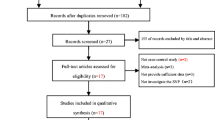
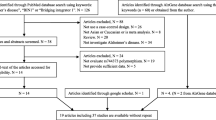
Abstract
Recent genome-wide association studies have identified an association between the bridging integrator 1 gene (BIN1) rs744373 polymorphism and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (LOAD) in individuals of European ancestry. Additionally, a number of studies have focused on the association between rs744373 and Alzheimer’s disease in Caucasian and East Asian populations. However, these results remain inconclusive because of the relatively small sample sizes investigated. Here, we reevaluated this association using samples from seven articles including 22 independent studies comprising 11,832 LOAD patients and 18,133 controls identified by searching PubMed, MEDLINE, and AlzGene databases up to December 2015. We observed no significant heterogeneity between Asian and Caucasian populations. Additive, dominant, and recessive models revealed a significant association between rs744373 and LOAD in the pooled population, while subgroup analysis also identified significant findings in the East Asian population under the additive model (odds ratio (OR) = 1.10, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 1.02–1.19, P = 0.01) and dominant model (OR = 1.13, 95 % CI 1.03–1.25, P = 0.01), but not under the recessive model. The current meta-analysis further supports previous findings that the rs744373 polymorphism may be associated with LOAD risk in Caucasian and Asian populations. To our knowledge, this is the first large meta-analysis to investigate the association between the rs744373 polymorphism and LOAD in East Asian, American, and European populations.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dye RV, Miller KJ, Singer EJ, Levine AJ (2012) Hormone replacement therapy and risk for neurodegenerative diseases. Int J Alzheimers Dis 2012:258454
Liu G, Yao L, Liu J, Jiang Y, Ma G, Chen Z et al (2014) Cardiovascular disease contributes to Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from large-scale genome-wide association studies. Neurobiol Aging 35(4):786–79
Lambert JC, Zelenika D, Hiltunen M, Chouraki V, Combarros O, Bullido MJ et al (2011) Evidence of the association of BIN1 and PICALM with the AD risk in contrasting European populations. Neurobiol Aging 32:756
Hollingworth P, Harold D, Sims R, Gerrish A, Lambert JC, Carrasquillo MM et al (2011) Common variants at ABCA7, MS4A6A/MS4A4E, EPHA1, CD33 and CD2AP are associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):429–435
Naj AC, Jun G, Beecham GW, Wang LS, Vardarajan BN, Buros J et al (2011) Common variants at MS4A4/MS4A6E, CD2AP, CD33 and EPHA1 are associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 43(5):436–441
Seshadri S, Fitzpatrick AL, Ikram MA, DeStefano AL, Gudnason V, Boada M et al (2010) Genome-wide analysis of genetic loci associated with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 303(18):1832–1840
Chapuis J, Hansmannel F, Gistelinck M, Mounier A, Cauwenberghe V, Di Paolo G et al (2013) Increased expression of BIN1 mediates Alzheimer genetic risk by modulating tau pathology. Mol Psychiatry 18(11):1225–1234
Tan MS, Yu JT, Tan L (2013) Bridging integrator 1 (BIN1): form, function, and Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Mol Med 19:594e603
Di Paolo G, Sankaranarayanan S, Wenk MR, Daniell L, Perucco E, Caldarone BJ et al (2002) Decreased synaptic vesicle recycling efficiency and cognitive deficits in amphiphysin 1 knockout mice. Neuron 33:789–804
Sun L, Tan MS, Hu N, Yu JT, Tan L (2013) Exploring the value of plasma BIN1 as a potential biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 37:291e295
Tan L, Yu JT, Zhang W, Wu ZC, Zhang Q, Liu QY et al (2013) Association of GWAS-linked loci with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in a northern Han Chinese population. Alzheimers Dement 9(5):546–553
Ohara T, Ninomiya T, Hirakawa Y, Ashikawa K, Monji A, Kiyohara Y et al (2012) Association study of susceptibility genes for late-onset Alzheimer’s disease in the Japanese population. Psychiatr Genet 22(6):290–293
Wang HZ, Bi R, Hu QX, Xiang Q, Zhang C, Zhang DF (2014) Validating GWAS-identified risk loci for Alzheimer’s disease in Han Chinese populations. Mol Neurobiol Dec 3. [Epub ahead of print].
Li HL, Yang P, Liu ZJ, Sun YM, Lu SJ, Tao QQ et al (2015) Common variants at Bin1 are associated with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in the Han Chinese population. Psychiatr Genet 25(1):21–25
Clark MF, Baudouin SV (2006) A systematic review of the quality of genetic association studies in human sepsis. Intensive Care Med 32:1706–1712
Tan MS, Yu JT, Jiang T, Zhu XC, Guan HS, Tan L (2014) Genetic variation in BIN1 gene and Alzheimer’s disease risk in Han Chinese individuals. Neurobiol Aging 35:1781
Hu X, Pickering E, Liu YC, Hall S, Fournier H, Katz E et al (2011) Meta-analysis for genome-wide association study identifies multiple variants at the BIN1 locus associated with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 6(2), e16616
Gharesouran J, Rezazadeh M, Khorrami A, Ghojazadeh M, Talebi M (2014) Genetic evidence for the involvement of variants at APOE, BIN1, CR1, and PICALM loci in risk of late-onset Alzheimer's disease and evaluation for interactions with APOE genotypes. J Mol Neurosci 54(4):780–786
Liu G, Zhang S, Cai Z, Li Y, Cui L, Ma G (2013) BIN1 gene rs744373 polymorphism contributes to Alzheimer’s disease in East Asian population. Neurosci Lett 7(544):47–51
Harold D, Abraham R, Hollingworth P, Sims R, Gerrish A, Hamshere ML et al (2009) Genome-wide association study identifies variants at CLU and PICALM associated with Alzheimer’s disease. Nat Genet 41(10):1088–1093
Carrasquillo MM, Belbin O, Hunter TA, Ma L, Bisceglio GD, Zou F (2011) Replication of BIN1 association with Alzheimer’s disease and evaluation of genetic interactions. J Alzheimers Dis 24:751–758
Meunier B, Quaranta M, Daviet L, Hatzoglou A, Leprince C (2009) The membrane-tubulating potential of amphiphysin 2/BIN1 is dependent on the microtubule-binding cytoplasmic linker protein 170 (CLIP-170). Eur J Cell Biol 88:91–102
Anekonda TS, Quinn JF (2011) Calcium channel blocking as a therapeutic strategy for Alzheimer’s disease: the case for isradipine. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812:1584–159
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400950, 81501006). We are deeply grateful to all participants of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, R., Liu, X. & He, Z. The Bridging Integrator 1 Gene Polymorphism rs744373 and the Risk of Alzheimer’s Disease in Caucasian and Asian Populations: An Updated Meta-Analysis. Mol Neurobiol 54, 1419–1428 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9760-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-9760-2