Abstract
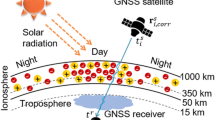
The positional accuracy of the Global Positioning System (GPS) is limited due to several error sources. The major error is ionosphere. By augmenting the GPS, the Category I (CAT I) Precision Approach (PA) requirements can be achieved. The Space-Based Augmentation System (SBAS) in India is known as GPS Aided Geo Augmented Navigation (GAGAN). One of the prominent errors in GAGAN that limits the positional accuracy is instrumental biases. Calibration of these biases is particularly important in achieving the CAT I PA landings. In this paper, a new algorithm is proposed to estimate the instrumental biases by modelling the TEC using 4th order polynomial. The algorithm uses values corresponding to a single station for one month period and the results confirm the validity of the algorithm. The experimental results indicate that the estimation precision of the satellite-plus-receiver instrumental bias is of the order of ±0.17 nsec. The observed mean bias error is of the order −3.638 nsec and −4.71 nsec for satellite 1 and 31 respectively. It is found that results are consistent over the period.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bishop G and Mazzella A “Self-Calibration of Pseudorange Errors by GPS Two-Frequency Receivers”, ION NTM, 95.
Brian D Wilson and Anthony J Mannucci 1999 Instrumental Biases in Ionospheric Measurements Derived from GPS Data; Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91109.
Coco D S, Coker C, Dahlke S R and Clynch J R 1991 Variability of GPS satellite differential group delay biases; IEEE Transaction on Aerospace and Electrical Systems 27(6) 931–938.
Lao-Sheng Lin Remote sensing of ionosphere using GPS measurements; 22nd Asian Conference on remote sensing, Singapore, 5–9 November 2001.
Ma G and Maruyama 2003 Derivation of TEC and estimation of instrumental biases from GEONET in Japan; Ann. Geophys. 21 2093, EGU.
Sarma A D, Sasibhushana Rao G and Venkata Rao V 2000 Ionospheric Reference Station Placement for INWAAS — A Preliminary Study; J. Indian Geophys. Union 4(1) 41–49.
Specifications for Wide Area Augmentation System (WAAS), U.S. DOT, Federal Aviation Administration, FAA-E2872B, March 10, 1997.
Suryanarayan Rao K N and Pal S The Indian SBAS System; India-United States Conference on Space Science Application and Commerce, Bangalore, India 21–25 June 2004.
Ramalingam K 2002 IONO-TROPO Modelling for Indian SBAS-GAGAN, presented at ‘The International Civil Aviation Organization, GNSS PANEL’; Working Group A&B Meeting, San Antonio, Texas, USA, Oct. 16–25.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasibhushana Rao, G. GPS satellite and receiver instrumental biases estimation using least squares method for accurate ionosphere modelling. J Earth Syst Sci 116, 407–411 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0039-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-007-0039-x