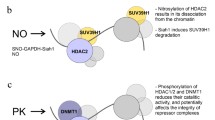
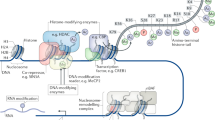
Abstract
Learning involves a usually adaptive response to an input (an external stimulus or the organism℉s own behaviour) in which the input-response relation is memorized; some physical traces of the relation persist and can later be the basis of a more effective response. Using toy models we show that this characterization applies not only to the paradigmatic case of neural learning, but also to cellular responses that are based on epigenetic mechanisms of cell memory. The models suggest that the research agenda of epigenetics needs to be expanded.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson C I, Garrido D J, Lawson A L, Browne B L and Thomas D G 2002 Bioelectrical potentials of Philodendron cordatum: a new method for investigation of behavior in plants; Psychol. Rep. 9 173–185
Agrawal A A, Laforsch C and Tollrian R 1999 Transgenerational induction of defences in animals and plants; Nature (London) 401 60–63
Allen N D, Norris M L and Surani M A 1990 Epigenetic control of transgene expression and imprinting by genotype-specific modifiers; Cell 61 853–861
Allis C D, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D and Caparros M-L 2007 Epigenetics (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press)
Anway M D, Cupp A S, Uzumcu M and Skinner M K 2005 Epigenetic transgenerational actions of endocrine disruptors and mate fertility; Science 308 1466–1469
Anway M D, Memon M A, Uzumcu M and Skinner M K 2006 Transgenerational effect of the endocrine disruptor vinclozolin on male spermatogenesis; J. Androl. 27 868–879
Applewhite P B 1975 Learning in bacteria, fungi and plants; in Invertebrate learning Vol 3: Cephalopods and echinoderms (eds) W C Corning, J A Dyal and A O D Willows (New York: Plenum Press) pp 179–186
Armus H L, Montgomery A R and Jellison J L 2006 Discrimination learning in paramecia (P. caudatum); Psychol. Rec. 56 489–498
Balaban N Q, Merrin J, Chait R, Kowalik L and Leibler S 2004 Bacterial persistence as a phenotypic switch; Science 305 1622–1625
Bernstein E and Allis C D 2005 RNA meets chromatin; Genes Dev. 19 1635–1655
Cavalier-Smith T 2004 The membranome and membrane heredity in development and evolution; in Organelles, genomes and eukaryote phylogeny (eds) R P Hirt and D S Horner (Boca Raton, Fl: CRC Press) pp 335–351
Csaba G 2008 Hormonal imprinting: phylogeny, ontogeny, diseases and possible role in present-day human evolution; Cell Biochem. Funct. 26 1–10
Csaba G and Kovacs P 1990 Impact of 5-azacytidine on insulin binding and insulin-induced receptor formation in Tetrahymena; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168 709–713
Csaba G and Kovacs P 1995 Insulin treatment (hormonal imprinting) increases the insulin production of the unicellular Tetrahymena long term. Is there a simultaneous formation of hormone receptor and hormone?; Cell. Biol. Int. 19 1011–1014
Cubas P, Vincent C and Coen E 1999 An epigenetic mutation responsible for natural variation in floral symmetry; Nature (London) 401 157–161
Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez O I and Melton D A 2004 Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation; Nature (London) 429 41–46
Dyal J A and Corning W C 1973 Invertebrate learning and behavior taxonomies; in Invertebrate learning Vol 1: Protozoans through annelids (eds) W C Corning, J A Dyal and A O D Willows (New York: Plenum Press) pp 1–48
Eisenstein E M, Eisenstein D and Smith J C 2001 The evolutionary significance of habituation and sensitization across phylogeny: a behavioral homeostasis model; Integr. Physiol. Behav. Sci. 36 251–265
Ettinger L and Doljanski F 1992 On the generation of form by the continuous interactions between cells and their extracellular matrix; Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 67 459–489
Gilbert S F 2006 Developmental biology 8th edition (Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates)
Ginsburg S and Jablonka E 2007 The transition to experiencing: I. Limited learning and limited experiencing; Biol. Theory 2 218–230
Gluckman P and Hanson M 2005 The fetal matrix: Evolution, development and disease (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press)
Gluckman P D, Hanson M A and Beedle A S 2007 Non-genomic transgenerational inheritance of disease risk; BioEssays 29 145–154
Gräff J and Mansuy I M 2008 Epigenetic codes in cognition and behavior; Behav. Brain Res. 192 70–87
Grimes G W and Aufderheide K J 1991 Cellular aspects of pattern formation: the problem of assembly; Monogr. Dev. Biol. 22 1–94
Hawkins R D, Kandel E R and Bailey C H 2006 Molecular mechanisms of memory storage in Aplysia; Biol. Bull. 210 174–191
Heard E 2005 Delving into the diversity of facultative heterochromatin: the epigenetics of the inactive X chromosome; Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 15 482–489
Hinkle D J and Wood D C 1994 Is tube-escape learning by protozoa associative learning?; Behav. Neurosci. 108 94–99
Hoffer S M, Westerhoff H V, Hellingwerf K J, Postma P W and Tommassen J 2001 Autoamplification of a two-component regulatory system results in “learning” behavior; J. Bacteriol. 183 4914–4917
Holliday R 1994 Epigenetics: an overview; Dev. Genet. 15 453–457
Jablonka E and Lamb M J 1995 Epigenetic inheritance and evolution: The Lamarckian dimension (Oxford: Oxford University Press)
Jablonka E and Lamb M J 2005 Evolution in four dimensions: Genetic, epigenetic, behavioral, and symbolic variation in the history of life (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press)
Jablonka E and Lamb M J 2007a Précis of Evolution in Four Dimensions; Behav. Brain Sci. 30 353–365
Jablonka E and Lamb M J 2007b Bridging the gap: the developmental aspects of evolution; Behav. Brain Sci. 30 378–392
Jablonka E and Raz G 2008 Transgenerational epigenetic inheritance: prevalence, mechanisms, and implications for the study of heredity; Q. Rev. Biol. (in press)
Jollos V 1921 Experimentelle Protistenstudien 1. Untersuchungen über Varabilität und Vererbung bei Infusorien; Arch. Protistenkunde 43 1–222
Kirschner M W and Gerhardt J C 2005 The plausibility of life: Resolving Darwin’s dilemma (New Haven, CT: Yale University Press)
Kirk D L 1998 Volvox: Molecular-genetic origins of multicellularity and cellular differentiation (Cambridge, UK: Cambridge University Press)
Kohidai L, Csaba G and Laszlo V 1990 Persistence of receptor “memory” induced in Tetrahymena by insulin imprinting; Acta Microbiol. Hung. 37 269–275
Lachmann M and Jablonka E 1996 The inheritance of phenotypes: an adaptation to fluctuating environments. J. Theor. Biol. 181 1–9
Levenson J M and Sweatt J D 2005 Epigenetic mechanisms in memory formation; Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 6 108–118
Lewis K 2007 Persister cells, dormancy and infectious disease; Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 5 48–56
Matzke M A and Birchler J A 2005 RNAi-mediated pathways in the nucleus; Nat. Rev. Genet. 6 24–35
Meaney M J 2001 Maternal care, gene expression, and the transmission of individual differences in stress reactivity across generations; Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 24 1161–1192
Meyer E and Chalker D L 2007 Epigenetics of ciliates; in Epigenetics (eds) D C Allis, T Jenuwein, D Reinberg and M-L Caparros (New York: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press) pp 127–150
Miller C A and Sweatt D W 2007 Covalent modification of DNA regulates memory formation; Neuron 53 857–869
Mochizuki K and Gorovsky M A 2004 Small RNAs in genome rearrangement in Tetrahymena; Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 14 181–187
Morange M 2006 What history tells us VI. The transfer of behaviours by macromolecules; J. Biosci. 31 323–327
Nowacki M, Vijajan V, Zhou Y, Schotanus K, Doak T G and Landweber L F 2008 RNA-mediated epigenetic programming of a genome rearrangement pathway; Nature (London) 451 153–159
Rando O J and Verstrepen K J 2007 Timescales of genetic and epigenetic inheritance; Cell 128 655–668
Razran G 1971 Mind in evolution: an East-West synthesis of learned behavior and cognition (Boston: Houghton Mifflin)
Saigusa T, Tero A, Nakagaki T and Kuramoto Y 2008 Amoebae anticipate periodic events; Phys. Rev. Lett. 100 [018101]
Schacter D L 2001 Forgotten ideas, neglected pioneers (Philadelphia: Psychology Press)
Shorter J and Lindquist S 2005 Prions as adaptive conduits of memory and inheritance; Nat. Rev. Genet. 6 435–450
Si K, Lindquist S and Kandel E R 2003 A neuronal isoform of the Aplysia CPEB has prion-like properties; Cell 115 879–891
Sung S and Amasino R M 2004 Vernalization and epigenetics: how plants remember winter; Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 7 4–10
Tagkopoulos I, Liu Y-C and Tavazoie S 2008 Predictive behavior within microbial genetic networks; Science 320 1313–1317
Trewavas, A 2003. Aspects of plant intelligence. Ann. Bot. 92 1–20
Weaver I C G, Cervoni N, Champagne F A, D’Alessio A C, Sharma S, Seckl J R, Dymov S, Szyf M and Meaney M J 2004 Epigenetic programming by maternal behavior; Nat. Neurosci. 7 847–854
Weaver I C G, Champagne F A, Brown S E, Dymov S, Sharma S, Meaney M J and Szyf M 2005 Reversal of maternal programming of stress responses in adult offspring through methyl supplementation: altering epigenetic marking later in life; J. Neurosci. 25 11045–11054
Wickner R B, Edskes H K, Ross E D, Pierce M M, Baxa U, Brachmann A and Shewmaker F 2004 Prion genetics: new rules for a new kind of gene; Ann. Rev. Genet. 38 681–707
Wood D C 1988a Habituation in Stentor: a response-dependent process; J. Neurosci. 8 2248–2253
Wood D C 1988b Habituation in Stentor: produced by mechanoreceptor channel modification; J. Neurosci. 8 2254–2258
Wood D C 1992 Learning and adaptive plasticity in unicellular organisms; in Encyclopedia of learning and memory (ed.) L R Squire (New York: Macmillan) pp 623–624
Zacharioudakis I, Gligoris T and Tzamarias D 2007 A yeast catabolic enzyme controls transcriptional memory; Curr. Biol. 17 2041–2046
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ginsburg, S., Jablonka, E. Epigenetic learning in non-neural organisms. J Biosci 34, 633–646 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-009-0081-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-009-0081-8