Abstract
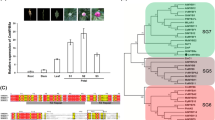
The flavonoids metabolic pathway plays central roles in floral coloration, in which anthocyanins and flavonols are derived from common precursors, dihydroflavonols. Flavonol synthase (FLS) catalyses dihydroflavonols into flavonols, which presents a key branch of anthocyanins biosynthesis. The yellow flower of Camellia nitidissima Chi. is a unique feature within the genus Camellia, which makes it a precious resource for breeding yellow camellia varieties. In this work, we characterized the secondary metabolites of pigments during floral development of C. nitidissima and revealed that accumulation of flavonols correlates with floral coloration. We first isolated CnFLS1 and showed that it is a FLS of C. nitidissima by gene family analysis. Second, expression analysis during floral development and different floral organs indicated that the expression level of CnFLS1 was regulated by developmental cues, which was in agreement with the accumulating pattern of flavonols. Furthermore, over-expression of CnFLS1 in Nicotiana tabacum altered floral colour into white or light yellow, and metabolic analysis showed significant increasing of flavonols and reducing of anthocyanins in transgenic plants. Our work suggested CnFLS1 plays critical roles in yellow colour pigmentation and is potentially a key point of genetic engineering toward colour modification in Camellia.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Cy3R:
-
cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside
- FLS:
-
flavonol synthase
- Qu:
-
quercetin
- Qu3G:
-
quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucoside
- Qu7G:
-
quercetin-7-O-β-d-glucoside
References
Aharoni A, De Vos CH, Wein M, Sun Z, Greco R, Kroon A, Mol JN and O'Connell AP 2001 The strawberry FaMYB1 transcription factor suppresses anthocyanin and flavonol accumulation in transgenic tobacco. Plant J. 28 319–332
Aida R, Yoshida K, Kondo T, Kishimoto S and Shibata M 2000 Copigmentation gives bluer flowers on transgenic torenia plants with the antisense dihydroflavonol-4-reductase gene. Plant Sci. 160 49–56
Buer CS, Imin N and Djordjevic MA 2010 Flavonoids: new roles for old molecules. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 52 98–111
Chang H and Ren S 1998 Theaceae. Flora reipublicae popularis sinicae (Beijing: Science Press) pp 87–133
Elomaa P, Honkanen J, Puska R, Seppanen P, Helariutta Y, Mehto M, Kotilainen M, Nevalainen L, et al. 1993 Agrobacterium-mediated transfer of antisense chalcone synthase Cdna to gerbera-hybrida inhibits flower pigmentation. Bio-Technology 11 508–511
Fukui Y, Tanaka Y, Kusumi T, Iwashita T and Nomoto K 2003 A rationale for the shift in colour towards blue in transgenic carnation flowers expressing the flavonoid 3',5'-hydroxylase gene. Phytochemistry 63 15–23
Fukusaki E, Kawasaki K, Kajiyama S, An CI, Suzuki K, Tanaka Y and Kobayashi A 2004 Flower color modulations of Torenia hybrida by downregulation of chalcone synthase genes with RNA interference. J. Biotechnol. 111 229–240
Gao J 2005 Collected species of the genus Camellia - An illustrated outline (Hangzhou: Zhejiang Science and Technology Publishing House)
Gou JY, Felippes FF, Liu CJ, Weigel D and Wang JW 2011 Negative regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in Arabidopsis by a miR156-targeted SPL transcription factor. Plant Cell 23 1512–1522
Grotewold E 2006 The genetics and biochemistry of floral pigments. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57 761–780
Harris NN, Javellana J, Davies KM, Lewis DH, Jameson PE, Deroles SC, Calcott KE, Gould KS, et al. 2012 Betalain production is possible in anthocyanin-producing plant species given the presence of DOPA-dioxygenase and L-DOPA. BMC Plant Biol. 12 34
Holton TA, Brugliera F and Tanaka Y 1993 Cloning and expression of flavonol synthase from Petunia hybrida. Plant J. 4 1003–1010
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG and Fraley RT 1985 A simple and general-method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227 1229–1231
Katsumoto Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Fukui Y, Brugliera F, Holton TA, Karan M, Nakamura N, Yonekura-Sakakibara K, et al. 2007 Engineering of the rose flavonoid biosynthetic pathway successfully generated blue-hued flowers accumulating delphinidin. Plant Cell Physiol. 48 1589–1600
Lepiniec L, Debeaujon I, Routaboul JM, Baudry A, Pourcel L, Nesi N and Caboche M 2006 Genetics and biochemistry of seed flavonoids. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 57 405–430
Li JB, Hashimoto F, Shimizu K and Sakata Y 2007 Anthocyanins from red flowers of Camellia reticulata LINDL. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 71 2833–2836
Li JB, Hashimoto F, Shimizu K and Sakata Y 2008 Anthocyanins from red flowers of Camellia cultivar 'Dalicha'. Phytochemistry 69 3166–3171
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD 2001 Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(-Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25 402–408
Mahajan M, Ahuja PS and Yadav SK 2011 Post-transcriptional silencing of flavonol synthase mRNA in tobacco leads to fruits with arrested seed set. PLoS One 6 e28315
Mahajan M, Joshi R, Gulati A and Yadav SK 2012 Increase in flavan-3-ols by silencing flavonol synthase mRNA affects the transcript expression and activity levels of antioxidant enzymes in tobacco. Plant Biol. 14 725–733
Marchler-Bauer A, Lu SN, Anderson JB, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, DeWeese-Scott C, Fong JH, Geer LY, et al. 2011 CDD: a Conserved Domain Database for the functional annotation of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 39 D225–D229
Markham KR and Hammett KRW 1994 The basis of yellow coloration in Lathyrus-Aphaca flowers. Phytochemistry 37 163–165
Miyajima I, Uemoto S, Sakata Y, Arisumi KI and Toki K 1985 Yellow pigment of Camellia chrysantha flowers. J. Faculty Agric. Kyushu Univ. 29 257–266
Nakatsuka T, Abe Y, Kakizaki Y, Yamamura S and Nishihara M 2007 Production of red-flowered plants by genetic engineering of multiple flavonoid biosynthetic genes. Plant Cell Rep. 26 1951–1959
Nielsen K, Deroles SC, Markham KR, Bradley MJ, Podivinsky E and Manson D 2002 Antisense flavonol synthase alters copigmentation and flower color in lisianthus. Mol. Breed. 9 217–229
Nielsen KM and Bloor SJ 1997 Analysis and developmental profile of carotenoid pigments in petals of three yellow petunia cultivars. Sci. Hortic. Amsterdam 71 257–266
Nishihara M and Nakatsuka T 2010 Genetic engineering of novel flower colors in floricultural plants: Recent advances via transgenic approaches; in Protocols for in vitro propagation of ornamental plants (eds) SM Jain and SJ Ochatt (Humana Press)
Owens DK, Alerding AB, Crosby KC, Bandara AB, Westwood JH and Winkel BS 2008 Functional analysis of a predicted flavonol synthase gene family in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 147 1046–1061
Park CR 2000 Breeding progress with yellow camellia (American Camellia Yearbook)
Peer WA and Murphy AS 2007 Flavonoids and auxin transport: modulators or regulators? Trends Plant Sci. 12 556–563
Pollak PE, Vogt T, Mo Y and Taylor LP 1993 Chalcone synthase and flavonol accumulation in stigmas and anthers of Petunia hybrida. Plant Physiol. 102 925–932
Preuss A, Stracke R, Weisshaar B, Hillebrecht A, Matern U and Martens S 2009 Arabidopsis thaliana expresses a second functional flavonol synthase. FEBS Lett. 583 1981–1986
Proost S, Van Bel M, Sterck L, Billiau K, Van Parys T, Van de Peer Y and Vandepoele K 2009 PLAZA: a comparative genomics resource to study gene and genome evolution in plants. Plant Cell 21 3718–3731
Scogin R 1986 Floral pigments of the yellow Camellia, Camellia chrysantha (Theaceae). Aliso 11 387–392
Shinichi N, Fumio H, Keiichi S and Yusuke S 2004 Petal coloration of interspecific hybrids between Camellia chrysantha X C. japonica. JJSHS 73 189–191
Stracke R, Ishihara H, Barsch GHA, Mehrtens F, Niehaus K and Weisshaar B 2007 Differential regulation of closely related R2R3-MYB transcription factors controls flavonol accumulation in different parts of the Arabidopsis thaliana seedling. Plant J. 50 660–677
Stracke R, Jahns O, Keck M, Tohge T, Niehaus K, Fernie AR and Weisshaar B 2010 Analysis of production of flavonol glycosides-dependent flavonol glycoside accumulation in Arabidopsis thaliana plants reveals MYB11-, MYB12-and MYB111-independent flavonol glycoside accumulation. New Phytol. 188 985–1000
Subramanian S, Stacey G and Yu O 2007 Distinct, crucial roles of flavonoids during legume nodulation. Trends Plant Sci. 12 282–285
Sun Y, Li H, Wang L and Dai S 2011 Rapid, effective method for anthocyanin analysis in tobacco corolla. Chin. Bull. Bot. 46 189–196
Takahashi R, Githiri SM, Hatayama K, Dubouzet EG, Shimada N, Aoki T, Ayabe S, Iwashina T, et al. 2007 A single-base deletion in soybean flavonol synthase gene is associated with magenta flower color. Plant Mol. Biol. 63 125–135
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M and Kumar S 2011 MEGA5 molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 28 2731–2739
Tanaka Y, Sasaki N and Ohmiya A 2008 Biosynthesis of plant pigments: anthocyanins, betalains and carotenoids. Plant J. 54 733–749
Taylor LP and Grotewold E 2005 Flavonoids as developmental regulators. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 8 317–323
Terahara N, Takeda Y, Nesumi A and Honda T 2001 Anthocyanins from red flower tea (Benibana-cha), Camellia sinensis. Phytochemistry 56 359–361
Treutter D 2005 Significance of flavonoids in plant resistance and enhancement of their biosynthesis. Plant Biol. 7 581–591
Tsuda S, Suzuki K, Xue H, Tanaka Y, Fukui Y, Fukuchi-Mizutani M, Katsumoto Y and Kusumi T 1999 Molecular breeding of flower color of Torenia hybrida. Curr. Plant Sci. Biot. 36 613–616
Van Bel M, Proost S, Wischnitzki E, Movahedi S, Scheerlinck C, Van de Peer Y and Vandepoele K 2012 Dissecting plant genomes with the PLAZA comparative genomics platform. Plant Physiol. 158 590–600
Vanderkrol AR, Lenting PE, Veenstra J, Vandermeer IM, Koes RE, Gerats AGM, Mol JNM and Stuitje AR 1988 An anti-sense chalcone synthase gene in transgenic plants inhibits flower pigmentation. Nature 333 866–869
Winkel-Shirley B 2001 Flavonoid biosynthesis. A colorful model for genetics, biochemistry, cell biology, and biotechnology. Plant Physiol. 126 485–493
Winkel BS 2004 Metabolic channeling in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 55 85–107
Zhai J, Liu J, Liu B, Li P, Meyers BC, et al. 2008 Small RNA-directed epigenetic natural variation in Arabidopsis thaliana. PLoS Genet. 4 e1000056
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the funds from Key Projects in the National Science & Technology Pillar Program during the Twelfth Five-Year Plan Period (NO.2012BAD01B0703). We also acknowledge International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2011DFA30490), Breeding New Flower Varieties Program of Zhejiang Province (2012C12909-6), the CAF Nonprofit Research Projects (RISF6141), and National Science Foundation of Guangxi Region (2012GXNSFBA053077). We greatly appreciate the two anonymous reviewers for their critical reading and helpful comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Corresponding editor: UTPAL NATH
[Zhou X-W, Fan Z-Q, Chen Y, Zhu Y-L, Li J-Y and Yin H-F 2013 Functional analyses of a flavonol synthase–like gene from Camellia nitidissima reveal its roles in flavonoid metabolism during floral pigmentation. J. Biosci. 38 1–12] DOI 10.1007/s12038-013-9339-2
Supplementary materials pertaining to this article are available on the Journal of Biosciences Website at http://www.ias.ac.in/jbiosci/sep2013/supp/Zhou.pdf
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Esm 1
(PDF 82.6 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, XW., Fan, ZQ., Chen, Y. et al. Functional analyses of a flavonol synthase–like gene from Camellia nitidissima reveal its roles in flavonoid metabolism during floral pigmentation. J Biosci 38, 593–604 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9339-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-013-9339-2