Wang T., Garten A. et al. 2007 Nampt/PBEF/Visfatin regulates insulin secretion in beta cells as a systemic NAD biosynthetic enzyme. Cell Metab. 6, 363–375.
Ripperger J. A. and Schibler U. 2001 Circadian regulation of gene expression in animals. Curr. Opin. Cell. Biol. 13, 357–362.
Ripperger J. A. and Schibler U. 2006 Rhythmic CLOCK-BMAL1 binding to multiple E-box motifs drives circadian Dbp transcription and chromatin transitions. Nat. Genet. 38, 369–374.
Rodgers R. J., Ishii Y., Halford J. C. and Blundell J. E. 2002 Orexins and appetite regulation. Neuropeptides 36, 303–325.
Rodgers J. T., Lerin C., Haas W., Gygi S. P., Spiegelman B. M. and Puigserver P. 2005 Nutrient control of glucose homeostasis through a complex of PGC-1alpha and SIRT1. Nature 434, 113–118.
Rodgers J. T., Lerin C., Gerhart-Hines Z. and Puigserver P. 2008 Metabolic adaptations through the PGC-1 alpha and SIRT1 pathways. FEBS Lett. 582, 46–53.
Ruiter M., Buijs R. M. and Kalsbeek A. 2006 Hormones and the autonomic nervous system are involved in suprachiasmatic nucleus modulation of glucose homeostasis. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2, 213–226.
Rutter J., Reick M., Wu L. C. and McKnight S. L. 2001 Regulation of clock and NPAS2 DNA binding by the redox state of NAD cofactors. Science 293, 510–514.
Rutter J., Reick M. and McKnight S. L. 2002 Metabolism and the control of circadian rhythms. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 71, 307–331.
Saper C. B., Cano G. and Scammell T. E. 2005a Homeostatic, circadian, and emotional regulation of sleep. J. Comp. Neurol. 493, 92–98.
Saper C. B., Lu J., Chou T. C. and Gooley J. 2005b The hypothalamic integrator for circadian rhythms. Trends Neurosci. 28, 152–157.
Sauve A. A., Wolberger C., Schramm V. L. and Boeke J. D. 2006 The biochemistry of sirtuins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 75, 435–465.
Sawaki Y., Nihonmatsu I. and Kawamura H. 1984 Transplantation of the neonatal suprachiasmatic nuclei into rats with complete bilateral suprachiasmatic lesions. Neurosci. Res. 1, 67–72.
Schibler U. 2003 Circadian rhythms. Liver regeneration clocks on. Science 302, 234–235.
Schibler U., Ripperger J. and Brown S. A. 2003 Peripheral circadian oscillators in mammals: time and food. J. Biol. Rhythms 18, 250–260.
Shearman L. P., Sriram S., Weaver D. R., Maywood E. S., Chaves I., Zheng B. et al. 2000 Interacting molecular loops in the mammalian circadian clock. Science 288, 1013–1019.
Silver R., LeSauter J., Tresco P. A. and Lehman M. N. 1996 A diffusible coupling signal from the transplanted suprachiasmatic nucleus controlling circadian locomotor rhythms. Nature 382, 810–813.
Stephan F. K. 2002 The “other” circadian system: food as a Zeitgeber. J. Biol. Rhythms 17, 284–292.
Stephan F. K. and Zucker I. 1972 Circadian rhythms in drinking behavior and locomotor activity of rats are eliminated by hypothalamic lesions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 69, 1583–1586.
Stokkan K. A., Yamazaki S., Tei H., Sakaki Y. and Menaker M. 2001 Entrainment of the circadian clock in the liver by feeding. Science 291, 490–493.
Storch K. F., Lipan O., Leykin I., Viswanathan N., Davis F. C., Wong W. H. and Weitz C. J. 2002 Extensive and divergent circadian gene expression in liver and heart. Nature 417, 78–83.
Sujino M., Masumoto K. H., Yamaguchi S., van der Horst G. T., Okamura H. and Inouye S. T. 2003 Suprachiasmatic nucleus grafts restore circadian behavioral rhythms of genetically arrhythmic mice. Curr. Biol. 13, 664–668.
Teboul M., Guillaumond F., Gréchez-Cassiau A. and Delaunay F. 2008 The Nuclear hormone receptors family round the clock. Mol. Endocrinol. (in press).
Tu B. P. and McKnight S. L. 2006 Metabolic cycles as an underlying basis of biological oscillations. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 7, 696–701.
Turek F. W., Joshu C., Kohsaka A., Lin E., Ivanova G., McDearmon E. et al. 2005 Obesity and metabolic syndrome in circadian Clock mutant mice. Science 308, 1043–1045.
Um J. H., Yang S., Yamazaki S., Kang H., Viollet B., Foretz M. and Chung J. H. 2007 Activation of 5′-AMP-activated kinase with diabetes drug metformin induces casein kinase I epsilon(CKIepsilon)-dependent degradation of clock protein mPer2. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 20794–20798.
Vujovic N., Davidson A. J. and Menaker M. 2008 Sympathetic input modulates, but does not determine, phase of peripheral circadian oscillators. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 295, R355–R360.
Wakamatsu H., Yoshinobu Y., Aida R., Moriya T., Akiyama M. and Shibata S. 2001 Restricted-feeding-induced anticipatory activity rhythm is associated with a phase-shift of the expression of mPer1 and mPer2 mRNA in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus but not in the suprachiasmatic nucleus of mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 13, 1190–1196.
Walker J. R. and Hogenesch J. B. 2005 RNA profiling in circadian biology. Methods Enzymol. 393, 366–376.
Wang J. and Lazar M. A. 2008 Bifunctional role of Rev-erbalpha in adipocyte differentiation. Mol. Cell Biol. 28, 2213–2220.
Wang T., Zhang X., Bheda P., Revollo J. R., Imai S. and Wolberger C. 2006 Structure of Nampt/PBEF/visfatin, a mammalian NAD+ biosynthetic enzyme. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 13, 661–662.
Wijnen H. and Young M. W. 2006 Interplay of circadian clocks and metabolic rhythms. Annu. Rev. Genet. 40, 409–448.
Wolk R. and Somers V. K. 2007 Sleep and the metabolic syndrome. Exp. Physiol. 92, 67–78.
Yang X., Lamia K. A. and Evans R. M. 2007 Nuclear receptors, metabolism, and the circadian clock. Cold. Spr. Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 72, 387–394.
Yang H., Yang T., Baur J. A., Perez E., Matsui T., Carmona J. J. et al. 2007 Nutrient-sensitive mitochondrial NAD+ levels dictate cell survival. Cell 130, 1095–1107.
Yildiz B. O., Suchard M. A., Wong M. L., McCann S. M. and Licinio J. 2004 Alterations in the dynamics of circulating ghrelin, adiponectin, and leptin in human obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 10434–10439.
Yoo S. H., Yamazaki S., Lowrey P. L., Shimomura K., Ko C. H., Buhr E. D. et al. 2004 PERIOD2::LUCIFERASE real-time reporting of circadian dynamics reveals persistent circadian oscillations in mouse peripheral tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 101, 5339–5346.
Yoon J. C., Puigserver P., Chen G., Donovan J., Wu Z., Rhee J. et al. 2001 Control of hepatic gluconeogenesis through the transcriptional coactivator PGC-1. Nature 413, 131–138.
Young M. E. and Bray M. S. 2007 Potential role for peripheral circadian clock dyssynchrony in the pathogenesis of cardiovascular dysfunction. Sleep Med. 8, 656–667.
Zvonic S., Floyd Z. E., Mynatt R. L. and Gimble J. M. 2007 Circadian rhythms and the regulation of metabolic tissue function and energy homeostasis. Obesity (Silver Spr.) 15, 539–543.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bechtold, D.A. Energy-responsive timekeeping. J Genet 87, 447–458 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-008-0067-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-008-0067-6