Abstract
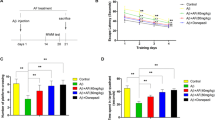
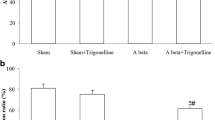
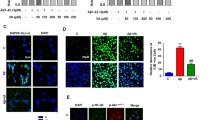
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a common cause of dementia that is clinically characterized by the loss of memory and cognitive functions. Currently, there is no specific cure for the management of AD, although natural compounds are showing promising therapeutic potentials because of their safety and easy availability. Herein, we evaluated the neuroprotective properties of kojic acid (KA) in an AD mouse model. Intracerebroventricular injection (i.c.v) of Aβ1-42 (5 μL/5 min/mouse) into wild-type adult mice induced AD-like pathological changes in the mouse hippocampus by increasing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, affecting memory and cognitive functions. Interestingly, oral treatment of kojic acid (50 mg/kg/mouse for 3 weeks) reversed the AD pathology by reducing the expression of amyloid-beta (Aβ) and beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme1 (BACE-1). Moreover, kojic acid reduced oxidative stress by enhancing the expression of nuclear factor erythroid-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and heme oxygenase 1 (HO1). Also, kojic acid reduced the lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species in the Aβ + kojic acid co-treated mice brains. Moreover, kojic acid decreased neuroinflammation by inhibiting Toll-like receptor 4, phosphorylated nuclear factor-κB, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin 1-beta (TLR-4, p-NFκB, TNFα, and IL-1β, respectively), and glial cells. Furthermore, kojic acid enhanced synaptic markers (SNAP-23, SYN, and PSD-95) and memory functions in AD model mice. Additionally, kojic acid treatment also decreased Aβ expression, oxidative stress, and neuroinflammation in vitro in HT-22 mouse hippocampal cells. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to show the neuroprotective effects of kojic acid against an AD mouse model. Our findings could serve as a favorable and alternative strategy for the discovery of novel drugs to treat AD-related neurodegenerative conditions.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors hereby declare that the generated datasets in this study will be presented upon request from the corresponding author.
References
Ali T, Rehman SU, Khan A, Badshah H, Abid NB, Kim MW, Jo MH, Chung SS, Lee HG, Rutten BPF, Kim MO (2021) Adiponectin-mimetic novel nonapeptide rescues aberrant neuronal metabolic-associated memory deficits in Alzheimers disease. Mol Neurodegener 16(1):23. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13024-021-00445-4
Hayashi Y, Lin HT, Lee CC, Tsai KJ (2020) Effects of neural stem cell transplantation in Alzheimer’s disease models. J Biomed Sci 27(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-020-0622-x
Andrews SJ, Fulton-Howard B, Goate A (2020) Interpretation of risk loci from genome-wide association studies of Alzheimer’s disease. The Lancet Neurology 19(4):326–335. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(19)30435-1
Brothers HM, Gosztyla ML, Robinson SR (2018) The physiological roles of amyloid-beta peptide hint at new ways to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 10:118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2018.00118
Padurariu M, Ciobica A, Mavroudis I, Fotiou D, Baloyannis S (2012) Hippocampal neuronal loss in the CA1 and CA3 areas of Alzheimer’s disease patients. Psychiatr Danub 24(2):152–158
Shah SA, Yoon GH, Chung SS, Abid MN, Kim TH, Lee HY, Kim MO (2017) Novel osmotin inhibits SREBP2 via the AdipoR1/AMPK/SIRT1 pathway to improve Alzheimer’s disease neuropathological deficits. Mol Psychiatry 22(3):407–416. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.23
Jeong S (2017) Molecular and cellular basis of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Cells 40(9):613–620. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2017.0096
Ali T, Yoon GH, Shah SA, Lee HY, Kim MO (2015) Osmotin attenuates amyloid beta-induced memory impairment, tau phosphorylation and neurodegeneration in the mouse hippocampus. Sci Rep 5:11708. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11708
Huang WJ, Zhang X, Chen WW (2016) Role of oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Rep 4(5):519–522. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2016.630
Nita M, Grzybowski A (2016) The Role of the Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress in the pathomechanism of the age-related ocular diseases and other pathologies of the anterior and posterior eye segments in adults. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2016:3164734. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3164734
Ikram M, Park TJ, Ali T, Kim MO (2020) Antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of caffeine against Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease: insight into the role of Nrf-2 and A2AR signaling. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(9). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9090902
Finkel T (2011) Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J Cell Biol 194(1):7–15. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201102095
Ma Q (2010) Transcriptional responses to oxidative stress: pathological and toxicological implications. Pharmacol Ther 125(3):376–393. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2009.11.004
Vomund S, Schafer A, Parnham MJ, Brune B, von Knethen A (2017) Nrf2, the master regulator of anti-oxidative responses. Int J Mol Sci 18(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122772
Muhammad T, Ali T, Ikram M, Khan A, Alam SI, Kim MO (2019) Melatonin Rescue oxidative stress-mediated neuroinflammation/ neurodegeneration and memory impairment in scopolamine-induced amnesia mice model. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 14(2):278–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-018-9824-3
Zhang R, Xu M, Wang Y, Xie F, Zhang G, Qin X (2017) Nrf2-a Promising Therapeutic Target for defensing against oxidative stress in stroke. Mol Neurobiol 54(8):6006–6017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0111-0
Blanken AE, Hurtz S, Zarow C, Biado K, Honarpisheh H, Somme J, Brook J, Tung S, Kraft E, Lo D, Ng DW, Vinters HV, Apostolova LG (2017) Associations between hippocampal morphometry and neuropathologic markers of Alzheimer’s disease using 7 T MRI. NeuroImage Clinical 15:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2017.04.020
Ola ARB, Metboki G, Lay CS, Sugi Y, Rozari P, Darmakusuma D, Hakim EH (2019) Single Production of kojic acid by aspergillus flavus and the revision of flufuran. Molecules 24(22). https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules24224200
Song L, Xie W, Zhao Y, Lv X, Yang H, Zeng Q, Zheng Z, Yang X (2019) Synthesis, antimicrobial, moisture absorption and retention activities of kojic acid-grafted konjac glucomannan oligosaccharides. Polymers 11(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11121979
Khan A, Ikram M, Hahm JR, Kim MO (2020) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of citrus flavonoid hesperetin: special focus on neurological disorders. Antioxidants (Basel) 9(7). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox9070609
Rodrigues AP, Farias LH, Carvalho AS, Santos AS, do Nascimento JL, Silva EO (2014) A novel function for kojic acid, a secondary metabolite from Aspergillus fungi, as antileishmanial agent. PLoS ONE 9(3):e91259. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0091259
Desai S, Ayres E, Bak H, Manco M, Lynch S, Raab S, Du A, Green D, Skobowiat C, Wangari-Talbot J, Zheng Q (2019) Effect of a tranexamic acid, kojic acid, and niacinamide containing serum on facial dyschromia: a clinical evaluation. J Drugs Dermatol 18(5):454–459
Wei Y, Zhang C, Zhao P, Yang X, Wang K (2011) A new salicylic acid-derivatized kojic acid vanadyl complex: synthesis, characterization and anti-diabetic therapeutic potential. J Inorg Biochem 105(8):1081–1085. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.05.008
Saeedi M, Eslamifar M, Khezri K (2019) Kojic acid applications in cosmetic and pharmaceutical preparations. Biomed Pharmacother 110:582–593. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.12.006
Moon KY, Ahn KS, Lee J, Kim YS (2001) Kojic acid, a potential inhibitor of NF-kappaB activation in transfectant human HaCaT and SCC-13 cells. Arch Pharmacal Res 24(4):307–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975097
Lee M, Rho HS, Choi K (2019) Anti-inflammatory effects of a P-coumaric acid and kojic acid derivative in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophage cells. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 24(4):653–657. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-018-0492-1
Gasparovic AC, Jaganjac M, Mihaljevic B, Sunjic SB, Zarkovic N (2013) Assays for the measurement of lipid peroxidation. Methods Mol Biol 965:283–296. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-239-1_19
Khan MS, Khan A, Ahmad S, Ahmad R, Rehman IUR, Ikram M, Kim MO (2020) Inhibition of JNK alleviates chronic hypoperfusion-related ischemia induces oxidative stress and brain degeneration via Nrf2/HO-1 and NF-kappaB signaling. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:5291852. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/5291852
Ahmad A, Ali T, Kim MW, Khan A, Jo MH, Rehman SU, Khan MS, Abid NB, Khan M, Ullah R, Jo MG, Kim MO (2019) Adiponectin homolog novel osmotin protects obesity/diabetes-induced NAFLD by upregulating AdipoRs/PPARalpha signaling in ob/ob and db/db transgenic mouse models. Metabolism 90:31–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.metabol.2018.10.004
Lawrence T (2009) The nuclear factor NF-kappaB pathway in inflammation. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 1(6):a001651. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001651
Kim HY, Lee DK, Chung BR, Kim HV, Kim Y (2016) Intracerebroventricular injection of amyloid-beta peptides in normal mice to acutely induce Alzheimer-like cognitive deficits. J Vis Exp (109). https://doi.org/10.3791/53308
Ikram M, Muhammad T, Rehman SU, Khan A, Jo MG, Ali T, Kim MO (2019) Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling in an abeta mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 56(9):6293–6309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1512-7
Yan R, Vassar R (2014) Targeting the beta secretase BACE1 for Alzheimer’s disease therapy. Lancet Neurol 13(3):319–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70276-X
Vassar R (2014) BACE1 inhibitor drugs in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 6(9):89. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13195-014-0089-7
Goncalez ML, Marcussi DG, Calixto GM, Correa MA, Chorilli M (2015) Structural characterization and in vitro antioxidant activity of kojic dipalmitate loaded w/o/w multiple emulsions intended for skin disorders. Biomed Res Int 2015:304591. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/304591
Gomes AJ, Lunardi CN, Gonzalez S, Tedesco AC (2001) The antioxidant action of polypodium leucotomos extract and kojic acid: reactions with reactive oxygen species. Braz J Med Biol Res 34(11):1487–1494. https://doi.org/10.1590/s0100-879x2001001100018
Lajis AF, Hamid M, Ariff AB (2012) Depigmenting effect of kojic acid esters in hyperpigmented B16F1 melanoma cells. J Biomed Biotechnol 2012:952452. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/952452
Khan A, Ikram M, Muhammad T, Park J, Kim MO (2019) Caffeine modulates cadmium-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and cognitive impairments by regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 in vivo and in vitro. J Clin Med 8(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm8050680
Ahmad S, Khan A, Ali W, Jo MH, Park J, Ikram M, Kim MO (2021) Fisetin rescues the mice brains against D-galactose-induced oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and memory impairment. Front Pharmacol 12:612078. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2021.612078
Chuang KA, Li MH, Lin NH, Chang CH, Lu IH, Pan IH, Takahashi T, Perng MD, Wen SF (2017) Rhinacanthin C alleviates amyloid-beta fibrils’ toxicity on neurons and attenuates neuroinflammation triggered by LPS, amyloid-beta, and interferon-gamma in glial cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:5414297. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5414297
Nordengen K, Kirsebom BE, Henjum K, Selnes P, Gisladottir B, Wettergreen M, Torsetnes SB, Grontvedt GR, Waterloo KK, Aarsland D, Nilsson LNG, Fladby T (2019) Glial activation and inflammation along the Alzheimer’s disease continuum. J Neuroinflammation 16(1):46. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-019-1399-2
Khan A, Ali T, Rehman SU, Khan MS, Alam SI, Ikram M, Muhammad T, Saeed K, Badshah H, Kim MO (2018) Neuroprotective effect of quercetin against the detrimental effects of LPS in the adult mouse brain. Front Pharmacol 9:1383. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.01383
Mucke L, Selkoe DJ (2012) Neurotoxicity of amyloid beta-protein: synaptic and network dysfunction. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 2(7):a006338. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a006338
Chen Y, Wang B, Liu D, Li JJ, Xue Y, Sakata K, Zhu LQ, Heldt SA, Xu H, Liao FF (2014) Hsp90 chaperone inhibitor 17-AAG attenuates Abeta-induced synaptic toxicity and memory impairment. J Neurosci 34(7):2464–2470. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0151-13.2014
Ikram M, Ullah R, Khan A, Kim MO (2020) Ongoing research on the role of gintonin in the management of neurodegenerative disorders. Cells 9(6). https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9061464
Ikram M, Muhammad T, Rehman SU, Khan A, Jo MG, Ali T, Kim MO (2019) Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling in an abeta mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 56(9):6293–6309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1512-7
Badshah H, Ikram M, Ali W, Ahmad S, Hahm JR, Kim MO (2019) Caffeine may abrogate LPS-induced oxidative stress and neuroinflammation by regulating Nrf2/TLR4 in adult mouse brains. Biomolecules 9(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom9110719
Ikram M, Saeed K, Khan A, Muhammad T, Khan MS, Jo MG, Rehman SU, Kim MO (2019) Natural dietary supplementation of curcumin protects mice brains against ethanol-induced oxidative stress-mediated neurodegeneration and memory impairment via Nrf2/TLR4/RAGE signaling. Nutrients 11(5). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu11051082
Muhammad T, Ali T, Ikram M, Khan A, Alam SI, Kim MO (2019) Melatonin rescue oxidative stress-mediated neuroinflammation/neurodegeneration and memory impairment in scopolamine-induced amnesia mice model. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 14(2):278–294. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-018-9824-3
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16(25):2766–2778. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210793176572
Tonnies E, Trushina E (2017) Oxidative stress, synaptic dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 57(4):1105–1121. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-161088
Funding
This research was supported by the Neurological Disorder Research Program of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean Government (MSIT) (2020M3E5D9080660).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
A.K, T.J.P, I.K, S.A, R.A, and M.G. J designed and conducted the experiments, wrote the manuscript, and performed the statistical analysis. M.O.K. supplied all of the chemicals and supervised and approved the final version of the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval
All the experiments with animal and other experimental protocols and procedures were approved (Approval ID: 125) by the Ethics Review Committee of the Gyeongsang National University, Republic of Korea.
Consent for Publication
Not applicable.
Consent to Participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khan, A., Park, T.J., Ikram, M. et al. Antioxidative and Anti-inflammatory Effects of Kojic Acid in Aβ-Induced Mouse Model of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 58, 5127–5140 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02460-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02460-4