Abstract
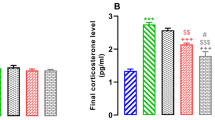
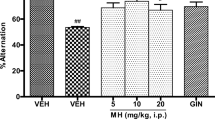
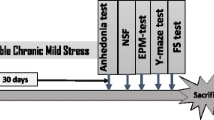
Over the last years, many studies reported on the antioxidant effects of ferulic acid (FA) in preclinical models of dementia through the activation of the heme oxygenase/biliverdin reductase (HO/BVR) system. However, only a few studies evaluated whether FA could improve neurological function under milder conditions, such as psychological stress. The aim of this study was to investigate the effects of FA (150 mg/kg intraperitoneal route) on cognitive function in male Wistar rats exposed to emotional arousal. Animals were randomly assigned to two experimental groups, namely not habituated or habituated to the experimental context, and the novel object recognition test was used to evaluate their cognitive performance. The administration of FA significantly increased long-term retention memory in not habituated rats. Ferulic acid increased the expression of HO-1 in the hippocampus and frontal cortex of not habituated rats only, whereas HO-2 resulted differently modulated in these cognitive brain areas. No significant effects on either HO-1 or HO-2 or BVR were observed in the cerebellum of both habituated and not habituated rats. Ferulic acid activated the stress axis in not habituated rats, as shown by the increase in hypothalamic corticotrophin-releasing hormone levels. Pre-treatment with Sn-protoporphyrin-IX [0.25 μmol/kg, intracerebroventricular route (i.c.v.)], a well-known inhibitor of HO activity through which carbon monoxide (CO) and biliverdin (BV) are generated, abolished the FA-induced improvement of cognitive performance only in not habituated rats, suggesting a role for HO-derived by-products. The CO-donor tricarbonyldichlororuthenium (II) (30 nmol/kg i.c.v.) mimicked the FA-related improvement of cognitive skills only in not habituated rats, whereas BV did not have any effect in any group. In conclusion, these results set the stage for subsequent studies on the neuropharmacological action of FA under conditions of psychological stress.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mancuso C, Santangelo R (2014) Ferulic acid: pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Food Chem Toxicol 65:185–195. doi:10.1016/j.fct.2013.12.024
Zhao Z, Moghadasian MH (2008) Chemistry, natural sources, dietary intake and pharmacokinetic properties of ferulic acid: a review. Food Chem 109(4):691–702. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.02.039
Calabrese V, Calafato S, Puleo E, Cornelius C, Sapienza M, Morganti P, Mancuso C (2008) Redox regulation of cellular stress response by ferulic acid ethyl ester in human dermal fibroblasts: role of vitagenes. Clin Dermatol 26(4):358–363. doi:10.1016/j.clindermatol.2008.01.005
Catino S, Paciello F, Miceli F, Rolesi R, Troiani D, Calabrese V, Santangelo R, Mancuso C (2015) Ferulic acid regulates the Nrf2/heme oxygenase-1 system and counteracts trimethyltin-induced neuronal damage in the human neuroblastoma cell line SH-SY5Y. Front Pharmacol 6:305. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00305
Fetoni AR, Mancuso C, Eramo SL, Ralli M, Piacentini R, Barone E, Paludetti G, Troiani D (2010) In vivo protective effect of ferulic acid against noise-induced hearing loss in the Guinea-pig. Neuroscience 169(4):1575–1588. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.06.022
Picone P, Bondi ML, Montana G, Bruno A, Pitarresi G, Giammona G, Di Carlo M (2009) Ferulic acid inhibits oxidative stress and cell death induced by ab oligomers: improved delivery by solid lipid nanoparticles. Free Radic Res 43(11):1133–1145
Trombino S, Cassano R, Ferrarelli T, Barone E, Picci N, Mancuso C (2013) Trans-ferulic acid-based solid lipid nanoparticles and their antioxidant effect in rat brain microsomes. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 109:273–279. doi:10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.04.005
Yan JJ, Cho JY, Kim HS, Kim KL, Jung JS, Huh SO, Suh HW, Kim YH et al (2001) Protection against beta-amyloid peptide toxicity in vivo with long-term administration of ferulic acid. Br J Pharmacol 133(1):89–96. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0704047
Yan JJ, Jung JS, Kim TK, Hasan A, Hong CW, Nam JS, Song DK (2013) Protective effects of ferulic acid in amyloid precursor protein plus presenilin-1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer disease. Biol Pharm Bull 36(1):140–143
Nabavi SF, Devi KP, Malar DS, Sureda A, Daglia M, Nabavi SM (2015) Ferulic acid and Alzheimer’s disease: promises and pitfalls. Mini Rev Med Chem 15(9):776–788
Sgarbossa A, Giacomazza D, di Carlo M (2015) Ferulic acid: a hope for Alzheimer’s disease therapy from plants. Nutrients 7(7):5764–5782. doi:10.3390/nu7075246
Maines MD (1997) The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 37:517–554. doi:10.1146/annurev.pharmtox.37.1.517
Mancuso C, Kostoglou-Athanassiou I, Forsling ML, Grossman AB, Preziosi P, Navarra P, Minotti G (1997) Activation of heme oxygenase and consequent carbon monoxide formation inhibits the release of arginine vasopressin from rat hypothalamic explants. Molecular linkage between heme catabolism and neuroendocrine function. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 50(1–2):267–276
Mancuso C, Santangelo R, Calabrese V (2013) The heme oxygenase/biliverdin reductase system: a potential drug target in Alzheimers disease. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 27(2 Suppl):75–87
Ewing JF, Maines MD (1992) In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical localization of heme oxygenase-2 mRNA and protein in normal rat brain: differential distribution of isozyme 1 and 2. Mol Cell Neurosci 3(6):559–570
Ewing JF, Maines MD (1995) Immunohistochemical localization of biliverdin reductase in rat brain: age related expression of protein and transcript. Brain Res 672(1–2):29–41
Ewing JF, Weber CM, Maines MD (1993) Biliverdin reductase is heat resistant and coexpressed with constitutive and heat shock forms of heme oxygenase in brain. J Neurochem 61(3):1015–1023
Mancuso C, Barone E (2009) The heme oxygenase/biliverdin reductase pathway in drug research and development. Curr Drug Metab 10(6):579–594
Hawkins RD, Zhuo M, Arancio O (1994) Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide as possible retrograde messengers in hippocampal long-term potentiation. J Neurobiol 25(6):652–665. doi:10.1002/neu.480250607
Shinomura T, Nakao S, Mori K (1994) Reduction of depolarization-induced glutamate release by heme oxygenase inhibitor: possible role of carbon monoxide in synaptic transmission. Neurosci Lett 166(2):131–134
Zhuo M, Small SA, Kandel ER, Hawkins RD (1993) Nitric oxide and carbon monoxide produce activity-dependent long-term synaptic enhancement in hippocampus. Science 260(5116):1946–1950
Errico S, Shohreh R, Barone E, Pusateri A, Mores N, Mancuso C (2010) Heme oxygenase-derived carbon monoxide modulates gonadotropin-releasing hormone release in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Neurosci Lett 471(3):175–178. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2010.01.036
Mancuso C, Preziosi P, Grossman AB, Navarra P (1997) The role of carbon monoxide in the regulation of neuroendocrine function. Neuroimmunomodulation 4(5–6):225–229
Mancuso C, Ragazzoni E, Tringali G, Liberale I, Preziosi P, Grossman A, Navarra P (1999) Inhibition of heme oxygenase in the central nervous system potentiates endotoxin-induced vasopressin release in the rat. J Neuroimmunol 99(2):189–194
Pozzoli G, Mancuso C, Mirtella A, Preziosi P, Grossman AB, Navarra P (1994) Carbon monoxide as a novel neuroendocrine modulator: inhibition of stimulated corticotropin-releasing hormone release from acute rat hypothalamic explants. Endocrinology 135(6):2314–2317. doi:10.1210/endo.135.6.7988414
Joshi G, Perluigi M, Sultana R, Agrippino R, Calabrese V, Butterfield DA (2006) In vivo protection of synaptosomes by ferulic acid ethyl ester (FAEE) from oxidative stress mediated by 2,2-azobis(2-amidino-propane)dihydrochloride (AAPH) or Fe(2+)/H(2)O(2): insight into mechanisms of neuroprotection and relevance to oxidative stress-related neurodegenerative disorders. Neurochem Int 48(4):318–327. doi:10.1016/j.neuint.2005.11.006
Perluigi M, Joshi G, Sultana R, Calabrese V, De Marco C, Coccia R, Cini C, Butterfield DA (2006) In vivo protective effects of ferulic acid ethyl ester against amyloid-beta peptide 1-42-induced oxidative stress. J Neurosci Res 84(2):418–426. doi:10.1002/jnr.20879
Kanski J, Aksenova M, Stoyanova A, Butterfield DA (2002) Ferulic acid antioxidant protection against hydroxyl and peroxyl radical oxidation in synaptosomal and neuronal cell culture systems in vitro: structure-activity studies. J Nutr Biochem 13(5):273–281
Sultana R, Ravagna A, Mohmmad-Abdul H, Calabrese V, Butterfield DA (2005) Ferulic acid ethyl ester protects neurons against amyloid beta- peptide(1-42)-induced oxidative stress and neurotoxicity: relationship to antioxidant activity. J Neurochem 92(4):749–758. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02899.x
Yabe T, Hirahara H, Harada N, Ito N, Nagai T, Sanagi T, Yamada H (2010) Ferulic acid induces neural progenitor cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Neuroscience 165(2):515–524. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.10.023
Zhang YJ, Huang X, Wang Y, Xie Y, Qiu XJ, Ren P, Gao LC, Zhou HH et al (2011) Ferulic acid-induced anti-depression and prokinetics similar to Chaihu-Shugan-san via polypharmacology. Brain Res Bull 86(3–4):222–228. doi:10.1016/j.brainresbull.2011.07.002
Morgese MG, Colaianna M, Mhillaj E, Zotti M, Schiavone S, D’Antonio P, Harkin A, Gigliucci V et al (2015) Soluble beta amyloid evokes alteration in brain norepinephrine levels: role of nitric oxide and interleukin-1. Front Neurosci 9:428. doi:10.3389/fnins.2015.00428
Okuda S, Roozendaal B, McGaugh JL (2004) Glucocorticoid effects on object recognition memory require training-associated emotional arousal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101(3):853–858. doi:10.1073/pnas.0307803100
Barone E, Di Domenico F, Sultana R, Coccia R, Mancuso C, Perluigi M, Butterfield DA (2012) Heme oxygenase-1 posttranslational modifications in the brain of subjects with Alzheimer disease and mild cognitive impairment. Free Radic Biol Med 52(11–12):2292–2301. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.03.020
Barone E, Mancuso C, Di Domenico F, Sultana R, Murphy MP, Head E, Butterfield DA (2012) Biliverdin reductase-a: a novel drug target for atorvastatin in a dog pre-clinical model of Alzheimer disease. J Neurochem 120(1):135–146. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2011.07538.x
Campolongo P, Morena M, Scaccianoce S, Trezza V, Chiarotti F, Schelling G, Cuomo V, Roozendaal B (2013) Novelty-induced emotional arousal modulates cannabinoid effects on recognition memory and adrenocortical activity. Neuropsychopharmacology 38(7):1276–1286. doi:10.1038/npp.2013.26
Maines MD, Eke BC, Weber CM, Ewing JF (1995) Corticosterone has a permissive effect on expression of heme oxygenase-1 in CA1-CA3 neurons of hippocampus in thermal-stressed rats. J Neurochem 64(4):1769–1779
Maines MD, Eke BC, Zhao X (1996) Corticosterone promotes increased heme oxygenase-2 protein and transcript expression in the newborn rat brain. Brain Res 722(1–2):83–94
Colpaert EE, Timmermans JP, Lefebvre RA (2002) Investigation of the potential modulatory effect of biliverdin, carbon monoxide and bilirubin on nitrergic neurotransmission in the pig gastric fundus. Eur J Pharmacol 457(2–3):177–186
Hsieh MT, Tsai FH, Lin YC, Wang WH, Wu CR (2002) Effects of ferulic acid on the impairment of inhibitory avoidance performance in rats. Planta Med 68(8):754–756. doi:10.1055/s-2002-33800
Kim MJ, Choi SJ, Lim ST, Kim HK, Heo HJ, Kim EK, Jun WJ, Cho HY et al (2007) Ferulic acid supplementation prevents trimethyltin-induced cognitive deficits in mice. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 71(4):1063–1068. doi:10.1271/bbb.60564
Tsai FS, Wu LY, Yang SE, Cheng HY, Tsai CC, Wu CR, Lin LW (2015) Ferulic acid reverses the cognitive dysfunction caused by amyloid beta peptide 1-40 through anti-oxidant activity and cholinergic activation in rats. Am J Chin Med 43(2):319–335. doi:10.1142/S0192415X15500214
Mamiya T, Kise M, Morikawa K (2008) Ferulic acid attenuated cognitive deficits and increase in carbonyl proteins induced by buthionine-sulfoximine in mice. Neurosci Lett 430(2):115–118. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.10.029
Mori T, Koyama N, Guillot-Sestier MV, Tan J, Town T (2013) Ferulic acid is a nutraceutical beta-secretase modulator that improves behavioral impairment and alzheimer-like pathology in transgenic mice. PLoS One 8(2):e55774. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0055774
Cropley V, Croft R, Silber B, Neale C, Scholey A, Stough C, Schmitt J (2012) Does coffee enriched with chlorogenic acids improve mood and cognition after acute administration in healthy elderly? A pilot study. Psychopharmacology 219(3):737–749. doi:10.1007/s00213-011-2395-0
Azzini E, Bugianesi R, Romano F, Di Venere D, Miccadei S, Durazzo A, Foddai MS, Catasta G et al (2007) Absorption and metabolism of bioactive molecules after oral consumption of cooked edible heads of Cynara scolymus L. (cultivar Violetto di Provenza) in human subjects: a pilot study. Br J Nutr 97(5):963–969. doi:10.1017/S0007114507617218
Antunes M, Biala G (2012) The novel object recognition memory: neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn Process 13(2):93–110. doi:10.1007/s10339-011-0430-z
Roozendaal B, Castello NA, Vedana G, Barsegyan A, McGaugh JL (2008) Noradrenergic activation of the basolateral amygdala modulates consolidation of object recognition memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90(3):576–579. doi:10.1016/j.nlm.2008.06.010
Roozendaal B, Okuda S, Van der Zee EA, McGaugh JL (2006) Glucocorticoid enhancement of memory requires arousal-induced noradrenergic activation in the basolateral amygdala. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103(17):6741–6746. doi:10.1073/pnas.0601874103
Stefanko DP, Barrett RM, Ly AR, Reolon GK, Wood MA (2009) Modulation of long-term memory for object recognition via HDAC inhibition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(23):9447–9452. doi:10.1073/pnas.0903964106
Ma ZC, Hong Q, Wang YG, Liang QD, Tan HL, Xiao CR, Tang XL, Shao S et al (2011) Ferulic acid induces heme oxygenase-1 via activation of ERK and Nrf2. Drug Discov Ther 5(6):299–305
Ma ZC, Hong Q, Wang YG, Tan HL, Xiao CR, Liang QD, Zhang BL, Gao Y (2010) Ferulic acid protects human umbilical vein endothelial cells from radiation induced oxidative stress by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated kinase pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 33(1):29–34
Song Y, Wen L, Sun J, Bai W, Jiao R, Hu Y, Peng X, He Y et al (2016) Cytoprotective mechanism of ferulic acid against high glucose-induced oxidative stress in cardiomyocytes and hepatocytes. Food Nutr Res 60:30323. doi:10.3402/fnr.v60.30323
Raju VS, McCoubrey WK Jr, Maines MD (1997) Regulation of heme oxygenase-2 by glucocorticoids in neonatal rat brain: characterization of a functional glucocorticoid response element. Biochim Biophys Acta 1351(1–2):89–104
Weber CM, Eke BC, Maines MD (1994) Corticosterone regulates heme oxygenase-2 and NO synthase transcription and protein expression in rat brain. J Neurochem 63(3):953–962
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Fondi Ateneo from Catholic University to C.M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare no conflicts of interest with the results shown in the current study.
Additional information
Vincenzo Cuomo and Cesare Mancuso share senior authorship
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mhillaj, E., Catino, S., Miceli, F.M. et al. Ferulic Acid Improves Cognitive Skills Through the Activation of the Heme Oxygenase System in the Rat. Mol Neurobiol 55, 905–916 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0381-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0381-1