Abstract
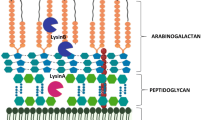
Bacteriophage induced lysis of host bacterial cell is mediated by a two component cell lysis cassette comprised of holin and lysozyme. Prophages are integrated forms of bacteriophages in bacterial genomes providing a repertoire for bacterial evolution. Analysis using the prophage database ( http://bicmku.in:8082 ) constructed by us showed 47 prophages were associated with putative two component cell lysis genes. These proteins cluster into four different subgroups. In this process, a putative holin (essd) and endolysin (ybcS), encoded by the defective lambdoid prophage DLP12 was found to be similar to two component cell lysis genes in functional bacteriophages like p21 and P1. The holin essd was found to have a characteristic dual start motif with two transmembrane regions and C-terminal charged residues as in class II holins. Expression of a fusion construct of essd in Escherichia coli showed slow growth. However, under appropriate conditions, this protein could be over expressed and purified for structure function studies. The second component of the cell lysis cassette, ybcS, was found to have an N-terminal SAR (Signal Arrest Release) transmembrane domain. The construct of ybcS has been over expressed in E. coli and the purified protein was functional, exhibiting lytic activity against E. coli and Salmonella typhi cell wall substrate. Such targeted sequence-structure-function characterization of proteins encoded by cryptic prophages will help understand the contribution of prophage proteins to bacterial evolution.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul S F and Koonin E V 1998 Iterated profile searches with PSI-BLAST-a tool for discovery in protein databases; TIBS 23 444–447
Atkins J F, Steitz J A, Anderson C W and Model P 1979 Binding of mammalian ribosomes to MS2 phage RNA reveals an overlapping gene encoding a lysis function; Cell 182 247–256
Baba T, Ara T, Hasegawa M, Yuki Takai Y, Yoshiko Okumura Y, Baba M, Datsenko K A, Tomita M, Wanner B L and Mori H 2006 Construction of Escherichia coli K-12 in-frame, single-gene knockout mutants the Keio collection; Mol. Syst. Biol. doi101038/
Barenboim M, Chang C Y, Dib H F and Young R 1999 Characterization of the dual start motif of a class II holin gene; Mol Microbiol. 32 715–727
Bernhardt T G, Roof W D and Young R 2000 Genetic evidence that the bacteriophage phi X174 lysis protein inhibits cell wall synthesis; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97 4297–4302
Blasi U and Young R 1996 Two beginnings for a single purpose the dual-start holins in the regulation of phage lysis; Mol Microbiol. 21 675–682
Bonovich M T and Young R 1991 Dual start motif in two Lambdoid genes unrelated to 1 S; J Bacteriol. 173 2897–2905
Boyd E F and Brussow H 2002 Common themes among bacteriophage-encoded virulence factors and diversity among the Bacteriophages involved; Trends Microbiol. 10 521–529
Brussow H, Canchaya C and Hardt W D 2004 Phages and the evolution of bacterial pathogens from genomic rearrangements to lysogenic conversion; Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 68 560–602
Casjens S 2003 Prophages and bacterial genomics what have we learned so far?; Mol Microbiol. 49 277–300
Chang C Y, Nam K and Young R 1995 S gene expression and the timing of lysis by bacteriophage lambda; J. Bacteriol. 177 3283–3294
Choi J H, Jung H Y, Kim HS and Cho HG 2000 PhyloDraw: a phylogenetic tree drawing system; Bioinformatics 16 1056–1058
Damman C J, Eggers C H, Samuels D S and Oliver D B 2000 Characterization of Borrelia burgdorferi BlyA and BlyB proteins a prophage-encoded holin-like system; J. Bacteriol. 182 6791–6797
Davis B M and Waldor M K 2000 Filamentous phages linked to virulence of Vibrio cholerae; Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 36 35–42
Deaton J Savva CG Sun J Holzenburg A Berry J and Young R 2004. Solubilization and delivery by GroEL of megadalton complexes of the lambda holing; Protein Sci. 13 1778–1786
Grundling A, Blasi U and Young R 2000a Genetic and biochemical analysis of dimer and oligomer interactions of the lambda S holin; J. Bacteriol. 182 6082–6090
Grundling A, Smith D L, Blasi U and Young R 2000b Dimerization between the holin and holin inhibitor of phage lambda; J. Bacteriol. 182 6075–6081
Grundling A, Manson M D and Young R 2001 Holins kill without warning; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98 9348–9352
Ito Y, Suzuk M and Husimi Y 1999 A Novel Mutant of Green Fluorescent Protein with Enhanced Sensitivity for Microanalysis at 488 nm Excitation; Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 264 556–560
Kitagawa M, Takeshi A, Arifuzzaman M, Ioka-Nakamichi T, Inamoto E, Toyonaga H and Mori H 2005 Complete set of ORF clones of Escherichia coli ASKA library A Complete Set of E coli K-12 ORF Archive Unique Resources for Biological Research; DNA Res. 12 291–299
Krogh S, Jorgensen S T and Devine K M 1998 Lysis genes of the Bacillus subtilis defective prophage PBSX; J. Bacteriol. 180 2110–2117
Lindsey D F, Mullin D A and Walker J R 1989 Characterization of the cryptic lambdoid prophage DLP12 of Escherichia coli and overlap of the DLP12 integrase gene with the tRNA gene argU; J. Bacteriol. 171 6197–205
Loessner M J 2005 Bacteriophage endolysins-current state of research and applications; Curr. Opin. Microbiol. 8 480–487
Low L Y, Yang C, Perego M, Osterman A and Liddington R C 2005 Structure and lytic activity of a Bacillus anthracis prophage endolysin; J. Biol. Chem. 280 35433–35439
Park T, Struck D K, Deaton J F and Young Ry 2006 Topological dynamics of holins in programmed bacterial lysis; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103 19713–19718
Perrière G and Gouy M 1996 WWW-Query: An on-line retrieval system for biological sequence banks. Biochimie 78 364–369
Raab R, Neal G, Sohaskey C, Smith J and Young R 1988 Dominance in lambda S mutations and evidence for translational control; J. Mol. Biol. 199 95–105
Rice P, Longden I and Bleasby A 2000 EMBOSS: The European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite; Trends Genet. 16 276–277
Sao-Jose C, Parreira R, Vieira G and Santos M A 2000 The N-terminal region of the Oenococcus oeni bacteriophage fOg44 lysin behaves as a bona fide signal peptide in Escherichia coli and as a cis-inhibitory element, preventing lytic activity on oenococcal cells; J. Bacteriol. 182 5823–5831
Smith D L, Struck D K Scholtz J M and Young R 1998a Purification and biochemical characterization of the lambda holin; J. Bacteriol. 180 2531–2540
Smith D L, Chang C Y and Young R 1998b The lambda holin accumulates beyond the lethal triggering concentration under hyperexpression conditions; Gene Expr. 7 39–52
Srividhya K V, Geeta V Rao, Raghavenderan L, Preeti Mehta, Jaime Pirulsky, Sankarnarayanan Manicka, Joel L. Sussman and S Krishnaswamy 2006, Database and Comparative Identification of prophages. LNCIS 344 863–868
Tan K S, We B Y and Song K P 2001 Evidence for holin function of tcdE gene in the pathogenicity of Clostridium difficile; J. Med. Microbiol. 50 613–619
Thompson J D, Gibson T J, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F and Higgins D G 1997 The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 244 876–4882
Vasala A, Valkkila M, Caldentey J and Alatossava T 1995 Genetic and biochemical characterization of the Lactobacillus subsp lactis bacteriophage LL-H lysin; Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61 4004–4011
Waldor M K 1998 Bacteriophage biology and bacterial virulence; Trends Microbiol. 6 295–297
Wang I N Smith D L and Young R 2000 Holins the protein clocks of bacteriophage infections; Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 54 799–825
Winter R B and Gold L 1983 Overproduction of bacteriophage Q3 maturation A, protein leads to cell lysis; Cell 33 877–885
Xu M, Struck D K, Deaton J, Wang N and Young R 2004 A signal-arrest-release sequence mediates export and control of the phage P1 endolysin; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci USA 101 6415–6420
Xu M, Arulandu A, Struck D K, Swanson S, Sacchettini J C and Young R 2005 Disulfide isomerization after membrane release of its SAR domain activates P1 lysozyme; Science 307 113–117
Young R 1992 Bacteriophage lysis mechanism and regulation; Microbiol. Rev. 56 430–481
Young R 2002 Bacteriophage holins deadly diversity; J. Mol. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 4 21–36
Young R, 2005 Phage lysis; in From phages-Their role in bacterial pathogenesis and biotechnology (eds) M K Waldor, D L Friedman and S L Adhya (Washington: ASM press) pp 92–127
Young R and Blasi U 1995 Holins form and function in bacteriophage lysis; FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 17 191–205
Young R, Wang I and Roof W D 2000 Phages will out strategies of host cell lysis; Trends Microbiol. 8 120–128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Srividhya, K.V., Krishnaswamy, S. Sub classification and targeted characterization of prophage-encoded two-component cell lysis cassette. J Biosci 32 (Suppl 1), 979–990 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0097-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-007-0097-x