Abstract
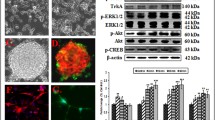
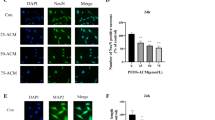
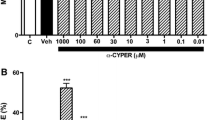
Expression of various cytochrome P450s (CYPs) in mammalian brain cells is well documented. However, such studies are hampered in neural/glial cells of human origin due to nonavailability of human brain cells. To address this issue, we investigated the expression and inducibility of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 and their responsiveness against cyclophosphamide (CPA) and organophosphorus pesticide monocrotophos (MCP), a known developmental neurotoxicant in human neural (SH-SY5Y) and glial (U373-MG) cell lines. CPA induced significant expression of CYP2C8 and CYP3A4 in both types of cells in a time-dependent manner. Neural cell line exhibited relatively higher constitutive and inducible expression of CYPs than the glial cell line. MCP exposure alone could not induce the significant expression of CYPs, whereas the cells preexposed to CPA showed a significant response to MCP. Similar to the case of CPA induced expressions, neural cells were found to be more vulnerable than glial cells. Our data indicate differential expressions of CYPs in cultured human neural and glial cell lines. The findings were synchronized with protein ligand docking studies, which showed a significant modulatory capacity of MCP by strong interaction with CYP regulators-CAR and PXR. Similarly, the known CYP inducer CPA has also shown significant high docking scores with the two studied CYP regulators. We also observed a significant induction in reactive oxygen species (ROS), lipid peroxides (LPO), micronucleus (MN), chromosomal aberration (CA), and reduction in reduced glutathione (GSH) and catalase following the exposure of MCP. Moreover, the expressions of apoptotic markers such as caspase-3, caspase-9, Bax, and p53 were significantly upregulated, whereas the levels of antiapoptotic marker, Bcl2, was downregulated after the exposure of MCP in both cell lines. These findings confirm the involvement of ROS-mediated oxidative stress, which subsequently triggers apoptosis pathways in both human neural (SH-SY5Y) and glial (U373-MG) cell lines following the exposure of MCP.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Korkina L, Scordo MG, Deeva I, Cesareo E, De Luca C (2009) The chemical defensive system in the pathobiology of idiopathic environment-associated diseases. Curr Drug Metab 10:914–931
Conde-Vancells J, Gonzalez E, Lu SC, Mato JM, Falcon-Perez JM (2010) Overview of extra cellular microvesicles in drug metabolism. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 6:543–554
Toselli F, de Waziers I, Dutheil M, Vincent M, Wilce PA, Dodd PR, Beaune P, Loriot MA et al (2015) Gene expression profiling of cytochromes P450, ABC transporters and their principal transcription factors in the amygdala and prefrontal cortex of alcoholics, smokers and drug-free controls by qRT-PCR. Xenobiotica 45:1129–1137
Singh AK, Kashyap MP, Jahan S, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Siddiqui MA, Yadav S, Khanna VK et al (2012) Expression and inducibility of cytochrome P450s (CYP1A1, 2B6, 2E1, 3A4) in human cord blood CD34(+) stem cell-derived differentiating neuronal cells. Toxicol Sci 129:392–410
Tripathi VK, Kumar V, Singh AK, Kashyap MP, Jahan S, Pandey A, Alam S, Khan F et al (2014) Monocrotophos induces the expression and activity of xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes in pre-sensitized cultured human brain cells. PLoS One 9:e91946
Miksys S, Tyndale RF (2006) Nicotine induces brain CYP enzymes: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 70:177–180
Meyer RP, Gehlhaus M, Knoth R, Volk B (2007) Expression and function of cytochrome p450 in brain drug metabolism. Curr Drug Metab 8:297–306
Delozier TC, Kissling GE, Coulter SJ, Dai D, Foley JF, Bradbury JA, Murphy E, Steenbergen C et al (2007) Detection of human CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2J2 in cardiovascular tissues. Drug Metab Dispos 35:682–688
Zanger UM, Turpeinen M, Klein K, Schwab M (2008) Functional pharmacogenetics/genomics of human cytochromes P450 involved in drug biotransformation. Anal Bioanal Chem 392:1093–1108
Goldstein JA (2001) Clinical relevance of genetic polymorphisms in the human CYP2C subfamily. Br J Clin Pharmacol 52:349–355
Marill J, Cresteil T, Lanotte M, Chabot GG (2000) Identification of human cytochrome P450s involved in the formation of all-trans-retinoic acid principal metabolites. Mol Pharmacol 58:1341–1348
Fleming I, Michaelis UR, Bredenkötter D, Fisslthaler B, Dehghani F, Brandes RP, Busse R (2001) Endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor synthase (Cytochrome P450 2C9) is a functionally significant source of reactive oxygen species in coronary arteries. Circ Res 88:44–51
Bu HZ (2006) A literature review of enzyme kinetic parameters for CYP3A4-mediated metabolic reactions of 113 drugs in human liver microsomes: structure-kinetics relationship assessment. Curr Drug Metab 7:231–249
Gervasini G, Carrillo JA, Benitez J (2004) Potential role of cerebral cytochrome P450 in clinical pharmacokinetics: modulation by endogenous compounds. Clin Pharmacokinet 43:693–706
Hendrychova T, Anzenbacherová E, Hudeček J, Skopalík J, Lange R, Hildebrandt P, Otyepka M, Anzenbacher P (2011) Flexibility of human cytochrome P450 enzymes: molecular dynamics and spectroscopy reveal important function-related variations. Biochim Biophys Acta 1814:58–68
Wang RW, Newton DJ, Scheri TD, Lu AY (1997) Human cytochrome P450 3A4-catalyzed testosterone 6 beta-hydroxylation and erythromycin N-demethylation. Competition during catalysis. Drug Metab Dispos 25:502–507
Lee AJ, Cai MX, Thomas PE, Conney AH, Zhu BT (2003) Characterization of the oxidative metabolites of 17beta-estradiol and estrone formed by 15 selectively expressed human cytochrome p450 isoforms. Endocrinology 144:3382–3398
McEwen BS (1994) How do sex and stress hormones affect nerve cells? Ann N Y Acad Sci 743:1–16
Munetsuna E, Hojo Y, Hattori M, Ishii H, Kawato S, Ishida A, Kominami SA, Yamazaki T (2009) Retinoic acid stimulates 17beta-estradiol and testosterone synthesis in rat hippocampal slice cultures. Endocrinology 150:4260–4269
Kwong TC (2002) Organophosphate pesticides: biochemistry and clinical toxicology. Ther Drug Monit 24:144–149
Kossmann S, Magner-Krezel Z, Sobieraj R, Szwed Z (1997) The assessment of nephrotoxic effect of organophosphorous pesticides based on the determination of the activity of some selected enzymes in urine. Przegl Lek 54:707–711
Rawlings NC, Cook SJ, Waldbillig D (1998) Effects of the pesticides carbofuran, chlorpyrifos, dimethoate, lindane, triallate, trifluralin, 2,4-D, and pentachlorophenol on the metabolic endocrine and reproductive endocrine system in ewes. J Toxicol Environ Health A 54:21–36
Gomes J, Dawodu AH, Lloyd O, Revitt DM, Anilal SV (1999) Hepatic injury and disturbed amino acid metabolism in mice following prolonged exposure to organophosphorus pesticides. Hum Exp Toxicol 18:33–37
McDaniel KL, Moser VC (2004) Differential profiles of cholinesterase inhibition and neurobehavioral effects in rats exposed to fenamiphos or profenofos. Neurotoxicol Teratol 26:407–415
Tiwari MN, Singh AK, Ahmad I, Upadhyay G, Singh D, Patel DK, Singh C, Prakash O et al (2010) Effects of cypermethrin on monoamine transporters, xenobiotic metabolizing enzymes and lipid peroxidation in the rat nigrostriatal system. Free Radic Res 44:1416–1424
Tiwari MN, Singh AK, Agrawal S, Gupta SP, Jyoti A, Shanker R, Prakash O, Singh MP (2012) Cypermethrin alters the expression profile of mRNAs in the adult rat striatum: a putative mechanism of postnatal pre-exposure followed by adulthood re-exposure-enhanced neurodegeneration. Neurotox Res 22:321–334
Ranjbar A, Pasalar P, Abdollahi M (2002) Induction of oxidative stress and acetylcholinesterase inhibition in organophosphorous pesticide manufacturing workers. Hum Exp Toxicol 21:179–182
Junior HV, de França Fonteles MM, Mendes de Freitas R (2009) Acute seizure activity promotes lipid peroxidation, increased nitrite levels and adaptive pathways against oxidative stress in the frontal cortex and striatum. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2:130–137
Masoud A, Kiran R, Sandhir R (2009) Impaired mitochondrial functions in organophosphate induced delayed neuropathy in rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 29:1245–1255
Kashyap MP, Singh AK, Siddiqui MA, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Khanna VK, Yadav S, Jain SK et al (2010) Caspase cascade regulated mitochondria mediated apoptosis in monocrotophos exposed PC12 cells. Chem Res Toxicol 23:1663–1672
Kashyap MP, Singh AK, Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Srivastava RK, Agrawal M, Khanna VK, Yadav S et al (2011) Monocrotophos induced apoptosis in PC12 cells: role of xenobiotic metabolizing cytochrome P450s. PLoS One 6:e17757
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Huey R, Olson AJ (1996) Distributed automated docking of flexible ligands to proteins: parallel applications of AutoDock 2.4. J Comput Aided Mol Des 10:293–304
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera--a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Wang J, Wang W, Kollman PA, Case DA (2006) Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J Mol Graph Model 25:247–260
Wang J, Wolf RM, Caldwell JW, Kollman PA, Case DA (2004) Development and testing of a general amber force field. J Comput Chem 25:1157–1174
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey R, Hart WE, Belew RK, Olson AJ (1998) Automated docking using a Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy function. J Comput Chem 19:1639–1662
Rarey M, Kramer B, Lengauer T, Klebe G (1996) A fast flexible docking method using an incremental construction algorithm. J Mol Biol 261:470–489
Goodsell DS, Morris GM, Olson AJ (1996) Automated docking of flexible ligands: applications of AutoDock. J Mol Recognit 9:1–5
Schagger H (2006) Tricine-SDS-PAGE. Nat Protoc 1:16–22
Siddiqui MA, Kashyap MP, Kumar V, Al-Khedhairy AA, Musarrat J, Pant AB (2010) Protective potential of trans-resveratrol against 4-hydroxynonenal induced damage in PC12 cells. Toxicol In Vitro 24:1592–1598
Srivastava RK, Lohani M, Pant AB, Rahman Q (2010) Cyto-genotoxicity of amphibole asbestos fibers in cultured human lung epithelial cell line: role of surface iron. Toxicol Ind Health 26:575–582
Hedlund E, Gustafsson JA, Warner M (2001) Cytochrome P450 in the brain; a review. Curr Drug Metab 2:245–263
McFayden MC, Melvin WT, Murray GI (1998) Regional distribution of individual forms of cytochrome P450 mRNA in normal adult human brain. Biochem Pharmacol 55:825–830
Malaplate-Armand C, Ferrari L, Masson C, Visvikis-Siest S, Lambert H, Batt AM (2005) Down-regulation of astroglial CYP2C, glucocorticoid receptor and constitutive androstane receptor genes in response to cocaine in human U373 MG astrocytoma cells. Toxicol Lett 159:203–211
Chen Y, Goldstein JA (2009) The transcriptional regulation of the human CYP2C genes. Curr Drug Metab 10:567–578
Feidt DM, Klein K, Hofmann U, Riedmaier S, Knobeloch D, Thasler WE, Weiss TS, Schwab M et al (2010) Profiling induction of cytochrome p450 enzyme activity by statins using a new liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry cocktail assay in human hepatocytes. Drug Metab Dispos 38:1589–1597
Zeldin DC, DuBois RN, Falck JR, Capdevila JH (1995) Molecular cloning, expression and characterization of an endogenous human cytochrome P450 arachidonic acid epoxygenase isoform. Arch Biochem Biophys 322:76–86
Gebremedhin D, Ma YH, Falck JR, Roman RJ, VanRollins M, Harder DR (1992) Mechanism of action of cerebral epoxyeicosatrienoic acids on cerebral arterial smooth muscle. Am J Physiol 263:H519–H525
Kapoor N, Pant AB, Dhawan A, Dwievedi UN, Seth PK, Parmar D (2007) Differences in the expression and inducibility of cytochrome P450 2B isoenzymes in cultured rat brain neuronal and glial cells. Mol Cell Biochem 305:199–207
Yamazaki H, Shimada T (1997) Progesterone and testosterone hydroxylation by cytochromes P450 2C19, 2C9, and 3A4 in human liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys 346:161–169
Pikuleva IA (2006) Cytochrome P450s and cholesterol homeostasis. Pharmacol Ther 112:761–773
Wolbold R, Klein K, Burk O, Nüssler AK, Neuhaus P, Eichelbaum M, Schwab M, Zanger UM (2003) Sex is a major determinant of CYP3A4 expression in human liver. Hepatology 38:978–988
Cotreau MM, von Moltke LL, Greenblatt DJ (2005) The influence of age and sex on the clearance of cytochrome P450 3A substrates. Clin Pharmacokinet 44:33–60
Waxman DJ, O’Connor C (2006) Growth hormone regulation of sex-dependent liver gene expression. Mol Endocrinol 20:2613–2629
Ghosh C, Marchi N, Desai NK, Puvenna V, Hossain M, Gonzalez-Martinez J, Alexopoulos AV, Janigro D (2011) Cellular localization and functional significance of CYP3A4 in the human epileptic brain. Epilepsia 52:562–571
Zaccara G, Cincotta M, Borgheresi A, Balestrieri F (2004) Adverse motor effects induced by antiepileptic drugs. Epileptic Disord 6:153–168
Schmidt D (2009) Drug treatment of epilepsy: options and limitations. Epilepsy Behav 15:56–65
Naspinski C, Gu X, Zhou GD, Mertens-Talcott SU, Donnelly KC, Tian Y (2008) Pregnane X receptor protects HepG2 cells from BaP-induced DNA damage. Toxicol Sci 104:67–73
Langmade SJ, Gale SE, Frolov A, Mohri I, Suzuki K, Mellon SH, Walkley SU, Covey DF et al (2006) Pregnane X receptor (PXR) activation: a mechanism for neuroprotection in a mouse model of Niemann-Pick C disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:13807–13812
Burman W, Orr L (2000) Carbamazepine toxicity after starting combination antiretroviral therapy including ritonavir and efavirenz. AIDS 14:2793–2804
Kazi AI, Oommen A (2012) Monocrotophos induced oxidative damage associates with severe acetylcholinesterase inhibition in rat brain. Neurotoxicology 33:156–161
Aschner M, Allen JW, Kimelberg HK, LoPachin RM, Streit WJ (1999) Glial cells in neurotoxicity development. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 39:151–173
Rossi DJ, Brady JD, Mohr C (2007) Astrocyte metabolism and signaling during brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 10:1377–1386
Kehrer JP (1993) Free radicals as mediators of tissue injury and disease. Crit Rev Toxicol 23:21–48
Kroemer G, Galluzzi L, Brenner C (2007) Mitochondrial membrane permeabilization in cell death. Physiol Rev 87:99–163
Cnubben NH, Rietjens IM, Wortelboer H, van Zanden J, van Bladeren PJ (2001) The interplay of glutathione-related processes in antioxidant defense. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 10:141–152
Zhang J, Hu J, Ding JH, Yao HH, Hu G (2005) 6-Hydroxydopamine-induced glutathione alteration occurs via glutathione enzyme system in primary cultured astrocytes. Acta Pharmacol Sin 26:799–805
Kumar V, Tripathi VK, Jahan S, Agrawal M, Pandey A, Khanna VK, Pant AB (2015) Lead Intoxication Synergies of the Ethanol-Induced Toxic Responses in Neuronal Cells--PC12. Mol Neurobiol 52:1504–1520
Kumar V, Gupta AK, Shukla RK, Tripathi VK, Jahan S, Pandey A, Srivastava A, Agrawal M et al (2015) Molecular Mechanism of Switching of TrkA/p75(NTR) Signaling in Monocrotophos Induced Neurotoxicity. Sci Rep 5:14038
Slotkin TA, Seidler FJ (2007) Comparative developmental neurotoxicity of organophosphates in vivo: transcriptional responses of pathways for brain cell development, cell signaling, cytotoxicity and neurotransmitter systems. Brain Res Bull 72:232–274
Gonzalez-Santiago L, Suárez Y, Zarich N, Muñoz-Alonso MJ, Cuadrado A, Martínez T, Goya L, Iradi A et al (2006) Aplidin induces JNK-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells via alteration of glutathione homeostasis, Rac1 GTPase activation, and MKP-1 phosphatase downregulation. Cell Death Differ 13:1968–1981
Sun F, Anantharam V, Latchoumycandane C, Kanthasamy A, Kanthasamy AG (2005) Dieldrin induces ubiquitin-proteasome dysfunction in alpha-synuclein overexpressing dopaminergic neuronal cells and enhances susceptibility to apoptotic cell death. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315:69–79
Perez-Maldonado IN, Herrera C, Batres LE, González-Amaro R, Díaz-Barriga F, Yáñez L (2005) DDT-induced oxidative damage in human blood mononuclear cells. Environ Res 98:177–184
Zhao M, Zhang Y, Wang C, Fu Z, Liu W, Gan J (2009) Induction of macrophage apoptosis by an organochlorine insecticide acetofenate. Chem Res Toxicol 22:504–510
Carlson K, Jortner BS, Ehrich M (2000) Organophosphorus compound-induced apoptosis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 168:102–113
Bunz F, Dutriaux A, Lengauer C, Waldman T, Zhou S, Brown JP, Sedivy JM, Kinzler KW et al (1998) Requirement for p53 and p21 to sustain G2 arrest after DNA damage. Science 282:1497–1501
Cui Q, Yu JH, Wu JN, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Minami M, Ikejima T (2007) P53-mediated cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through a caspase-3- independent, but caspase-9-dependent pathway in oridonin-treated MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin 28:1057–1066
Tripathy NK, Patnaik KK (1992) Studies on the genotoxicity of monocrotophos in somatic and germ-like cells of Drosophila. Mutat Res 278:23–29
Bhunya SP, Jena GB (1993) Studies on the genotoxicity of monocrotophos, an organophosphate insecticide, in the chick in vivo test system. Mutat Res 292:231–239
Hour TC, Chen L, Lin JK (1998) Comparative investigation on the mutagenicities of organophosphate, phthalimide, pyrethroid and carbamate insecticides by the Ames and lactam tests. Mutagenesis 13:157–166
Zahran MM, Abdel-Aziz KB, Abdel-Raof A, Nahas EM (2005) The effect of subacute doses of organophosphorus pesticide, Nuvacron, on the biochemical and cytogenetic parameters of mice and their embryos. Res J Agricul Biochem Sci 1:277–283
Acknowledgments
This work was carried out with the support of a grant from the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 Program (Project No. PJ011101) and a grant for FTA issues (Project No. PJ01017003) of Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors of this manuscript have no conflict of interest among them or anybody else regarding the scientific contents, financial matters, or otherwise.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tripathi, V.K., Kumar, V., Pandey, A. et al. Monocrotophos Induces the Expression of Xenobiotic Metabolizing Cytochrome P450s (CYP2C8 and CYP3A4) and Neurotoxicity in Human Brain Cells. Mol Neurobiol 54, 3633–3651 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9938-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9938-7