Abstract
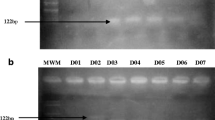
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a disease induced by complex interactions between environmental factors and certain genetic factors. Genetic variants in the Adenosine Binding Cassette Transporter Proteins 1 (ABCA1) have been associated with abnormalities of serum lipid levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL-C). Decreased serum levels of HDL-C have often been observed in T2DM cases, and this condition has been considered to be involved in the mechanism of insulin resistance (IR). Therefore, we investigated possible association between ABCA1 C69T gene polymorphism and T2DM in a Saudi population. This study was carried out with 380 healthy control subjects and 376 T2DM patients. Genotyping of ABCA1 C69T polymorphism was carried out by Polymerase Chain Reaction-Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism technique. We observed that the frequency of the T allele of the ABCA1 C69T gene was significantly higher in healthy subjects compared to T2DM patients (0.28 vs 0.45; p<0.0001; OR (95% CI) = 0.4624 (0.3732–0.5729), and therefore the T allele may be a protective factor against T2DM in the Saudi population.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balderelli IP, Pean F, Emery N, Maimaitiming S, Bellili N, Travert F, Mohammedi K, Roussel R, et al. 2009 Relationships between common polymorphisms of adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette transporter A1 and high density cholesterol and coronary artery disease in a population with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metab. Clin. Exp. 58 74–79
Brunham LR, Kruit JK, Pape TD, Timmins JM, Reuwer AQ, Vasanji Z, Marsh BJ, Rodrigues B, et al. 2007 ABCA1 influences insulin secretion, glucose homeostasis and response to thiazolidinedione treatment. Nat. Med. 13 340–347
Daimon M, Ji G, Saitoh T, Oizumi T, Tominaga M, Nakamura T, Ishii K, Matsuura T, et al. 2003 Large scale search of SNPs for type 2 DM susceptibility genes in a Japanese population. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 302 751–758
Daimona M, Kidob T, Baba M, Oizumi T, Jimbu Y, Kameda W, Yamaguchi H, Ohnuma H, et al. 2005 Association of the ABCA1 gene polymorphism with type 2 DM in a Japanese population. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 329 205–210
Ergen A, Isbir S, Tekeli A and Isbir T 2008 Investigation of ABCA1 C69T and G-191C polymorphisms in coronary artery disease. In Vivo 22 187–190
Ergen HA, Zeybek U, Gok O and Karaali ZE 2012 Investigation of ABCA1 C69T polymorphism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biochem. Med. 22 114–120
Gao F, Yan T, Zhao Y, Yin F and Hu C 2010 A possible mechanism linking hyperglycemia and reduced high density lipoprotein cholesterol levels in diabetes. J. Huazhong Univ. Sci. Technol. Med. Sci. 30 318–321
Jenkins AB, Batterham M, Samocha-Bonet D, Tonks K, Greenfield JR and Campbell LV 2013 Segregation of a latent high adiposity phenotype in families with a history of type 2 diabetes mellitus implicates rare obesity-susceptibility genetic variants with large effects in diabetes-related obesity. PLoS One 8 e70435
Lorenzo C, Greco A, Fiorentino TV, Mannino GC and Hribal ML 2013 Variants of insulin-signaling inhibitor genes in type 2 diabetes and related metabolic abnormalities. Int. J. Genom. 376454 1–13 doi:10.1155/2013/376454
Mooradian AD 2009 Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 5 150–159
Oram JF 2000 Tanger disease and ABCA1. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 15 321–330
Patel DC, Albrecht C, Pavitt D, Paul V, Pourreyron C, Newman SP, Godsland IF, Valabhji J, et al. 2011 Type 2 diabetes is associated with reduced ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 gene expression, protein and function. PLoS One 6 e22124
Porchay I, Pean F, Belili N, Royer B, Cogneau J, Chesnier MC, Caradec A, Tichet J, et al. 2006 ABCA1 single nucleotide polymorphism on high density lipoprotein cholesterol and overweight: the D.E.S.I.R study. Obesity 14 1874–1879
Saleheen D, Nazir A, Khatun S, Haider SR and Frossard PM 2006 R1615P: a novel mutation in ABCA1 associated with low levels of HDL and type II diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Cardiol. 110 259–260
Salinas CA, Cruz-Bautista I, Mehta R, Villarreal-Molina MT, Perez FJ, Tusie-Luna MT and Canizales-Quinteros S 2007 The ATP binding cassette transporter subfamily A member 1 (ABCA1) and type 2 diabetes: an association beyond HDL cholesterol. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 3 264–267
Sheidina AM, Pchelina SN, Demidova DV, Rodygina TI, Taraskina AE, Toperverg OB, Berkovich OA and Demina EV 2004 Allele frequency analysis of four single nucleotide polymorphisms located in promoted and 5’-untranslated regions of ABCA1 gene in young men-survivors from myocardial Infarction. Kardiologiia 44 40–45
Stefkova J, Poledne R and Hubacek JA 2004 Polymorphisms in ABCA1 transporter and plasma lipids. Physiol. Res. 53 235–243
Vergeer M, Brunham LR, Koetsveld J, Kruit JK, Verchere CB, Kastelein JJ, Hayden MR and Stroes ES 2010 Carriers of loss-of-function mutations in ABCA1 display pancreatic beta-cell dysfunction. Diabetes Care 33 869–874
Wilson JB, Meigs L, Sullivan L, Fox CS, Nathan DM and D’Agostino RB Sr 2007 Prediction of incident diabetes mellitus in middle aged adults: the Framingham offspring study. Arch. Intern. Med. 167 1068–1074
Yamada Y, Matsuo H, Segawa T, Watanabe S, Kato K, Kameyama T, Yokoi K and Ichihara S 2006 Assessment of genetic factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Med. 18 299–308
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to extend their sincere appreciation to the Deanship of Scientific Research at King Saud University for its funding of this research through the Research Group Project no RGP-VPP-244.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: SARAH H ELSEA
[Alharbi KK, Khan IA, Al-Daghri NM, Munshi A, Sharma V, Mohammed AK, Wani KA, Al-Sheikh YA, Al-Nbaheen MS, Ansari MGA and Syed R 2013 ABCA1 C69T gene polymorphism and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Saudi population. J. Biosci. 38 1–5] DOI
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 39.4 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alharbi, K.K., Khan, I.A., Al-Daghri, N.M. et al. ABCA1 C69T gene polymorphism and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Saudi population. J Biosci 38, 893–897 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9384-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9384-x