Abstract
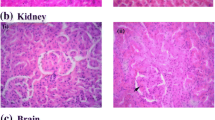
The roots of Achyranthes bidentata Blume (AB) is commonly used in the treatment of osteoporosis and dementia in traditional Chinese medicine. Pharmacological reports evidenced that AB possessed anti-osteoarthritis effects. However, there is little literature about the anti-dementia activities of AB. The present study was designed to prepare steroid-enriched fraction of AB (ABS) and investigate whether ABS can protect from cognitive dysfunction and neuroinflammation against Aβ 1–40-induced Alzheimer’s disease (AD) model in rats. ABS only contained 135.11 ± 4.28 mg of ecdysterone per gram. ABS (50 mg/kg) reversed the dysfunction of exploratory activity and memory function on plus-maze and Morris water maze caused by Aβ 1–40 in rats. ABS (50 mg/kg) also decreased amyloid deposition, neurofibrillary tangle, neural damage, activated astrocyte, and microglial caused by Aβ 1–40. Furthermore, ABS reversed the phenomenon of neural oxidative damage and neuroinflammation, including the higher levels of MDA and cytokines, and the lower activities of antioxidant enzymes and GSH levels caused by Aβ 1–40 in rat cortex and hippocampus. Finally, ABS restored the activation of ERK pathway and decreased NF-κB phosphorylation and translocation altered by Aβ 1–40. ABS alone (50 mg/kg) promoted cognitive function, activated brain antioxidant defense system, and decreased brain TNF-α levels in sham group. Therefore, ABS has the cognition-promoting and antidementia potential. Steroids especial ecdysterone are major active components of AB. The action mechanism is due to decreasing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation through modulating ERK pathway, NF-κB phosphorylation, and translocation in Aβ 1–40-induced AD rat model.














Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
amyloid β peptide
- AB:
-
Achyranthes bidentata
- ABS:
-
steroid-enriched fraction of Achyranthes bidentata
- AChE:
-
acetylcholinesterase
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- DTNB:
-
5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid)
- ERK:
-
extracellular signal–regulated kinase
- GADPH:
-
glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- GFAP:
-
glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GPx:
-
glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- IBA-1:
-
ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1
- IL-1β:
-
interleukin-1β
- IL-6:
-
interleukin-6
- JNK:
-
c-Jun N-terminal kinase
- MAPKs:
-
mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- NADPH:
-
nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NF-κB:
-
nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells
- NFT:
-
neurofibrillary tangle
- p-ERK:
-
phospho-ERK
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- p-JNK:
-
phospho-JNK
- p-p38:
-
phospho-p38
- p-p65:
-
phospho-p65
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- TBA:
-
thiobarbituric acid
- TBARS:
-
thiobarbituric acid reactive substances
- TNF-α:
-
tumor necrosis factor alpha.
References
Karran E, De Strooper B (2016) The amyloid cascade hypothesis: are we poised for success or failure? J Neurochem 139(Suppl 2):237–252
Karran E, Mercken M, De Strooper B (2011) The amyloid cascade hypothesis for Alzheimer’s disease: an appraisal for the development of therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 10(9):698–712
Serrano-Pozo A, Frosch MP, Masliah E, Hyman BT (2011) Neuropathological alterations in Alzheimer disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 1(1):a006189
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 362(4):329–344
Mhillaj E, Morgese MG, Tucci P, Furiano A, Luongo L, Bove M, Maione S, Cuomo V et al (2018) Celecoxib prevents cognitive impairment and neuroinflammation in soluble amyloid beta-treated rats. Neuroscience 372:58–73
Zhang Y, Chen C, Jiang Y, Wang S, Wu X, Wang K (2017) PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha (PGC-1alpha) protects neuroblastoma cells against amyloid-beta (Abeta) induced cell death and neuroinflammation via NF-kappaB pathway. BMC Neurosci 18(1):69
Budni J, Feijo DP, Batista-Silva H, Garcez ML, Mina F, Belletini-Santos T, Krasilchik LR, Luz AP et al (2017) Lithium and memantine improve spatial memory impairment and neuroinflammation induced by beta-amyloid 1-42 oligomers in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 141:84–92
Zhang X, He X, Chen Q, Lu J, Rapposelli S, Pi R (2018) A review on the hybrids of hydroxycinnamic acid as multi-target-directed ligands against Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg Med Chem 26(3):543–550
Seo EJ, Fischer N, Efferth T (2017) Phytochemicals as inhibitors of NF-kappaB for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacol Res
Lee JK, Kim NJ (2017) Recent advances in the inhibition of p38 MAPK as a potential strategy for the treatment of Alzheimer's disease. Molecules 22(8)
He X, Wang X, Fang J, Chang Y, Ning N, Guo H, Huang L, Huang X (2017) The genus Achyranthes: A review on traditional uses, phytochemistry, and pharmacological activities. J Ethnopharmacol 203:260–278
Zhang S, Zhang Q, Zhang D, Wang C, Yan C (2018) Anti-osteoporosis activity of a novel Achyranthes bidentata polysaccharide via stimulating bone formation. Carbohydr Polym 184:288–298
He G, Guo W, Lou Z, Zhang H (2014) Achyranthes bidentata saponins promote osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells through the ERK MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys 70(1):467–473
Luo H, Gu F, Li X (2003) Inhibiting effect of ethanol extract from Achyranthes bidentata on a beta 42 aggregation. J Chin Med Mat 26(6):412–415
Peng S, Wang C, Ma J, Jiang K, Jiang Y, Gu X, Sun C (2018) Achyranthes bidentata polypeptide protects dopaminergic neurons from apoptosis in Parkinson's disease models both in vitro and in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 175(4):631–643
Pharmacopeia of People’s Republic of China (2015). China medical science press, Beijing
Chang YS (2018). Achyranthis bidentatae radix. In: Chen SC (ed) Taiwan Herbal Pharmacopeia. 3rd Edn. Ministry of health and welfare, Taipei, pp 73–74.
Yang SF, Yang ZQ, Zhou QX, Wu Q, Huang XN, Shi JS (2004) Effect of ecdysterone on the expression of c-fos in the brain of rats induced by microinjection beta-AP25-35 into the hippocampus. Acta Pharm Sin 39(4):241–244
Zhang MM, Zhao HQ, Zhou SD, Wang DJ, Wang X, Liu DC, Geng YL, Mu DJ (2015) Content determination of β-ecdysterone and oleanolic acid in Achyranthes bidentata Blume by HPLC and their fingerprints. ShanDong Sci 28(5):1–6
Tsai FS, Cheng HY, Hsieh MT, Wu CR, Lin YC, Peng WH (2010) The ameliorating effects of luteolin on beta-amyloid-induced impairment of water maze performance and passive avoidance in rats. Am J Chin Med 38(2):279–291
Shiao YJ, Su MH, Lin HC, Wu CR (2017) Echinacoside ameliorates the memory impairment and cholinergic deficit induced by amyloid beta peptides via the inhibition of amyloid deposition and toxicology. Food Funct 8(6):2283–2294
Da Cunha IC, Jose RF, Orlandi Pereira L, Pimenta JA, Oliveira de Souza IA, Reiser R, Moreno H Jr, Marino Neto J et al (2005) The role of nitric oxide in the emotional learning of rats in the plus-maze. Physiol Behav 84(3):351–358
Uchihara T (2007) Silver diagnosis in neuropathology: principles, practice and revised interpretation. Acta Neuropathol 113(5):483–499
Glowinski J, Iversen LL (1966) Regional studies of catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of [3H]norepinephrine, [3H]dopamine and [3H]dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem 13(8):655–669
Kuo HC, Chang HC, Lan WC, Tsai FH, Liao JC, Wu CR (2014) Protective effects of Drynaria fortunei against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced oxidative damage in B35 cells via the PI3K/AKT pathway. Food Funct 5(8):1956–1965
Pan Z, Niu Y, Liang Y, Zhang X, Dong M (2016) beta-Ecdysterone protects SH-SY5Y cells against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced apoptosis via mitochondria-dependent mechanism: involvement of p38(MAPK)-p53 signaling pathway. Neurotox Res 30(3):453–466
Zou Y, Wang R, Guo H, Dong M (2015) Phytoestrogen beta-ecdysterone protects PC12 cells against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in vitro: involvement of PI3K-Nrf2-regulated pathway. Toxicol Sci 147(1):28–38
Yang SF, Wu ZJ, Yang ZQ, Wu Q, Gong QH, Zhou QX, Shi JS (2005) Protective effect of ecdysterone on PC12 cells cytotoxicity induced by beta-amyloid25-35. Chin J Integr Med 11(4):293–296
Kumar K, Kumar A, Keegan RM, Deshmukh R (2018) Recent advances in the neurobiology and neuropharmacology of Alzheimer’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 98:297–307
Suh KS, Lee YS, Choi EM (2014) The protective effects of Achyranthes bidentata root extract on the antimycin A induced damage of osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Cytotechnology 66(6):925–935
Xu XX, Zhang XH, Diao Y, Huang YX (2017) Achyranthes bidentate saponins protect rat articular chondrocytes against interleukin-1beta-induced inflammation and apoptosis in vitro. Kaohsiung J Med Sci 33(2):62–68
Lu T, Mao C, Zhang L, Xu W (1997) The research on analgestic and anti-inflammatory action of different processed products of Achyranthes bidentata. J Chin Med Mat 20(10):507–509
Feng CY, Huang XR, Qi MX (2012) Effects of ecdysterone on the expression of NF-kappaB p65 in H2O2 induced oxidative damage of human lens epithelial cells. Chin J Integr Med 32(1):76–79
Zhang X, Xu X, Xu T, Qin S (2014) Beta-ecdysterone suppresses interleukin-1beta-induced apoptosis and inflammation in rat chondrocytes via inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Drug Dev Res 75(3):195–201
Faucher P, Mons N, Micheau J, Louis C, Beracochea DJ (2015) Hippocampal injections of oligomeric amyloid beta-peptide (1-42) induce selective working memory deficits and long-lasting alterations of ERK signaling pathway. Front Aging Neurosci 7:245
Fan CD, Li Y, Fu XT, Wu QJ, Hou YJ, Yang MF, Sun JY, Fu XY et al (2017) Reversal of beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity in PC12 cells by curcumin, the important role of ROS-mediated signaling and ERK pathway. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(2):211–222
Li J, Ding X, Zhang R, Jiang W, Sun X, Xia Z, Wang X, Wu E et al (2015) Harpagoside ameliorates the amyloid-beta-induced cognitive impairment in rats via up-regulating BDNF expression and MAPK/PI3K pathways. Neuroscience 303:103–114
Omanakuttan A, Bose C, Pandurangan N, Kumar GB, Banerji A, Nair BG (2016) Nitric oxide and ERK mediates regulation of cellular processes by Ecdysterone. Exp Cell Res 346(2):167–175
Liu H, Deng Y, Gao J, Liu Y, Li W, Shi J, Gong Q (2015) Sodium hydrosulfide attenuates beta-amyloid-induced cognitive deficits and neuroinflammation via modulation of MAPK/NF-kappaB pathway in rats. Curr Alzheimer Res 12(7):673–683
Kim TI, Lee YK, Park SG, Choi IS, Ban JO, Park HK, Nam SY, Yun YW et al (2009) l-Theanine, an amino acid in green tea, attenuates beta-amyloid-induced cognitive dysfunction and neurotoxicity: reduction in oxidative damage and inactivation of ERK/p38 kinase and NF-kappaB pathways. Free Radic Biol Med 47(11):1601–1610
Song YS, Park HJ, Kim SY, Lee SH, Yoo HS, Lee HS, Lee MK, Oh KW et al (2004) Protective role of Bcl-2 on beta-amyloid-induced cell death of differentiated PC12 cells: reduction of NF-kappaB and p38 MAP kinase activation. Neurosci Res 49(1):69–80
Gawande DY, Goel RK (2015) Pharmacological validation of in-silico guided novel nootropic potential of Achyranthes aspera L. J Ethnopharmacol 175:324–334
Li M (2015) Achyranthes bidentata Bl. In: Liu Y, Wang Z, Zhang J (ed) Dietary Chinese herbs chemistry. Pharmacol Clin Evid. 1st edn. Springer, Vienna, 45–52.
Funding
Financial support is from the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (NSC 100-2320-B-214 -001, MOST104-2320-B-039-027-MY2, and MOST105-2622-B-039-003-CC2) and ISU-103-01-E-02.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of I-Shou University approved the experimental protocol (IACUC-ISU-9905), and the animals were cared according to the Guiding Principles for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, LW., Tsai, FH., Lan, WC. et al. Steroid-Enriched Fraction of Achyranthes bidentata Protects Amyloid β Peptide 1–40-Induced Cognitive Dysfunction and Neuroinflammation in Rats. Mol Neurobiol 56, 5671–5688 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1436-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-1436-7