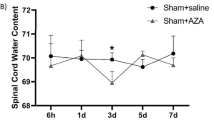
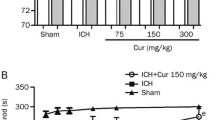
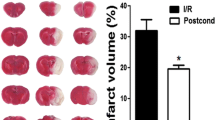
Abstract
Aquaporin-4 (AQP4), a water-channel protein, controls water fluxes into and out of the brain parenchyma. The role of AQP4 in brain edema formation and resolution remains controversial. This study therefore determined the roles of AQP4 in brain edema and explored the underlying molecular mechanism. We established hypoxia-ischemia (HI) neonatal rat model in vivo and HI cell model in vitro, which were administrated with lentiviral or shRNA vector, respectively. We found that the neurologic deficit and motor dysfunction could be induced by HI with more serious brain damage after longer HI time, and swollen cells with enlarged surrounding space were observed after HI induction. The quantity of water in the brain tissues was significantly increased in the HI rats when compared with the control group. However, the downregulation AQP4 by lentiviral or shRNA vector reversed the brain edema and neurologic deficit induced by HI. The underlying mechanism of beneficial effects of AQP4 downregulation may be due to interactive regulation of AQP4 and inflammatory cytokines including IL-1β, IL-6, IL-10, and TNFα. Our data demonstrate that the silence of AQP4 results in a significant decrease in the expression of IL-1β, IL-10, and TNFα, but had no direct effect on IL-6 expression. AQP4 could indirectly regulate the expression of IL-6 via IL-1β, IL-10, and TNFα. In summary, these findings provide a novel mechanism to explain the role of AQP4 in HI pathogenesis and are instrumental for the development of treatment for HI-induced brain edema.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nico B, Ribatti D (2011) Role of aquaporins in cell migration and edema formation in human brain tumors. Exp Cell Res 317(17):2391–2396. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2011.07.006
Sales AD, Lobo CH, Carvalho AA, Moura AA, Rodrigues AP (2013) Structure, function, and localization of aquaporins: their possible implications on gamete cryopreservation. Genet Mol Res 12(4):6718–6732. doi:10.4238/2013.December.13.5
Azuma M, Nagae T, Maruyama M, Kataoka N, Miyake S (2012) Two water-specific aquaporins at the apical and basal plasma membranes of insect epithelia: molecular basis for water recycling through the cryptonephric rectal complex of lepidopteran larvae. J Insect Physiol 58(4):523–533. doi:10.1016/j.jinsphys.2012.01.007
He Z, Wang X, Wu Y, Jia J, Hu Y, Yang X, Li J, Fan M et al (2014) Treadmill pre-training ameliorates brain edema in ischemic stroke via down-regulation of aquaporin-4: an MRI study in rats. PLoS One 9(1):e84602. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0084602
Goodyear MJ, Crewther SG, Junghans BM (2009) A role for aquaporin-4 in fluid regulation in the inner retina. Vis Neurosci 26(2):159–165. doi:10.1017/s0952523809090038
Nagelhus EA, Ottersen OP (2013) Physiological roles of aquaporin-4 in brain. Physiol Rev 93(4):1543–1562. doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2013
Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2007) Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatr Nephrol 22(6):778–784. doi:10.1007/s00467-006-0411-0
Xu M, Su W, Xu QP (2010) Aquaporin-4 and traumatic brain edema. Chin J Traumatol 13(2):103–110
Wang BF, Cui ZW, Zhong ZH, Sun YH, Sun QF, Yang GY, Bian LG (2015) Curcumin attenuates brain edema in mice with intracerebral hemorrhage through inhibition of AQP4 and AQP9 expression. Acta Pharmacol Sin 36(8):939–948. doi:10.1038/aps.2015.47
Fu X, Li Q, Feng Z, Mu D (2007) The roles of aquaporin-4 in brain edema following neonatal hypoxia ischemia and reoxygenation in a cultured rat astrocyte model. Glia 55(9):935–941. doi:10.1002/glia.20515
Manley GT, Fujimura M, Ma T, Noshita N, Filiz F, Bollen AW, Chan P, Verkman AS (2000) Aquaporin-4 deletion in mice reduces brain edema after acute water intoxication and ischemic stroke. Nat Med 6(2):159–163. doi:10.1038/72256
Dmytrenko L, Cicanic M, Anderova M, Vorisek I, Ottersen OP, Sykova E, Vargova L (2013) The impact of alpha-syntrophin deletion on the changes in tissue structure and extracellular diffusion associated with cell swelling under physiological and pathological conditions. PLoS One 8(7):e68044. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0068044
Meng S, Qiao M, Lin L, Del Bigio MR, Tomanek B, Tuor UI (2004) Correspondence of AQP4 expression and hypoxic-ischaemic brain oedema monitored by magnetic resonance imaging in the immature and juvenile rat. Eur J Neurosci 19(8):2261–2269. doi:10.1111/j.0953-816X.2004.03315.x
Song TT, Bi YH, Gao YQ, Huang R, Hao K, Xu G, Tang JW, Ma ZQ et al (2016) Systemic pro-inflammatory response facilitates the development of cerebral edema during short hypoxia. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):63. doi:10.1186/s12974–016–0528-4
Li D, Song T, Yang L, Wang X, Yang C, Jiang Y (2016) Neuroprotective actions of pterostilbene on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats throughupregulation of heme oxygenase-1. Int J Dev Neurosci:22–31. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.08.005
Ambalavanan N, Carlo WA, McDonald SA, Das A, Schendel DE, Thorsen P, Hougaard DM, Skogstrand K, Higgins RD (2012) Cytokines and posthemorrhagic ventricular dilation in premature infants. Am J Perinatol29(9):731–40
Huang LQ, Zhu GF, Deng YY, Jiang WQ, Fang M, Chen CB, Cao W, Wen MY et al (2014) Hypertonic saline alleviates cerebral edema by inhibiting microglia-derived TNF-α and IL-1β-induced Na-K-Cl Cotransporter up-regulation. J Neuroinflammation 11:102. doi:10.1186/1742–2094–11-102
Lee JH, Espinera AR, Chen D, Choi KE, Caslin AY, Won S, Pecoraro V, Xu GY et al (2016) Neonatal inflammatory pain and systemic inflammatory responses as possible environmental factors in the development of autism spectrum disorder of juvenile rats. J Neuroinflammation 13(1):109. doi:10.1186/s12974-016-0575-x
Sameshima H, Ikenoue T (2013) Hypoxic-ischemic neonatal encephalopathy: animal experiments for neuroprotective therapies. Stroke Res Treat 2013:659374. doi:10.1155/2013/659374
Barks JD, Post M, Tuor UI (1991) Dexamethasone prevents hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the neonatal rat. Pediatr Res 29(6):558–563. doi:10.1203/00006450-199106010-00008
Fang CZ, Yang YJ, Wang QH, Yao Y, Zhang XY, He XH (2013) Intraventricular injection of human dental pulp stem cells improves hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in neonatal rats. PLoS One 8(6):e66748. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0066748
Garrett MC, Komotar RJ, Starke RM, Merkow MB, Otten ML, Sciacca RR, Connolly ES (2009) The efficacy of direct extracranial-intracranial bypass in the treatment of symptomatic hemodynamic failure secondary to athero-occlusive disease: a systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 111(4):319–326. doi:10.1016/j.clineuro.2008.12.012
Chipperfield AR, Harper AA (2000) Chloride in smooth muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 74(3–5):175–221
Davalos A, Shuaib A, Wahlgren NG (2000) Neurotransmitters and pathophysiology of stroke: evidence for the release of glutamate and other transmitters/mediators in animals and humans. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 9(6 Pt 2):2–8. doi:10.1053/jscd.2000.18908
Iacovetta C, Rudloff E, Kirby R (2012) The role of aquaporin 4 in the brain. Vet Clin Pathol 41(1):32–44. doi:10.1111/j.1939-165X.2011.00390.x
Manley GT, Binder DK, Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2004) New insights into water transport and edema in the central nervous system from phenotype analysis of aquaporin-4 null mice. Neuroscience 129(4):983–991. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2004.06.088
Rice JE 3rd, Vannucci RC, Brierley JB (1981) The influence of immaturity on hypoxic-ischemic brain damage in the rat. Ann Neurol 9(2):131–141. doi:10.1002/ana.410090206
Chang KH, Yeh CM, Yeh CY, Huang CC, Hsu KS (2013) Neonatal dexamethasone treatment exacerbates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury. Mol Brain 6:18. doi:10.1186/1756-6606-6-18
Sun MC, Honey CR, Berk C, Wong NL, Tsui JK (2003) Regulation of aquaporin-4 in a traumatic brain injury model in rats. J Neurosurg 98(3):565–569. doi:10.3171/jns.2003.98.3.0565
Papadopoulos MC, Verkman AS (2005) Aquaporin-4 gene disruption in mice reduces brain swelling and mortality in pneumococcal meningitis. J Biol Chem 280(14):13906–13912. doi:10.1074/jbc.M413627200
Malaeb S, Dammann O (2009) Fetal inflammatory response and brain injury in the preterm newborn. J Child Neurol 24(9):1119–1126. doi:10.1177/0883073809338066
Lee JH, Wei ZZ, Cao W, Won S, Gu X, Winter M, Dix TA, Wei L, Yu SP (2016) Regulation of therapeutic hypothermia on inflammatory cytokines, microglia polarization, migration and functional recovery after ischemic stroke in mice. Neurobiol Dis96:248–260. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2016.09.013
Bastek JA, Gómez LM, Elovitz MA (2011) The role of inflammation and infection in preterm birth. Clin Perinatol 38(3):385–406. doi:10.1016/j.clp.2011.06.003
Chevin M, Guiraut C, Maurice-Gelinas C, Deslauriers J, Grignon S, Sébire G (2016) Neuroprotective effects of hypothermia in inflammatory-sensitized hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy. Int J Dev Neurosci:1–8. doi:10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2016.09.002
Liu F, McCullough LD (2013) Inflammatory responses in hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy. Acta Pharmacol Sin 34(9):1121–1130. doi:10.1038/aps.2013.89
Liu S, Zhu S, Zou Y, Wang T, Fu X (2015) Knockdown of IL-1beta improves hypoxia-ischemia brain associated with IL-6 up-regulation in cell and animal models. Mol Neurobiol 51(2):743–752. doi:10.1007/s12035-014-8764-z
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by a grant from the National High-tech R&D Program (863 Program No. 2015AA020310), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81501071, 815300045, 81373166), Shenzhen Development and Reform Commission and Shenzhen Municipal Science and Technology Innovation Council (20140405201035).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, S., Mao, J., Wang, T. et al. Downregulation of Aquaporin-4 Protects Brain Against Hypoxia Ischemia via Anti-inflammatory Mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 54, 6426–6435 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0185-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0185-8