Abstract
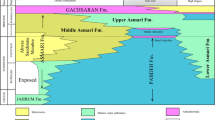
The shallow marine sedimentary sequence of the Jaisalmer Basin exhibits one of the important and well-developed Tithonian sedimentary outcrops for western India. The ichnology and ichnofabric of the lower part of Bhadasar Formation (i.e., Kolar Dongar Member) belonging to Tithonian age are presented and discussed. The Kolar Dongar Member represents a shallow marine succession that contains 16 ichnotaxa: Ancorichnus ancorichnus, Conichnus conicus, Gyrochorte comosa, cf. Jamesonichnites heinbergi, Imponoglyphus kevadiensis, Laevicyclus mongraensis, Monocraterion tentaculatum, Ophiomorpha nodosa, Palaeophycus tubularis, P. bolbiterminus, Phycodes palmatus, Planolites beverleyensis, Rhizocorallium isp., Rosselia rotatus, R. socialis, and Teichichnus rectus. The ichnofabric analysis divulges five distinct ichnofabrics, each typifying distinct depositional environment within shallow marine conditions. The ichnofabric Ophiomorpha 1 with syn-sedimentary faulting exemplifies high energy conditions typical of lower shoreface environment, whereas the Ophiomorpha 2 ichnofabric typifies upper shoreface environment. The Ancorichnus ichnofabric reflects lower offshore condition of deposition. The high ichnodiversity Ancorichnus–Rosselia ichnofabric is indicative of inner shelf conditions, while low ichno-diversity Teichichnus ichnofabric indicates prevalence of low energy brackish bay environment. Thus, Tithonian Kolar Dongar Member indicates depositional environment ranging from shoreface to offshore to inner shelf and finally to brackish bay environment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badve R M 1987 A reassessment of stratigraphy of Bagh Beds, Barwah area, Madhya Pradesh with description of trace fossils; J. Geol. Soc. India 30 106–120.
Badve R M and Ghare M A 1980 Ichnofauna of the Bagh beds from Devaganga river valley, south of Narmada; Biovigynam 6 121–130.
Benyon B M and Pemberton S G 1992 Ichnological signature of a brackish water deposit: An example from the Lower Cretaceous Grand Rapids Formation, Cold Lake Oil Sands area, Alberta; In: Applications of ichnology to petroleum exploration (ed.) Pemberton S G, Soc. Sedim. Geol., pp. 199–221.
Bhowmick P K and Mishra R 2008 Indian oil and gas potential; In: Glimpses of Geoscience research in India (eds) Singhvi A K, Bhattacharya A and Guha S, The Indian Report to IUGS 2004-2008, INSA Publication, Bangalore.
Billings E 1862 New species of fossils from different parts of the Lower, Middle and Upper Silurian rocks of Canada; In: Palaeozoic fossils 1 (1861–1865), Geol. Surv. Can., pp. 96–168.
Borkar V D and Kulkarni K G 2001 On the occurrence of Rhizocorallium Zenker from the Habur Formation (Aptian), Rajasthan; Gond. Geol. Mag. 16 15–20.
Borkar V D and Kulkarni K G 2006 Parallel succession of ichnologic and diagenetic events from Baisakhi Formation (Kimmeridgian), Rajasthan; Curr. Sci. 91 429–431.
Bose P K, Ghosh G, Shome S, and Bardhan S 1988 Evidence of superimposition of storm waves on tidal currents in rocks from Tithonian to Neocomian Umia member Kutch, India; Sedim. Geol. 54 321–329.
Bromley R G and Uchman A 2003 Trace fossils from the Lower and Middle Jurassic marginal marine deposits of the Sorthat Formation, Bornholm, Denmark; Bull. Geol. Soc. Denmark 52 185–208.
Bromley R G, Uchman A, Gregory N, and Martin A J 2003 Hillichnus lobosensis igen.et isp.nov., a compels trace fossil produced by tellinacean bivalves, Paleocene, Monterey, California, U.S.A; Paleogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 192 157–186.
Buck S G and Goldring R 2003 Conical sedimentary structures, trace fossils or not? Observation, experiments, and reviews; J. Sedim. Res. 73 338–353.
Buckman J O 1995 A comment on annulate forms of Palaeophycus Hall 1847 with particular reference to P.‘annulatus’ sensu Pemberton and Frey 1982 and the erection of P. crenulatus ichnosp. nov.; Ichnos 4 131–140.
Chamberlain C K 1977 Ordovician and Devonian Trace fossils from Nevada; Nevada Bureau Min. Geol. 90 1–24.
Chiplonkar G W and Badve R M 1970 Trace fossils from the Bagh Beds; J. Paleontol. Soc. India 14 1–10.
Chiplonkar G W, Ghare M A, and Badve R M 1981 On the occurrence of Ichnogenus Ichnyspica Linck from Upper Jurassic Series, Rajasthan; Curr. Sci. 50 147–148.
Curran H A 1994 The paleobiology of ichnocoenoses in Quaternary, Bahamian-style carbonate environments: The modern to fossil transition; In: The Palaeobiology of Trace Fossils (ed.) Donovan S K, The John Hopkins University Press, Baltimore, pp. 83–104.
Dahmer G 1937 Lebensspurenausdem Taunusquarzit und den Siegener Schichten (Unterdevon); Jahrb. Preuss, Geol. Landesanst. 57 523–539.
Dam G 1990 Paleoenvironmental significance of trace fossils from the shallow marine Lower Jurassic Neill Klinter Formation, East Greenland; Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 79 221–248.
Dasgupta S K 1975 A revision of the Mesozoic–Tertiary stratigraphy of the Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan; Indian J. Earth. Sci. 2 (1) 77–94.
Dashtgard S E, Gingras M K, and MacEachem J A 2009 Tidally modulated shoreface; J. Sedim. Res. 79 793–807.
Dave A and Chatterjee T K 1996 Biostratigraphy of Jurassic sediments; J. Geol. Soc. India 47 477–490.
De Gibert J M and Benner J S 2002 The trace fossil Gyrochorte: Ethology and paleoecology; Rev. Espa. Paleont. 17 (1) 1–12.
De Gibert J M and Martinell Y J 1998 Ichnofabrics of the Pliocene marginal marine basins of the northwestern Mediterranean; Rev. Soc. Geo. Espana 11 (1–2) 43–56.
Desai B G and Patel S J 2004 Kachchh earthquake of 2001. Seismically triggered deformed structures in intertidal sediments of Mandvi coast in the Gulf of Kachchh Gujarat; J. Geol. Soc. India 64 (5) 637–646.
Desai B G and Patel S J 2008 Trace fossil assemblages (Ichnocoenoses) of the tectonically uplifted Holocene shorelines, Kachchh, Western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 71 527–540.
Desai B G, Patel S J, Shukla R, and Surve D 2008 Analysis of ichnoguilds and their significance in interpreting ichnological events: A study from Jhuran Formation (Upper Jurassic), Western Kachchh, India; J. Geol. Soc. India 72 458–466.
Desai B G, Rajita S., and Saklani R D 2010 Ichnology of the Early Cambrian Tal Group, Nigalidhar Syncline, Lesser Himalaya, India; Ichnos 17 (4) 233–245.
Ekdale A A, Bromley R G, and Pemberton S G 1984 Ichnology: Trace fossils in sedimentology and stratigraphy; SEPM Short Course, No. 15.
Frey R W 1990 Trace fossils and hummocky cross-stratification, Upper Cretaceous of Utah; Palaios 5 203–218.
Frieling D 2007 Rosselia socialis in the Upper Marine Molasse of southwestern Germany; Facies 53 479–492.
Fürsich F T 1998 Environmental distribution of trace fossils in the Jurassic of Kachchh (western India); Facies 39 243–272.
Fürsich F T and Pandey D K 2003 Sequence stratigraphic siginificance of sedimentary cycles and shell concentrations in the Upper Jurassic–Lower Cretaceous of Kachchh, western India; Palaeogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Palaeoecol. 193 285–309.
Fürsich F T, Pandey D K, Kasyap D, and Wilmsen M 2006 The trace fossil Ctenopholeus Seilacher & Hemleben, 1966 from the Jurassic of India and Iran: Distinction from related ichnogenera; Neus. Jahrb. Geol. Paläont. S 641–654.
Gerard J R F and Bromley R. 2008 Ichnofabrics in clastic sediments: Applications to sedimentological core studies, a practical guide; Ibergraphi, Madrid, 100p.
Goodwin P W and Anderson E J 1974 Structures of a Cambrian tidal sand body; Geol. 82 779–799.
Hall J 1847 Palaeontology of New York; C. Van Benthuysen, Albany 1 338p.
Hall J 1852 Palaeontology of New York; C. Van Benthuysen, Albany 2 362.
Häntzschel W 1975 Trace fossils and problematica (2nd edn). In: Treatise on Invertebrate Paleontology (ed.) Teichert C, Miscellanea, suppl. 1, p. W1–W269, Geol. Soc. Amer. and Univ. Kan. Press.
Heer O 1865 Die Urwelt der Schweiz; FriedrichSchulthess (Zurich) 622 368.
Heinberg C 1974 A dynamic model for a meniscus filled tunnel (Ancorichnus n. ichnogen.) from the Jurassic Pecten sandstone of Milne Land, East Greenland; Rapp. Grønlands Geol. Unders. 62 20.
Jain S P and Garg R 2012 Biostratigraphic implications of the record of genus Himalayites from the Late Tithonian sediments of Jaisalmer, western India; J. Paleontol. Soc. India 57 (2) 105–111.
Keighley D G and Pickerill R K 1994 The Ichnogenus Beaconites and its distinction from Ancorichnus and Taenidium; Palaeontology 37 305–337.
Kim J Y, Pickerill R K, and Wilson R A 2000 Palaeophycusbolbitermilus isp. nov. from the lower Silurian Upsalquitch Formation of New Brunswick, Eastern Canada; Atlantic Geology 36 131–137.
Krishna J 1987 An overview of the Mesozoic stratigraphy of Kachchh and Jaisalmer Basin; J. Paleontol. Soc. India 32 136–149.
Kulkarni K G, Borkar V D, and Petare T J 2008 Ichnofossils from the Fort Member (Middle Jurassic), Jaisalmer Formation, Rajasthan; J. Geol. Soc. India 71 731–738.
Kundal P and Sanganwar B N 2000 Ichnofossils from the Nimar Sandstone Formation, Bagh Group of Manawar Area, Dhar District, M.P.; Geol. Soc. India Memoir 46 229–243.
Kumar A 1979 Report on the occurrence of Gyrochorte and other bilobed trace fossils in the Jaisalmer Formation, Rajasthan; Curr. Sci. 48 817.
Lundgren S A B 1891 Studier öfverfossilförandelösa block; Geol. Fören Stockh. Förh 13 111–121.
MacEachern J A and Pemberton S G 1992 Ichnological aspects of cretaceous shoreface successions and shoreface variability in the western interior seaway of North America; In: Applications of Ichnology to Petroleum Exploration: A Core Workshop (ed.) Pemberton S G, SEPM, Core Workshop 17 57–84.
Männil R 1966 [Development of the Baltic Basin during the Ordovician], Tallinn: Valgus, 201p. (in Russian).
McCarthy B 1979 Trace fossils from a Permian shoreface foreshore environment, Eastern Australia; J. Paleontol. 53 345–366.
Miller M F and Smail S E 1997 A semi-quantitative field method for evaluating bioturbation on bedding plane; Palaios 12 (4) 391–396.
Nara M 1997 High resolution analytical method for event sedimentation using Rosselia socialis; Palaios 12 489–494.
Pandey B and Krishna J 2002 Ammonoid biostratigraphy in the Tithonian (Late Jurassic) of Jaisalmer, western India; Geophytology 30 (1–2) 17–25.
Pandey D K, Sha J, and Choudhary S 2006a Depositional history of the early part of the Jurassic succession on the Rajasthan Shelf, western India; Prog. Nat. Sci. 16 176–185.
Pandey D K, Sha J, and Choudhary S 2006b Depositional environment of Bathonian sediments of the Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, western India; Prog. Nat. Sci. 16 163–175.
Pandey D K, Fürsich F T, and Baron-Szabo R 2009 Jurassic corals from the Jaisalmer Basin, western Rajasthan, India; Zitteliana A 48/49 13–37.
Pandey D K, Sha J, and Choudhary S 2010 Sedimentary cycles in the Callovian–Oxfordian of the Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, western India; Vol. Jura. 8 131–162.
Pandey D K, Choudhary S, Bahadur T, Swami N, Poonia D, and Sha J 2012 A review of the Lower-lowermost Upper Jurassic facies and stratigraphy of the Jaisalmer Basin, western Rajasthan, India; Vol. Jura. 10 61–82.
Pareekh H S 1981 Basin configuration and sedimentary stratigraphy of western Rajasthan; J. Geol. Soc. India 22 517–527.
Patel S J and Desai B G 2001 The Republic day Kachchh Earthquake of 2001: Trauma in Oratosquillastriata ; J. Geol. Soc. India 58 215–216.
Patel S J and Desai B G 2009 Animal-sediment relationship of the crustaceans and Polychaetes in the intertidal zone around Mandvi Gulf of Kachchh, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 74 233–259.
Patel S J, Desai B G, Vaidya A D, and Shukla R 2008 Middle Jurassic trace fossils from Habo Dome, mainland Kachchh, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 71 345–362.
Patel S J, Desai B G and Shukla R 2009 Paleoecological significance of the trace fossils of Dhosa Oolite Member (Jumara Formation), Jhura Dome, mainland Kachchh, western India; J. Geol. Soc. India 74 601–614.
Prasad S 2006 Ammonite biostratigraphy of Middle to Late Jurassic rocks of Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, India; Geol Surv. India Memoir 52 146p.
Powell J H 1992 Gyrochorte burrows from Scarborough Formation (Middle Jurassic) of the Cleveland Basin, and their sedimentological settings; Proc. Yorkshire Geol. Soc. 49 41–47.
Rai J, Singh A, and Pandey D K 2013 Early to Middle Albian age Calcareous nanofossils from Pariwar Formation of Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan, western India and their significance; Curr. Sci. 105 (11) 1604–1611.
Reineck H E and Singh I B 1980 Depositional sedimentary environments; 2nd edn, Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 551p.
Schlirf M 2000 Upper Jurassic trace fossils from the Boulonnais (Northern France); Geol. Palaeontol. 34 145–213.
Seilacher A 1955 Spuren und Faziesim Unyerkambrium; In: O.H. Schindewolf and Seilacher, BeitragezurKenntnis des Kambriums in der Salt range (Pakistan); Akad. Wiss. Lit. Mainz. Math.-nat. Kl., Abhandl. 10 11–143.
Shinn E A 1968 Burrowing in recent lime sediments of Florida and the Bahamas; J. Paleontol. 42 879–894.
Singh N P 2006 Mesozoic lithostratigraphy of the Jaisalmer Basin; J. Paleontol. Soc. India 52 (2) 53–56.
Singh M C, Kundal P, and Kushwaha R A S 2010 Ichnology of Bhuban and Bokabil Formations, Oligocene–Miocene deposits of Manipur Western Hill, Northeast India ; J. Geol. Soc. India 76 573–586.
Sudan C S, Sahni A K, and Sharma U K 2000 Trace fossils from the Jurassic sequence of Jaisalmer Basin, Rajasthan; J. Pal. Soc. India 45 165–171.
Taylor A M and Goldring R 1993 Description and analysis of bioturbation and ichnofabric; J. Geol. Soc. London 150 141–148.
Taylor A, Goldring R, and Gowland S 2003 Analysis and application of ichnofabrics; Earth Sci. Rev. 60 227–259.
Tiwari R P, Rajkonwar C, Lalchawimawii, Lalnuntluanga P, Malsawma J, Victor Z R, and Patel S J 2011 Trace fossils from Bhuban Formation, Surma Group (Lower to Middle Miocene) of Mizoram India and their palaeoenvironmental significance; J. Earth Syst. Sci. 120 (6) 1127–1143.
Torell O 1870 PetrificatasuecanaFormationisCambricae; Lunds. Univ. Arsskr. 6. Avdel 2 (8) 1–14.
Uchman A 1995 Taxonomy and palaeoecology of flysch trace fossils: The Marnoso-arenacea Formation and associated facies (Miocene, Northern Apennines, Italy); Beringeria 15 3–115.
Verma K K 1969 Occurrence of trace fossils in the Bagh Beds of Amba Dongar Area, Gujarat State; J. Indian Geosci. Assoc. 12 37–40.
Vyalov O S 1971 RedkieproblematikiizmezozojaPamiraiKavkaza. [Rare problematica from the Mesozoic of Pamir and Caucasus.] Paleontologicheskii SbornikIzdatel’stvoL’vovskogo Universiteta; Vypuskvtoroi 7 85–93 (in Russian).
Zaigham N A and Malick K A 2000 Prospect of hydrocarbon associated with fossil-rift structures of the southern Indus basin, Pakistan; Am. Assoc. Petrol. Geol. Bull. 84 1833–1848.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, B.G., Saklani, R.D. Ichnofabric analysis of the Tithonian shallow marine sediments (Bhadasar Formation) Jaisalmer Basin, India. J Earth Syst Sci 123, 1413–1431 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0462-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-014-0462-8