Abstract
In the present study, the dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose (DCMC) was cross-linked covalently to gelatin via the Schiff base reaction to form a three-dimensional hydrogel (DCMC-cl-G). The crosslinking degree of DCMC and gelatin was estimated to be 50.31 ± 2.65. The maximum swelling capacity of the hydrogel in aqueous medium was around 74 g/g at pH 10.0 and 37 °C with equilibrium swelling attained in three hours and the compressive strength of the hydrogel was found to be 55 ± 0.76 kPa at 60% strain. The biodegradation studies confirmed 82.67% degradation of the hydrogel sample within a period of twelve weeks. Further, the hydrogel was evaluated as a bio adsorbent for the removal of hazardous dyes, namely Rhodamine B (RhB) and Methyl Violet (MV) from water due to its decent swelling capacity and good mechanical strength. The maximum percentage of RhB and MV removed from the respective dye solutions using DCMC-cl-G hydrogel was 96.5% and 90% at pH 6.0, respectively. Both dyes followed Langmuir adsorption isotherm, which considers monolayer adsorption of adsorbate over adsorbent, with a pseudo-second-order kinetic model.
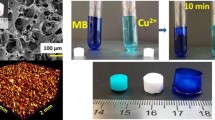
Graphic abstract
An environment friendly hybrid hydrogel of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose was fabricated by crosslinking with gelatin. The use of gelatin improved the compressive strength and thermal characteristics of the hydrogel. It was utilized for the efficient removal of hazardous dyes such as Rhodamine B and Methyl violet. The biodegradation of the hydrogel was achieved up to 82.67% for a period of twelve weeks.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
(a) Akan J C, Abdulrahman F I, Ayodele J T and Ogugbuaja V 2009 Impact of Tannery and Textile Effluent on the Chemical Characteristics of Challawa River, Kano State, Nigeria Aust. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 3 1933; (b) Lotfy S and Abou Taleb M F 2018 Free radical polymerization of polyvinyl butyral/polyethylene glycol diacrylate copolymer for removing organic dyes from waste water Polym. Bull. 75 2865; and (c) Shah M P 2016 Industrial Wastewater Treatment: A Challenging Task in the Industrial Waste Management Adv. Recycl. Waste Manage.: Open Access 2 115
Capar G, Yetis U and Yilmaz L 2006 Membrane based strategies for the pre-treatment of acid dye bath wastewaters J. Hazard. Mater. 135 423; (b) Zahrim A Y, Tizaoui C and Hilal N 2011 Coagulation with polymers for nanofiltration pre-treatment of highly concentrated dyes: A review Desalination 266 1; (c) Liu C H, Wu J S, Chiu H C, Suen S Y and Chu K H 2007 Removal of anionic reactive dyes from water using anion exchange membranes as adsorbers Water Res. 41 1491; and (d) Sheshmani S, Ashori A, Hasanzadeh S 2014 Removal of Acid Orange 7 from aqueous solution using magnetic graphene/chitosan: A promising nano-adsorbent Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 68 218
(a) Bhatia J K, Kaith B S and Kalia S 2013 Polysaccharide Hydrogels: Synthesis, Characterization, and Applications In: Polysaccharide Based Graft Copolymers (Berlin: Springer) Ch. 7 pp. 271–290; (b) Pathania D, Verma C, Negi P, Tyagi I, Asif M, Kumar N S, Al-Ghurabi E. H, Agarwal S and Gupta V K 2018 Novel nanohydrogel based on itaconic acid grafted tragacanth gum for controlled release of ampicillin Carbohydr. Polym. 196 262; (c) Wang W B, Zhang H X, Shen J F and Ye M X 2018 Facile preparation of magnetic chitosan/poly (vinyl alcohol) hydrogel beads with excellent adsorption ability via freezing-thawing method Colloid. Surf. A 553 672; (d) Sampath S, Choudhury N A and Shukla A K 2009 Hydrogel membrane electrolyte for electrochemical capacitors J. Chem. Sci. 121 727
Vadivelan V and Kumar K V 2005 Equilibrium, kinetics, mechanism, and process design for the sorption of methylene blue onto rice husk J. Colloid. Interf. Sci. 286 90
Liu S, Kang M, Li K, Yao F, Oderinde O, Fu G and Xu L 2018 Polysaccharide-templated preparation of mechanically-tough, conductive and self-healing hydrogels Chem. Eng. J. 334 2222
Monier M, Abdel-Latif D A and Ji H F 2016 Synthesis and application of photo-active carboxymethyl cellulose derivatives React. Funct. Polym. 102 137
Capanema N S V, Mansur A A P, deJesus A C, Carvalho S M, de Oliveira L C and Mansur H S 2018 Superabsorbent crosslinked carboxymethyl cellulose-PEG hydrogels for potential wound dressing applications Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 106 1218
Benhalima T, Ferfera-Harrar H and Lerari D 2017 Optimization of carboxymethyl cellulose hydrogels beads generated by an anionic surfactant micelle templating for cationic dye uptake: Swelling, sorption and reusability studies Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 105 1025
Cui L, Jia J, Guo Yi, Liu Y and Zhu P 2014 Preparation and characterization of IPN hydrogels composed of chitosan and gelatin cross-linked by genipin Carbohyd. Polym. 99 31
Nieuwenhove I V, Salamon A, Petersb K, Graulusa G-J, Martinsc J C, Frankeld D, Kersemanse K, Vose F D, Vlierberghea S V and Dubruela P 2016 Gelatin- and starch-based hydrogels. Part A: Hydrogel Development, characterization and coating Carbohyd. Polym. 152 129
Manna P J, Mitra T, Pramanik N, Kavith V, Gnanamani A and Kundu P P 2015 Potential use of curcumin loaded carboxymethylated guar gum grafted gelatin film for biomedical applications Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 75 437
Li H, Wu B, Mu C and Lin W 2011 Concomitant degradation in periodate oxidation of carboxymethyl cellulose Carbohyd. Polym. 84 881
(a) Balakrishnan B, Joshi N and Banerjee R 2013 Borate aided Schiff’s base formation yields in situ gelling hydrogels for cartilage regeneration J. Mater. Chem. B 1 5564; (b) EL-Sayed N S, El-Ziaty A K, El-Meligy G, Nagieb Z A 2017 Syntheses of New Antimicrobial Cellulose Materials Based 2-((2-aminoethyl)amino)-4-aryl-6-indolylnicotinonitriles Egypt. J. Chem. 60 465
Dash R, Foston M and Ragauskas A J 2013 Improving the mechanical and thermal properties of gelatin hydrogels cross-linked by cellulose nanowhiskers Carbohyd. Polym. 91 638
Zheng X, Zhang Q, Liu J, Pei Y and Tang K 2013 A unique high mechanical strength dialdehyde microfibrillated cellulose/gelatin composite hydrogel with a giant network structure RSC Adv. 6 71999
Sethi S, Kaith B S, Saruchi, Kumar V 2019 Fabrication and characterization of microwave assisted carboxymethyl cellulose-gelatin silver nanoparticles imbibed hydrogel: Its evaluation as dye degradation React. Funct. Polym. 142 134
Hofreiter B T, Alexander B H and Wolff I A 1955 Rapid Estimation of Dialdehyde Content of Periodate Oxystarch through Quantitative Alkali Consumption Anal. Chem. 27 1930
Mandal B and Ray S K 2014 Swelling, diffusion, network parameters and adsorption properties of IPN hydrogel of chitosan and acrylic copolymer Mater. Sci. Eng. C 44 132
Mittal H, Mishra S B, Mishra A K, Kaith B S, Jindal R and Kalia S 2013 Preparation of poly (acrylamide-co-acrylic acid)-grafted gum and its flocculation and biodegradation studies Carbohyd. Polym. 98 397
Sannino A, Demitri C and Madaghiele M. 2009 Biodegradable Cellulose-based Hydrogels: Design and Applications Materials 2 353
Guilherme M R, Aouada F A, Fajarado A R, Martins A F, Paulino A T, Davi M F T, Rubira A F and Muniz E C 2015 Superabsorbent hydrogels based on polysaccharides for application in agriculture as soil conditioner and nutrient carrier: A review Eur. Polym. J. 72 365
Wu S C, Chang W H, Dong G C, Chen K Y, Chen Y S, Yao C H 2011 Cell adhesion and proliferation enhancement by gelatin nanofiber scaffolds J. Bioact. Compat. Polym. 26 565
Li D, Ye Y, Li D, Li X and Mu C 2016 Biological properties of dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose crosslinked gelatin–PEG composite hydrogel fibers for wound dressings Carbohyd. Polym. 137 508
Khorshidi S and Karkhaneh A 2016 A self-crosslinking tri-component hydrogel based on functionalized polysaccharides and gelatin for tissue engineering applications Mater. Lett. 164 468
(a) Wang W-B, Huang D-J, Kang Y-R and Wang A-Q 2013 One-step in situ fabrication of a granular semi-IPN hydrogel based on chitosan and gelatin for fast and efficient adsorption of Cu2+ ion Colloid. Surf. B: Biointerf. 106 51; (b) Tong Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Cai H, Zhang W and Tan W-S 2018 POSS-enhanced thermo sensitive hybrid hydrogels for cell adhesion and detachment RSC Adv. 8 13813
Tu H, Yu Y, Chen J, Shi X, Zhou J, Deng H and Du Y 2017 Highly cost-effective and high-strength hydrogels as dye adsorbents from natural polymers: chitosan and cellulose Polym. Chem. 8 2913
Zhu L, Guan C, Zhou B, Zhang Z, Yang R, Tang Y and Yang J 2017 Adsorption of Dyes onto Sodium Alginate Graft Poly(Acrylic Acidco-2-Acrylamide-2-Methyl Propane Sulfonic Acid)/ Kaolin Hydrogel Composite Polym. Polym. Compos. 25 627
(a) Gong R, Ye J J, Dai W, Yan X Y, Hu J, Hu X, Li S and Huang H 2013 Adsorptive Removal of Methyl Orange and Methylene Blue from Aqueous Solution with Finger-Citron-Residue-Based Activated Carbon Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 52 14297; (b) Kumar N, Mittal H, Parashar V, Ray S S and Ngila J C 2016 Efficient removal of rhodamine 6G dye from aqueous solution using nickel sulphide incorporated polyacrylamide grafted gum karaya bionanocomposite hydrogel RSC Adv. 6 21929
Mittal H, Maity A and Ray S S 2015 Effective removal of cationic dyes from aqueous solution using gum ghatti-based biodegradable hydrogel Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 79 8
Dumeignil F, Paul J-F and Paul S 2017 Heterogeneous Catalysis with Renewed Attention: Principles, Theories, and Concepts J. Chem. Edu. 94 675
Itodo A U and Itodo H U 2010 Sorption Energies Estimation Using Dubinin-Radushkevich and Temkin Adsorption Isotherms Life Sci. J. 7 31
Fosso-Kankeu E, Mittal H, Mishra S B and Mishra A K 2015 Gum ghatti and acrylic acid based biodegradable hydrogels for the effective adsorption of cationic dyes J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 22 171
Mittal H, Kumar V, Saruchi and Ray S S 2016 Synthesis and flocculation properties of gum ghatti and poly(acrylamide-co-acrylonitrile) based biodegradable hydrogels Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 89 1
Ghorai S, Sarkar A, Raoufi M, Panda A B, Schönherr H and Pal S 2016 Enhanced Removal of Methylene Blue and Methyl Violet Dyes from Aqueous Solution Using a Nanocomposite of Hydrolyzed Polyacrylamide Grafted Xanthan Gum and Incorporated Nanosilica Appl. Mater. Interf. 6 4766
Mittal H, Jindal R, Kaith B S, Maity A and Ray S S 2014 Synthesis and flocculation properties of gum ghatti and poly(acrylamide-co-acrylonitrile) based biodegradable hydrogels Carbohyd. Polym. 114 321
Acknowledgements
X-ray facility at Dr. B R Ambedkar is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sethi, S., Kaith, B.S., Kaur, M. et al. A hydrogel based on dialdehyde carboxymethyl cellulose–gelatin and its utilization as a bio adsorbent. J Chem Sci 132, 15 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-019-1700-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12039-019-1700-z