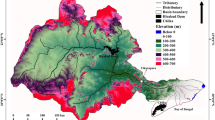
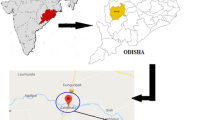
The annual sediment load of a river is generally determined either from direct measurements of the sediment load throughout the year or from any of the many sediment transport equations that are available today. Due to lack of a long-term sediment concentration data, sediment rating curves and flux estimation are the most widely applied. This paper has investigated the abilities of statistical models to improve the accuracy of streamflow–suspended sediment relationships in daily and annual suspended sediment estimation. In this study, a comparison was made between suspended sediment rating curves and artificial neural networks (ANNs) for the El Kebir catchment. Daily water discharge and daily suspended sediment data from the gauging station of Ain Assel, were used as inputs and targets in the models which were based on the cascade-forward and feed-forward back-propagation using Levenberg–Marquardt and Bayesian regularization algorithms. The model results have shown that the ANN models have the highest efficiency to reproduce the daily sediment load and the global annual sediment yields. Our estimation based on the available data indicated that the areas along the El Kebir River have experienced high sediment fluxes that could have obvious impacts on the sediment trapping and siltation in the Mexa reservoir.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adeloye A J and Munari A D 2006 Artificial neural network based generalized storage yield–reliability models using the Levenberg–Marquardt algorithm; J. Hydrol. 362 215–230.
Agarwal A, Singh R D, Mishra S K and Bhunya P K 2005 ANN-based sediment yield models for Vamsadhara river basin (India); Water SA 31(1) 95–100.
Asselman N E M 2000 Fitting and interpretation of sediment rating curves; J. Hydrol. 234 228–248.
Cigizoglu H K 2002 Suspended sediment estimation and forecasting using artificial neural networks; Turk. J. Eng. Environ. Sci. 26 15–25.
Cigizoglu H K 2004 Estimation and forecasting of daily suspended sediment data by multilayer perceptrons; Adv. Water Resour. 27 185–195.
Gupta H and Chakrapani G J 2007 Temporal and spatial variations in water flow and sediment load in the Narmada river; Curr. Sci. 92(5) 679–684.
Hassan A E 2001 Prediction of plume migration in heterogeneous media using artificial neural networks; Water Resour. Res. 37(3) 605–623.
Horowitz A J 2003 An evaluation of sediment rating curve for estimating suspended sediment concentration for subsequent flux calculations; Hydrol. Proc. 17 3387–3409.
Jain S K 2001 Development of integrated sediment rating curves using ANNs; J. Hydraul. Eng. ASCE 127(1) 30–37.
Jansson M B 1997 Comparison of sediment rating curves developed on load and on concentration; Nordic Hydrol. 28(3) 189–200.
Khanchoul K and Jansson M B 2008 Sediment rating curves developed on stage and seasonal means in discharge classes for the Mellah wadi, Algeria; Geogr. Ann. 90A(3) 227–236.
Kisi O 2004 Multi-layer perceptrons with Levenberg–Marquardt optimization algorithm for suspended sediment concentration prediction and estimation; Hydrol. Sci. J. 49(6) 1025–1040.
Merritt W S, Letcher R A and Jakeman A J 2003 A review of erosion and sediment transport models; Environ. Modell. Softw. 18(8–9) 761–799.
Nagy H M, Watanabe K and Hirano M 2002 Prediction of sediment load concentration in rivers using artificial neural network model; J. Hydraul. Eng. 128(6) 588–595.
Rai R K and Mathur B S 2008 Event-based sediment yield modeling using artificial neural network; Water Resour. Manag. 22(4) 423–441.
Rojas R 1996 Neural Networks: A systematic introduction (Berlin: Springer Verlag), pp. 151–184.
Subramanian N, Yajnik A and Murthy R S R 2004 Artificial neural network as an alternative to multiple regression analysis in optimizing formulation parameters of Cytarabine Liposomes; AAPS Pharm. Sci. Tech. 5(1) 1–9.
Tayfur G 2002 Artificial neural networks for sheet sediment transport; Hydrol. Sci. J. 47(6) 879–892.
Walling D E 1978 Suspended sediment and solute response characteristics of the river Exe, Devon, England; In: Research in fluvial systems (eds) Davidson-Arnott R and Nickling W, Geoabstracts (Norwich, UK), pp. 169–197.
Wang Y M and Traore S 2009 Time-lagged recurrent network for forecasting episodic event suspended sediment load in typhoon prone area; Int. J. Phys. Sci. 4(9) 519–528.
Wang Y M, Juaug S C, Lai C C and Kerh T 2006 Estimation of suspended sediment discharge for a storm; J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 28(2) 152–156.
Yenigun K, Gumus V and Bulut H 2008 Trends in streamflow of Euphrates Basin, Turkey, ICE; Water Manag. 161(4) 189–198.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
BOUKHRISSA, Z.A., KHANCHOUL, K., LE BISSONNAIS, Y. et al. Prediction of sediment load by sediment rating curve and neural network (ANN) in El Kebir catchment, Algeria. J Earth Syst Sci 122, 1303–1312 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0347-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0347-2