Abstract
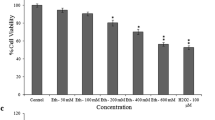
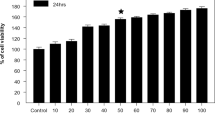
We previously demonstrated that arsenic, cadmium, and lead mixture at environmentally relevant doses induces astrocyte apoptosis in the developing brain. Here, we investigated the mechanism and contribution of each metal in inducing the apoptosis. We hypothesized participation of transcription factor, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ), reported to affect astrocyte survival. We treated cultured rat astrocytes with single metals and their combinations and performed apoptosis assay and measured PPARγ expression levels. We found that cadmium demonstrated maximum increase in PPARγ as well as apoptosis, followed by arsenic and then lead. Interestingly, we observed that the metals mimicked PPARγ agonist, troglitazone, and enhanced PPARγ-transcriptional activity. Co-treatment with PPARγ-siRNA or PPARγ-antagonist, GW9662, suppressed the astrocyte apoptosis, suggesting a prominent participation of PPARγ in metal(s)-induced astrocyte loss. We explored PPARγ-transcriptional activity and identify its target gene in apoptosis, performed in silico screening. We spotted PPARγ-response elements (PPREs) within poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) gene, and through gel-shift assay verified metal(s)-mediated increased PPARγ binding to PARP-PPREs. Chromatin-immunoprecipitation and luciferase-reporter assays followed by real-time PCR and Western blotting proved PPRE-mediated PARP expression, where cadmium contributed most and lead least, and the effects of metal mixture were comparable with troglitazone. Eventually, dose-dependent increased cleaved-PARP/PARP ratio confirmed astrocyte apoptosis. Additionally, we found that PPARγ and PARP expressions were c-Jun N-terminal kinases and cyclin-dependent kinase5-dependent. In vivo treatment of developing rats with the metals corroborated enhanced PPARγ-dependent PARP and astrocyte apoptosis, where yet again cadmium contributed most. Overall, our study enlightens a novel PPARγ-dependent mechanism of As-, Cd-, and Pb-induced astrocyte apoptosis.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma
- PARP:
-
Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase
- LC:
-
Lethal concentration
- PPRE:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptorresponse elements
- As:
-
Arsenic
- Cd:
-
Cadmium
- Pb:
-
Lead
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- ABA:
-
3-aminobenzamide
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescence protein
- PND:
-
Postnatal day
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling
- TBP:
-
Tata-binding protein
- Trog:
-
Troglitazone
References
Montgomery DL (1994) Astrocytes: form, functions, and roles in disease. Vet Pathol 31(2):145–167
Allen NJ (2014) Astrocyte regulation of synaptic behavior. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 30:439–463. doi:10.1146/annurev-cellbio-100913-013053
Cohly HH, Panja A (2005) Immunological findings in autism. Int Rev Neurobiol 71:317–341
Schreiner B, Romanelli E, Liberski P, Ingold-Heppner B, Sobottka-Brillout B, Hartwig T, Chandrasekar V, Johannssen H et al (2015) Astrocyte depletion impairs redox homeostasis and triggers neuronal loss in the adult CNS. Cell Rep 12(9):1377–1384. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2015.07.051
Sobieski C, Jiang X, Crawford DC, Mennerick S (2015) Loss of local astrocyte support disrupts action potential propagation and glutamate release synchrony from unmyelinated hippocampal axon terminals in vitro. J Neurosci 35(31):11105–11117. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1289-15.2015
Jadhav SH, Sarkar SN, Patil RD, Tripathi HC (2007) Effects of subchronic exposure via drinking water to a mixture of eight water-contaminating metals: a biochemical and histopathological study in male rats. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 53(4):667–677. doi:10.1007/s00244-007-0031-0
Ashok A, Rai NK, Tripathi S, Bandyopadhyay S (2015) Exposure to As-, Cd-, and Pb-mixture induces Abeta, amyloidogenic APP processing and cognitive impairments via oxidative stress-dependent neuroinflammation in young rats. Toxicol Sci 143(1):64–80. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfu208
Bui AT, Nguyen HT, Nguyen MN, Tran TH, Vu TV, Nguyen CH, Reynolds HL (2016) Accumulation and potential health risks of cadmium, lead and arsenic in vegetables grown near mining sites in northern Vietnam. Environ Monit Assess 188(9):525. doi:10.1007/s10661-016-5535-5
Obiri S, Yeboah PO, Osae S, Adu-Kumi S (2016) Levels of arsenic, mercury, cadmium, copper, lead, zinc and manganese in serum and whole blood of resident adults from mining and non-mining communities in Ghana. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 23(16):16589–16597. doi:10.1007/s11356-016-6537-0
Rai NK, Ashok A, Rai A, Tripathi S, Nagar GK, Mitra K, Bandyopadhyay S (2013) Exposure to as, Cd and Pb-mixture impairs myelin and axon development in rat brain, optic nerve and retina. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 273(2):242–258. doi:10.1016/j.taap.2013.05.003
Rai A, Maurya SK, Khare P, Srivastava A, Bandyopadhyay S (2010) Characterization of developmental neurotoxicity of as, Cd, and Pb mixture: synergistic action of metal mixture in glial and neuronal functions. Toxicol Sci 118(2):586–601. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfq266
Rai A, Tripathi S, Kushwaha R, Singh P, Srivastava P, Sanyal S, Bandyopadhyay S (2014) CDK5-induced p-PPARgamma(Ser 112) downregulates GFAP via PPREs in developing rat brain: effect of metal mixture and troglitazone in astrocytes. Cell Death Dis 5:e1033. doi:10.1038/cddis.2013.514
Bordet R, Ouk T, Petrault O, Gele P, Gautier S, Laprais M, Deplanque D, Duriez P et al (2006) PPAR: a new pharmacological target for neuroprotection in stroke and neurodegenerative diseases. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 6):1341–1346. doi:10.1042/BST0341341
Cullingford TE, Bhakoo K, Peuchen S, Dolphin CT, Patel R, Clark JB (1998) Distribution of mRNAs encoding the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, beta, and gamma and the retinoid X receptor alpha, beta, and gamma in rat central nervous system. J Neurochem 70(4):1366–1375
Chattopadhyay N, Singh DP, Heese O, Godbole MM, Sinohara T, Black PM, Brown EM (2000) Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARS) in human astrocytic cells: PPARgamma agonists as inducers of apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 61(1):67–74
Cristiano L, Bernardo A, Ceru MP (2001) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) and peroxisomes in rat cortical and cerebellar astrocytes. J Neurocytol 30(8):671–683
Spagnolo A, Grant EN, Glick R, Lichtor T, Feinstein DL (2007) Differential effects of PPARgamma agonists on the metabolic properties of gliomas and astrocytes. Neurosci Lett 417(1):72–77. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.02.036
Zander T, Kraus JA, Grommes C, Schlegel U, Feinstein D, Klockgether T, Landreth G, Koenigsknecht J et al (2002) Induction of apoptosis in human and rat glioma by agonists of the nuclear receptor PPARgamma. J Neurochem 81(5):1052–1060
Perez-Ortiz JM, Tranque P, Vaquero CF, Domingo B, Molina F, Calvo S, Jordan J, Cena V et al (2004) Glitazones differentially regulate primary astrocyte and glioma cell survival. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. J Biol Chem 279(10):8976–8985. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308518200
Varga T, Czimmerer Z, Nagy L (2011) PPARs are a unique set of fatty acid regulated transcription factors controlling both lipid metabolism and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(8):1007–1022. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2011.02.014
Chiu SC, Lin YJ, Huang SY, Lien CF, Chen SP, Pang CY, Lin JH, Yang KT (2015) The role of intermittent hypoxia on the proliferative inhibition of rat cerebellar astrocytes. PLoS One 10(7):e0132263. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0132263
Wang J, Deng X, Zhang F, Chen D, Ding W (2014) ZnO nanoparticle-induced oxidative stress triggers apoptosis by activating JNK signaling pathway in cultured primary astrocytes. Nanoscale Res Lett 9(1):117. doi:10.1186/1556-276X-9-117
Chistyakov DV, Aleshin SE, Astakhova AA, Sergeeva MG, Reiser G (2015) Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) alpha and -gamma of rat brain astrocytes in the course of activation by toll-like receptor agonists. J Neurochem 134(1):113–124. doi:10.1111/jnc.13101
Xiao Y, Yuan T, Yao W, Liao K (2010) 3T3-L1 adipocyte apoptosis induced by thiazolidinediones is peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma-dependent and mediated by the caspase-3-dependent apoptotic pathway. FEBS J 277(3):687–696. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07514.x
Kang DW, Choi CH, Park JY, Kang SK, Kim YK (2008) Ciglitazone induces caspase-independent apoptosis through down-regulation of XIAP and survivin in human glioma cells. Neurochem Res 33(3):551–561. doi:10.1007/s11064-007-9475-x
Liu DC, Zang CB, Liu HY, Possinger K, Fan SG, Elstner E (2004) A novel PPAR alpha/gamma dual agonist inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human glioblastoma T98G cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25(10):1312–1319
Alano CC, Ying W, Swanson RA (2004) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-mediated cell death in astrocytes requires NAD+ depletion and mitochondrial permeability transition. J Biol Chem 279(18):18895–18902. doi:10.1074/jbc.M313329200
Ying W, Chen Y, Alano CC, Swanson RA (2002) Tricarboxylic acid cycle substrates prevent PARP-mediated death of neurons and astrocytes. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22(7):774–779. doi:10.1097/00004647-200207000-00002
Alam S, Pal A, Kumar R, Mir SS, Ansari KM (2015) Nexrutine inhibits azoxymethane-induced colonic aberrant crypt formation in rat colon and induced apoptotic cell death in colon adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Carcinog. doi:10.1002/mc.22368
Campbell SE, Stone WL, Whaley SG, Qui M, Krishnan K (2003) Gamma (gamma) tocopherol upregulates peroxisome proliferator activated receptor (PPAR) gamma (gamma) expression in SW 480 human colon cancer cell lines. BMC Cancer 3:25. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-3-25
Maurya SK, Mishra J, Abbas S, Bandyopadhyay S (2016) Cypermethrin stimulates GSK3beta-dependent Abeta and p-tau proteins and cognitive loss in young rats: reduced HB-EGF signaling and downstream neuroinflammation as critical regulators. Mol Neurobiol 53(2):968–982. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-9061-6
Lee KW, Ku YH, Kim M, Ahn BY, Chung SS, Park KS (2011) Effects of sulfonylureas on peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma activity and on glucose uptake by thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Metab J 35(4):340–347. doi:10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.340
Dwivedi SK, Singh N, Kumari R, Mishra JS, Tripathi S, Banerjee P, Shah P, Kukshal V et al (2011) Bile acid receptor agonist GW4064 regulates PPARgamma coactivator-1alpha expression through estrogen receptor-related receptor alpha. Mol Endocrinol 25(6):922–932. doi:10.1210/me.2010-0512
Yadav M, Singh AK, Kumar H, Rao G, Chakravarti B, Gurjar A, Dogra S, Kushwaha S et al (2016) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitor cancer drug gefitinib modulates cell growth and differentiation of acute myeloid leukemia cells via histamine receptors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1860(10):2178–2190. doi:10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.05.011
Podvinec M, Kaufmann MR, Handschin C, Meyer UA (2002) NUBIScan, an in silico approach for prediction of nuclear receptor response elements. Mol Endocrinol 16(6):1269–1279. doi:10.1210/mend.16.6.0851
Ashok A, Rai NK, Raza W, Pandey R, Bandyopadhyay S (2016) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced impairment of Abeta clearance requires HB-EGF-dependent sequential activation of HIF1alpha and MMP9. Neurobiol Dis 95:179–193. doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2016.07.013
Sundararajan S, Gamboa JL, Victor NA, Wanderi EW, Lust WD, Landreth GE (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma ligands reduce inflammation and infarction size in transient focal ischemia. Neuroscience 130(3):685–696. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.10.021
Jensen EC (2013) Quantitative analysis of histological staining and fluorescence using ImageJ. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 296(3):378–381. doi:10.1002/ar.22641
Maurya SK, Rai A, Rai NK, Deshpande S, Jain R, Mudiam MK, Prabhakar YS, Bandyopadhyay S (2012) Cypermethrin induces astrocyte apoptosis by the disruption of the autocrine/paracrine mode of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling. Toxicol Sci 125(2):473–487. doi:10.1093/toxsci/kfr303
Glass CK, Rosenfeld MG (2000) The coregulator exchange in transcriptional functions of nuclear receptors. Genes Dev 14(2):121–141
Gronemeyer H, Gustafsson JA, Laudet V (2004) Principles for modulation of the nuclear receptor superfamily. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3(11):950–964. doi:10.1038/nrd1551
Dello Russo C, Gavrilyuk V, Weinberg G, Almeida A, Bolanos JP, Palmer J, Pelligrino D, Galea E et al (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma thiazolidinedione agonists increase glucose metabolism in astrocytes. J Biol Chem 278(8):5828–5836. doi:10.1074/jbc.M208132200
Harada S, Hiromori Y, Nakamura S, Kawahara K, Fukakusa S, Maruno T, Noda M, Uchiyama S et al (2015) Structural basis for PPARgamma transactivation by endocrine-disrupting organotin compounds. Sci Rep 5:8520. doi:10.1038/srep08520
Soldani C, Scovassi AI (2002) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 cleavage during apoptosis: an update. Apoptosis 7(4):321–328
Choi SK, Galan M, Kassan M, Partyka M, Trebak M, Matrougui K (2012) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibition improves coronary arteriole function in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 59(5):1060–1068. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.190140
Stoltenburg-Didinger G, Punder I, Peters B, Marcinkowski M, Herbst H, Winneke G, Wiegand H (1996) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and RNA expression in adult rat hippocampus following low-level lead exposure during development. Histochem Cell Biol 105(6):431–442
Cobbina SJ, Chen Y, Zhou Z, Wu X, Zhao T, Zhang Z, Feng W, Wang W et al (2015) Toxicity assessment due to sub-chronic exposure to individual and mixtures of four toxic heavy metals. J Hazard Mater 294:109–120. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.03.057
Check L, Marteel-Parrish A (2013) The fate and behavior of persistent, bioaccumulative, and toxic (PBT) chemicals: examining lead (Pb) as a PBT metal. Rev Environ Health 28(2–3):85–96. doi:10.1515/reveh-2013-0005
Garcia-Arenas G, Ramirez-Amaya V, Balderas I, Sandoval J, Escobar ML, Rios C, Bermudez-Rattoni F (2004) Cognitive deficits in adult rats by lead intoxication are related with regional specific inhibition of cNOS. Behav Brain Res 149(1):49–59
Middeldorp J, Hol EM (2011) GFAP in health and disease. Prog Neurobiol 93(3):421–443. doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2011.01.005
Eddleston M, Mucke L (1993) Molecular profile of reactive astrocytes--implications for their role in neurologic disease. Neuroscience 54(1):15–36
Dahlke C, Saberi D, Ott B, Brand-Saberi B, Schmitt-John T, Theiss C (2015) Inflammation and neuronal death in the motor cortex of the wobbler mouse, an ALS animal model. J Neuroinflammation 12:215. doi:10.1186/s12974-015-0435-0
Lee Y, Chun HJ, Lee KM, Jung YS, Lee J (2015) Silibinin suppresses astroglial activation in a mouse model of acute Parkinson's disease by modulating the ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Brain Res 1627:233–242. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2015.09.029
Kim EH, Yoon MJ, Kim SU, Kwon TK, Sohn S, Choi KS (2008) Arsenic trioxide sensitizes human glioma cells, but not normal astrocytes, to TRAIL-induced apoptosis via CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein-dependent DR5 up-regulation. Cancer Res 68(1):266–275. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-2444
Belanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 14(6):724–738. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2011.08.016
Yi CX, Habegger KM, Chowen JA, Stern J, Tschop MH (2011) A role for astrocytes in the central control of metabolism. Neuroendocrinology 93(3):143–149. doi:10.1159/000324888
Sarruf DA, Yu F, Nguyen HT, Williams DL, Printz RL, Niswender KD, Schwartz MW (2009) Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in key neuronal subsets regulating glucose metabolism and energy homeostasis. Endocrinology 150(2):707–712. doi:10.1210/en.2008-0899
Dentesano G, Serratosa J, Tusell JM, Ramon P, Valente T, Saura J, Sola C (2014) CD200R1 and CD200 expression are regulated by PPAR-gamma in activated glial cells. Glia 62(6):982–998. doi:10.1002/glia.22656
Boes K, Russmann V, Ongerth T, Licko T, Salvamoser JD, Siegl C, Potschka H (2015) Expression regulation and targeting of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma following electrically-induced status epilepticus. Neurosci Lett 604:151–156. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.08.007
Barroso E, del Valle J, Porquet D, Vieira Santos AM, Salvado L, Rodriguez-Rodriguez R, Gutierrez P, Anglada-Huguet M et al (2013) Tau hyperphosphorylation and increased BACE1 and RAGE levels in the cortex of PPARbeta/delta-null mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(8):1241–1248. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2013.03.006
Defaux A, Zurich MG, Braissant O, Honegger P, Monnet-Tschudi F (2009) Effects of the PPAR-beta agonist GW501516 in an in vitro model of brain inflammation and antibody-induced demyelination. J Neuroinflammation 6:15. doi:10.1186/1742-2094-6-15
De Rosa A, Pellegatta S, Rossi M, Tunici P, Magnoni L, Speranza MC, Malusa F, Miragliotta V et al (2012) A radial glia gene marker, fatty acid binding protein 7 (FABP7), is involved in proliferation and invasion of glioblastoma cells. PLoS One 7(12):e52113. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052113
Zang C, Wachter M, Liu H, Posch MG, Fenner MH, Stadelmann C, von Deimling A, Possinger K et al (2003) Ligands for PPARgamma and RAR cause induction of growth inhibition and apoptosis in human glioblastomas. J Neuro-Oncol 65(2):107–118
Benedetti E, Galzio R, Cinque B, Biordi L, D'Amico MA, D'Angelo B, Laurenti G, Ricci A et al (2008) Biomolecular characterization of human glioblastoma cells in primary cultures: differentiating and antiangiogenic effects of natural and synthetic PPARgamma agonists. J Cell Physiol 217(1):93–102. doi:10.1002/jcp.21479
Strakova N, Ehrmann J, Bartos J, Malikova J, Dolezel J, Kolar Z (2005) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPAR) agonists affect cell viability, apoptosis and expression of cell cycle related proteins in cell lines of glial brain tumors. Neoplasma 52(2):126–136
Fern R, Black JA, Ransom BR, Waxman SG (1996) Cd(2+)-induced injury in CNS white matter. J Neurophysiol 76(5):3264–3273
Sagara J, Makino N, Bannai S (1996) Glutathione efflux from cultured astrocytes. J Neurochem 66(5):1876–1881
Dringen R, Spiller S, Neumann S, Koehler Y (2016) Uptake, metabolic effects and toxicity of arsenate and arsenite in astrocytes. Neurochem Res 41(3):465–475. doi:10.1007/s11064-015-1570-9
Zhang Y, Sun LG, Ye LP, Wang B, Li Y (2008) Lead-induced stress response in endoplasmic reticulum of astrocytes in CNS. Toxicol Mech Methods 18(9):751–757. doi:10.1080/15376510802390908
Nair AR, Lee WK, Smeets K, Swennen Q, Sanchez A, Thevenod F, Cuypers A (2015) Glutathione and mitochondria determine acute defense responses and adaptive processes in cadmium-induced oxidative stress and toxicity of the kidney. Arch Toxicol 89(12):2273–2289. doi:10.1007/s00204-014-1401-9
Boulares AH, Yakovlev AG, Ivanova V, Stoica BA, Wang G, Iyer S, Smulson M (1999) Role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) cleavage in apoptosis. Caspase 3-resistant PARP mutant increases rates of apoptosis in transfected cells. J Biol Chem 274(33):22932–22940
Chaitanya GV, Steven AJ, Babu PP (2010) PARP-1 cleavage fragments: signatures of cell-death proteases in neurodegeneration. Cell communication and signaling : CCS 8:31. doi:10.1186/1478-811X-8-31
Chistyakov DV, Aleshin S, Sergeeva MG, Reiser G (2014) Regulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor beta/delta expression and activity levels by toll-like receptor agonists and MAP kinase inhibitors in rat astrocytes. J Neurochem 130(4):563–574. doi:10.1111/jnc.12757
Johnston-Wilson NL, Sims CD, Hofmann JP, Anderson L, Shore AD, Torrey EF, Yolken RH (2000) Disease-specific alterations in frontal cortex brain proteins in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder. The Stanley neuropathology consortium. Mol Psychiatry 5(2):142–149
Messing A, Goldman JE, Johnson AB, Brenner M (2001) Alexander disease: new insights from genetics. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60(6):563–573
Acknowledgement
We acknowledge Miss. Shipra Kartik and Mr. Devendra Pratap Singh for their help in Western blotting and primary rat astrocyte culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding Information
This work was supported by Council of Scientific and Industrial Research-network miND; Department of Biotechnology, Govt. of India [GAP285] and Science and Engineering Research Board, Govt. of India [GAP278].
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
.
Supplementary Fig S1
(DOCX 532 kb)
.
Supplementary Fig S2
(DOCX 317 kb)
.
Supplementary Fig S3
(DOCX 207 kb)
.
Supplementary Fig S4
(DOCX 671 kb)
.
Supplementary Fig S5
(DOCX 219 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kushwaha, R., Mishra, J., Tripathi, S. et al. Arsenic, Cadmium, and Lead Like Troglitazone Trigger PPARγ-Dependent Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Expression and Subsequent Apoptosis in Rat Brain Astrocytes. Mol Neurobiol 55, 2125–2149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0469-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0469-7