Abstract
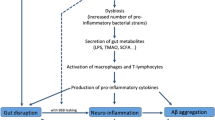
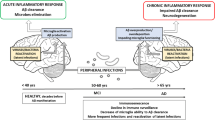
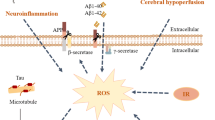
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that develops insidiously and causes dementia finally. There are also clinical complications in advanced dementia, such as eating problems, infections, which will lead to the decline of patients’ life quality, and the rising cost of care for AD to our society. AD will be important public health challenge. Early detection of AD may be a key issue to prevent, delay, and stop the disease. Gut microbiome and neuroinflammation are closely related with nervous system diseases, although the specific mechanism is not clear. This review introduces the relationship between neuroinflammation, gut microbiome, and AD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Honig LS, Vellas B, Woodward M, Boada M, Bullock R, Borrie M, Hager K, Andreasen N et al (2018) Trial of solanezumab for mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 378(4):321–330
Mitchell SL (2015) CLINICAL PRACTICE. Advanced dementia. N Engl J Med 372(26):2533–2540
Association A (2015) 2015 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 11(3):332–384
Association A (2016) 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 12(4):459–509
Selkoe DJ, Hardy J (2016) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer’s disease at 25 years. EMBO Mol Med 8(6):595–608
Zhang B, Gaiteri C, Bodea LG, Wang Z, McElwee J, Podtelezhnikov AA, Zhang C, Xie T et al (2013) Integrated systems approach identifies genetic nodes and networks in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Cell 153(3):707–720
Trovato Salinaro A, Pennisi M, Di Paola R, Scuto M, Crupi R, Cambria MT, Ontario ML, Tomasello M et al (2018) Neuroinflammation and neurohormesis in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and Alzheimer-linked pathologies: modulation by nutritional mushrooms. Immun Ageing 15:8
Varley J, Brooks DJ, Edison P (2015) Imaging neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias: recent advances and future directions. Alzheimers Dement 11(9):1110–1120
Wang C, Wang Q, Lou Y, Xu J, Feng Z, Chen Y, Tang Q, Zheng G et al (2018) Salidroside attenuates neuroinflammation and improves functional recovery after spinal cord injury through microglia polarization regulation. J Cell Mol Med 22(2):1148–1166
Mantovani A, Sozzani S, Locati M, Allavena P, Sica A (2002) Macrophage polarization: tumor-associated macrophages as a paradigm for polarized M2 mononuclear phagocytes. Trends Immunol 23(11):549–555
Koenigsknecht-Talboo J, Landreth GE (2005) Microglial phagocytosis induced by fibrillar beta-amyloid and IgGs are differentially regulated by proinflammatory cytokines. J Neurosci 25(36):8240–8249
Zelcer N, Khanlou N, Clare R, Jiang Q, Reed-Geaghan EG, Landreth GE, Vinters HV, Tontonoz P (2007) Attenuation of neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease pathology by liver x receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(25):10601–10606
Minter MR, Taylor JM, Crack PJ (2016) The contribution of neuro-inflammation to amyloid toxicity in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurochem 136(3):457–474
Heneka MT, Carson MJ, El Khoury J, Landreth GE, Brosseron F, Feinstein DL, Jacobs AH, Wyss-Coray T et al (2015) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 14(4):388–405
Lee CY, Landreth GE (2010) The role of microglia in amyloid clearance from the AD brain. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 117(8):949–960
Swanson A, Wolf T, Sitzmann A (2018) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease: pleiotropic roles for cytokines and neuronal pentraxins. Behav Brain Res S0166-4328(17):31862–31864
Bhaskar K, Maphis N, Xu G, Varvel NH, Kokiko-Cochran ON, Weick JP, Staugaitis SM, Cardona A et al (2014) Microglial derived tumor necrosis factor-alpha drives Alzheimer’s disease-related neuronal cell cycle events. Neurobiol Dis 62:273–285
Mawuenyega KG, Sigurdson W, Ovod V, Munsell L, Kasten T, Morris JC, Yarasheski KE, Bateman RJ (2010) Decreased clearance of CNS beta-amyloid in Alzheimer’s disease. Science 330(6012):1774
Hickman SE, Allison EK, El Khoury J (2008) Microglial dysfunction and defective beta-amyloid clearance pathways in aging Alzheimer’s disease mice. J Neurosci 28(33):8354–8360
Clarke LE, Liddelow SA, Chakraborty C, Münch AE, Heiman M, Barres BA (2018) Normal aging induces A1-like astrocyte reactivity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115(8):E1896–E1905
Sofroniew MV, Vinters HV (2010) Astrocytes: biology and pathology. Acta Neuropathol 119(1):7–35
Rodriguez JJ, Yeh CY, Terzieva S, Olabarria M, Kulijewicz-Nawrot M, Verkhratsky A (2014) Complex and region-specific changes in astroglial markers in the aging brain. Neurobiol Aging 35(1):15–23
Walsh DM, Selkoe DJ (2004) Deciphering the molecular basis of memory failure in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 44(1):181–193
Simpson JE, Ince PG, Lace G, Forster G, Shaw PJ, Matthews F, Savva G, Brayne C et al (2010) Astrocyte phenotype in relation to Alzheimer-type pathology in the ageing brain. Neurobiol Aging 31(4):578–590
Perez-Nievas BG, Stein TD, Tai HC, Dols-Icardo O, Scotton TC, Barroeta-Espar I, Fernandez-Carballo L, de Munain EL et al (2013) Dissecting phenotypic traits linked to human resilience to Alzheimer's pathology. Brain 136(8):2510–2526
Schwab C, Klegeris A, McGeer PL (2010) Inflammation in transgenic mouse models of neurodegenerative disorders. Biochim Biophys Acta 1802(10):889–902
Batarseh YS, Duong QV, Mousa YM, Al Rihani SB, Elfakhri K, Kaddoumi A (2016) Amyloid-β and astrocytes interplay in amyloid-β related disorders. Int J Mol Sci 17(3):338
Li C, Zhao R, Gao K, Wei Z, Yin MY, Lau LT, Chui D, Yu AC (2011) Astrocytes: Implications for neuroinflammatory pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Alzheimer Res 8(1):67–80
Savchenko VL, McKanna JA, Nikonenko IR, Skibo GG (2000) Microglia and astrocytes in the adult rat brain: comparative immunocytochemical analysis demonstrates the efficacy of lipocortin 1 immunoreactivity. Neuroscience 96(1):195–203
Zou C, Shi Y, Ohli J, Schuller U, Dorostkar MM, Herms J (2016) Neuroinflammation impairs adaptive structural plasticity of dendritic spines in a preclinical model of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 131(2):235–246
González-Reyes RE, Nava-Mesa MO, Vargas-Sánchez K, Ariza-Salamanca D, Mora-Muñoz L (2017) Involvement of astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease from a neuroinflammatory and oxidative stress perspective. Front Mol Neurosci 10:427
Kitazawa M, Oddo S, Yamasaki TR, Green KN, LaFerla FM (2005) Lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation exacerbates tau pathology by a cyclin-dependent kinase 5-mediated pathway in a transgenic model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci 25(39):8843–8853
Saha RN, Pahan K (2006) Signals for the induction of nitric oxide synthase in astrocytes. Neurochem Int 49(2):154–163
Edison P, Archer HA, Gerhard A, Hinz R, Pavese N, Turkheimer FE, Hammers A, Tai YF et al (2008) Microglia, amyloid, and cognition in Alzheimer’s disease: an [11C](R)PK11195-PET and [11C]PIB-PET study. Neurobiol Dis 32(3):412–419
Carter SF, Schöll M, Almkvist O, Wall A, Engler H, Långström B, Nordberg A (2012) Evidence for astrocytosis in prodromal Alzheimer disease provided by 11C-deuterium-L-deprenyl: a multitracer PET paradigm combining 11C-Pittsburgh compound B and 18F-FDG. J Nucl Med 53(1):37–46
Esposito G, Giovacchini G, Liow JS, Bhattacharjee AK, Greenstein D, Schapiro M, Hallett M, Herscovitch P et al (2008) Imaging neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease with radiolabeled arachidonic acid and PET. J Nucl Med 49(9):1414–1421
Minett T, Classey J, Matthews FE, Fahrenhold M, Taga M, Brayne C, Ince PG, Nicoll JA et al (2016) Microglial immunophenotype in dementia with Alzheimer’s pathology. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):1–10
Ching AS, Kuhnast B, Damont A, Roeda D, Tavitian B, Dolle F (2012) Current paradigm of the 18-kDa translocator protein (TSPO) as a molecular target for PET imaging in neuroinflammation and neurodegenerative diseases. Insights Imaging 3(1):111–119
Jacobs AH, Tavitian B (2012) Noninvasive molecular imaging of neuroinflammation. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 32(7):1393–1415
Wiley CA, Lopresti BJ, Venneti S, Price J, Klunk WE, DeKosky ST, Mathis CA (2009) Carbon 11-labeled Pittsburgh compound B and carbon 11-labeled (R)-PK11195 positron emission tomographic imaging in Alzheimer disease. Arch Neurol 66(1):60–67
Hamelin L, Lagarde J, Dorothée G, Leroy C, Labit M, Comley RA, de Souza LC, Corne H et al (2016) Early and protective microglial activation in Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective study using 18F-DPA-714 PET imaging. Brain 139(Pt 4):1252–1264
Imbimbo BP, Solfrizzi V, Panza F (2010) Are NSAIDs useful to treat Alzheimer’s disease or mild cognitive impairment? Front Aging Neurosci 2:19
Stewart WF, Kawas C, Corrada M, Metter EJ (1997) Risk of Alzheimer’s disease and duration of NSAID use. Neurology 48(3):626–632
McGeer PL, Rogers J, McGeer EG (2016) Inflammation, antiinflammatory agents, and Alzheimer’s disease: the last 22 years. J Alzheimers Dis 54(3):853–857
Zandi PP, Anthony JC, Hayden KM, Mehta K, Mayer L, Breitner JC (2002) Reduced incidence of AD with NSAID but not H2 receptor antagonists: the Cache County study. Neurology 59(6):880–886
Yip AG, Green RC, Huyck M, Cupples LA, Farrer LA (2005) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and Alzheimer’s disease risk: the MIRAGE study. BMC Geriatr 5:2
Szekely CA, Green RC, Breitner JC, Østbye T, Beiser AS, Corrada MM, Dodge HH, Ganguli M et al (2008) No advantage of A beta 42-lowering NSAIDs for prevention of Alzheimer dementia in six pooled cohort studies. Neurology 70(24):2291–2298
Szekely CA, Thorne JE, Zandi PP, Ek M, Messias E, Breitner JC, Goodman SN (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for the prevention of Alzheimer's disease: a systematic review. Neuroepidemiology 23(4):159–169
Szekely CA, Breitner JC, Fitzpatrick AL, Rea TD, Psaty BM, Kuller LH, Zandi PP (2008) NSAID use and dementia risk in the Cardiovascular Health Study: role of APOE and NSAID type. Neurology 70(1):17–24
Fu AK, Hung KW, Yuen MY, Zhou X, Mak DS, Chan IC, Cheung TH, Zhang B et al (2016) IL-33 ameliorates Alzheimer’s disease-like pathology and cognitive decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(19):E2705–E2713
Hill JM, Bhattacharjee S, Pogue AI, Lukiw WJ (2014) The gastrointestinal tract microbiome and potential link to Alzheimer’s disease. Front Neurol 5:43
Kim BS, Jeon YS, Chun J (2013) Current status and future promise of the human microbiome. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr 16(2):71–79
Wang HX, Wang YP (2016) Gut microbiota-brain axis. Chin Med J 129(19):2373–2380
Jenkins TA, Nguyen JC, Polglaze KE, Bertrand PP (2016) Influence of tryptophan and serotonin on mood and cognition with a possible role of the gut-brain Axis. Nutrients 8(1)
Schmidt C (2015) Mental health: thinking from the gut. Nature 518(7540):S12–S15
Smith PA (2015) The tantalizing links between gut microbes and the brain. Nature 526(75573):312–314
Mayer EA, Knight R, Mazmanian SK, Cryan JF (2014) Gut microbes and the brain: paradigm shift in neuroscience. J Neurosci 34(46):15490–15496
Pinto-Sanchez MI, Hall GB, Ghajar K, Nardelli A, Bolino C, Lau JT, Martin FP, Cominetti O et al (2017) Probiotic Bifidobacterium longum NCC3001 reduces depression scores and alters brain activity: A pilot study in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology 153(2):448–459
Tillisch K, Mayer E, Gupta A, Gill Z, Brazeilles R, Le Nevé B, van Hylckama Vlieg JET, Guyonnet D et al (2017) Brain structure and response to emotional stimuli as related to gut microbial profiles in healthy women. Psychosom Med 79(8):905–913
Sharon G, Sampson TR, Geschwind DH, Mazmanian SK (2016) The central nervous system and the gut microbiome. Cell 167(4):915–932
Ogbonnaya ES, Clarke G, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF, O'Leary OF (2015) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis is regulated by the microbiome. Biol Psychiatry 78(4):e7–e9
Luczynski P, Whelan SO, O'Sullivan C, Clarke G, Shanahan F, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2016) Adult microbiota-deficient mice have distinct dendritic morphological changes: differential effects in the amygdala and hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 44(9):2654–2666
Erny D, Hrabě de Angelis AL, Jaitin D, Wieghofer P, Staszewski O, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mahlakoiv T et al (2015) Host microbiota constantly control maturation and function of microglia in the CNS. Nat Neurosci 18(7):965–977
Matcovitch-Natan O, Winter DR, Giladi A, Vargas Aguilar S, Spinrad A, Sarrazin S, Ben-Yehuda H, David E et al (2016) Microglia development follows a stepwise program to regulate brain homeostasis. Science 353(6301):aad8670
Braniste V, Al-Asmakh M, Kowal C, Anuar F, Abbaspour A, Tóth M, Korecka A, Bakocevic N et al (2014) The gut microbiota influences blood-brain barrier permeability in mice. Sci Transl Med 6(263):263ra158
O'Brien SM, Scott LV, Dinan TG (2004) Cytokines: abnormalities in major depression and implications for pharmacological treatment. Hum Psychopharmacol 19(6):397–403
Dinan TG, Borre YE, Cryan JF (2014) Genomics of schizophrenia: time to consider the gut microbiome? Mol Psychiatry 19(12):1252–1257
Nemani K, Hosseini Ghomi R, McCormick B, Fan X (2015) Schizophrenia and the gut-brain axis. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 56:155–160
Rogers GB, Keating DJ, Young RL, Wong ML, Licinio J, Wesselingh S (2016) From gut dysbiosis to altered brain function and mental illness: mechanisms and pathways. Mol Psychiatry 21(6):738–748
Neufeld KA, Foster JA (2009) Effects of gut microbiota on the brain: implications for psychiatry. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34(3):230–231
Grenham S, Clarke G, Cryan JF, Dinan TG (2011) Brain-gut-microbe communication in health and disease. Front Physiol 2:94
Mayer EA, Tillisch K (2011) The brain-gut axis in abdominal pain syndromes. Annu Rev Med 62(1):381–396
Gareau MG (2016) Cognitive function and the microbiome. Int Rev Neurobiol 131:227–246
Gareau MG, Wine E, Rodrigues DM, Cho JH, Whary MT, Philpott DJ, Macqueen G, Sherman PM (2011) Bacterial infection causes stress-induced memory dysfunction in mice. Gut 60(3):307–317
Savignac HM, Kiely B, Dinan TG, Cryan JF (2014) Bifidobacteria exert strain-specific effects on stress-related behavior and physiology in BALB/c mice. Neurogastroenterol Motil 26(11):1615–1627
Ohland CL, Kish L, Bell H, Thiesen A, Hotte N, Pankiv E, Madsen KL (2013) Effects of Lactobacillus helveticus on murine behavior are dependent on diet and genotype and correlate with alterations in the gut microbiome. Psychoneuroendocrinology 38(9):1738–1747
Tillisch K, Labus J, Kilpatrick L, Jiang Z, Stains J, Ebrat B, Guyonnet D, Legrain-Raspaud S et al (2013) Consumption of fermented milk product with probiotic modulates brain activity. Gastroenterology 144:1394–1401 1401.e1–4
Messaoudi M, Lalonde R, Violle N, Javelot H, Desor D, Nejdi A, Bisson JF, Rougeot C et al (2011) Assessment of psychotropic-like properties of a probiotic formulation (Lactobacillus helveticus R0052 and Bifidobacterium longum R0175) in rats and human subjects. Br J Nutr 105(5):755–764
Maheshwari P, Eslick GD (2015) Bacterial infection and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Alzheimers Dis 43(3):957–966
Agostini S, Clerici M, Mancuso R (2014) How plausible is a link between HSV-1 infection and Alzheimer’s disease? Expert Rev Anti-Infect Ther 12(3):275–278
Alonso R, Pisa D, Marina AI, Morato E, Rabano A, Carrasco L (2014) Fungal infection in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 41(1):301–311
Alonso R, Pisa D, Marina AI, Morato E, Rábano A, Rodal I, Carrasco L (2015) Evidence for fungal infection in cerebrospinal fluid and brain tissue from patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Int J Biol Sci 11(5):546–558
Harach T, Marungruang N, Duthilleul N, Cheatham V, Mc Coy KD, Frisoni G, Neher JJ, Fåk F et al (2017) Reduction of Abeta amyloid pathology in APPPS1 transgenic mice in the absence of gut microbiota. Sci Rep 7:41802
Cappellano G, Carecchio M, Fleetwood T, Magistrelli L, Cantello R, Dianzani U, Comi C (2013) Immunity and inflammation in neurodegenerative diseases. Am J Neurodegener Dis 2(2):89–107
Glass CK, Saijo K, Winner B, Marchetto MC, Gage FH (2010) Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 140(6):918–934
Koprich JB, Reske-Nielsen C, Mithal P, Isacson O (2008) Neuroinflammation mediated by IL-1beta increases susceptibility of dopamine neurons to degeneration in an animal model of Parkinson's disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:8
McCoy MK, Tansey MG (2008) TNF signaling inhibition in the CNS: implications for normal brain function and neurodegenerative disease. J Neuroinflammation 5:45
Zhao Y, Lukiw WJ (2015) Microbiome-generated amyloid and potential impact on amyloidogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). J Nat Sci 1(7)
Zhao Y, Dua P, Lukiw WJ (2015) Microbial sources of amyloid and relevance to amyloidogenesis and Alzheimer’s disease (AD). J Alzheimers Dis Parkinsonism 5(1):177
Köhler CA, Maes M, Slyepchenko A, Berk M, Solmi M, Lanctôt KL, Carvalho AF (2016) The gut-brain axis, including the microbiome, leaky gut and bacterial translocation: mechanisms and pathophysiological role in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 22(40):6152–6166
Lukiw WJ (2016) Bacteroides fragilis lipopolysaccharide and inflammatory signaling in Alzheimer’s disease. Front Microbiol 7:1544
Schwartz K, Boles BR (2013) Microbial amyloids—functions and interactions within the host. Curr Opin Microbiol 16(1):93–99
Hufnagel DA, Tukel C, Chapman MR (2013) Disease to dirt: the biology of microbial amyloids. PLoS Pathog 9(11):e1003740
Friedland RP (2015) Mechanisms of molecular mimicry involving the microbiota in neurodegeneration. J Alzheimers Dis 45(2):349–362
Chen SG, Stribinskis V, Rane MJ, Demuth DR, Gozal E, Roberts AM, Jagadapillai R, Liu R et al (2016) Exposure to the functional bacterial amyloid protein curli enhances alpha-synuclein aggregation in aged Fischer 344 rats and Caenorhabditis elegans. Sci Rep 6:34477
Acknowledgements
Supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant nos. 81322020 and 81230032 to L.J.Z.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, L., Zheng, L.J. & Zhang, L.J. Neuroinflammation, Gut Microbiome, and Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurobiol 55, 8243–8250 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0983-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-018-0983-2