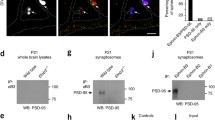
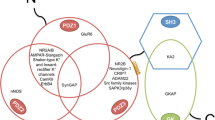
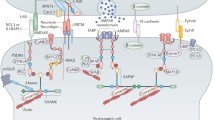
Abstract
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) are expressed in postmitotic neurons and act as important regulators in intracellular signaling. In addition to their nuclear distribution and roles in regulating gene expression, MAPKs, especially the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) subclass, reside in peripheral dendritic spines and synapses, including the postsynaptic density (PSD) microdomain. This peripheral pool of MAPKs/ERKs is either constitutively active or sensitive to changing synaptic input. Active MAPKs directly interact with and phosphorylate local substrates to alter their trafficking and subcellular/subsynaptic distributions, through which MAPKs regulate function of substrates and contribute to long-lasting synaptic plasticity. A number of physiologically relevant substrates of MAPKs have been identified at synaptic sites. Central among them are key synaptic scaffold proteins (PSD-95 and PSD-93), cadherin-associated proteins (δ-catenin), Kv4.2 K+ channels, and metabotropic glutamate receptors. Through a reversible phosphorylation event, MAPKs rapidly and efficiently modulate the function of these substrates and thus determine the strength of synaptic transmission. This review summarizes the recent progress in cell biology of synaptic MAPKs and analyzes roles of this specific pool of MAPKs in regulating local substrates and synaptic plasticity.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Volmat V, Pouyssegur J (2001) Spatiotemporal regulation of the p42/p44 MAPK pathway. Biol Cell 93:71–79
Gallo KA, Johnson GL (2002) Mixed-lineage kinase control of JNK and p38 MAPK pathways. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:663–672
Songyang Z, Lu KP, Kwon YT, Tsai LH, Filhol O, Cochet C, Brickey DA, Soderling TR, Bartleson C, Graves DJ, DeMaggio AJ, Hoekstra MF, Blenis J, Hunter T, Cantley LC (1996) A structure basis for substrate specificities of protein Ser/Thr kinases: primary sequence preference of casein kinases I and II, NIMA, phosphorylase kinase, calmodulin-dependent kinase II, CDK5, and Erk1. Mol Cell Biol 16:6486–6493
Sweatt JD (2004) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in synaptic plasticity and memory. Curr Opin Neurobiol 14:311–317
Thomas GM, Huganir RL (2004) MAPK cascade signaling and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:173–183
Wang JQ, Fibuch EE, Mao LM (2007) Regulation of mitogen-activated protein kinases by glutamate receptors. J Neurochem 100:1–11
Ortiz J, Harris HW, Guitart X, Terwilliger RZ, Haycock JW, Nestler EJ (1995) Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases (ERKs) and ERK kinase (MEK) in brain: regional distribution and regulation by chronic morphine. J Neurosci 15:1285–1297
Boggio EM, Putignano E, Sassoe-Pognetto M, Pizzorusso T, Glustetto M (2007) Visual stimulation activates ERK in synaptic and somatic compartments of rat cortical neurons with parallel kinetics. PLoS ONE 2:e604
Sindreu CB, Scheiner ZS, Storm DR (2007) Ca2+-stimulated adenylyl cyclases regulate ERK-dependent activation of MSK1 during fear conditioning. Neuron 53:79–89
Mao LM, Reusch JM, Fibuch EE, Liu Z, Wang JQ (2013) Amphetamine increases phosphorylation of MAPK/ERK at synaptic sites in the rat striatum and medial prefrontal cortex. Brain Res 1494:101–108
Suzuki T, Okumura-Noji K, Nishida E (1995) ERK2-type mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and its substrates in postsynaptic density fractions from the rat brain. Neurosci Res 22:277–285
Suzuki T, Mitake S, Murata S (1999) Presence of up-stream and downstream components of a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in the PSD of the rat forebrain. Brain Res 840:36–44
Xue B, Mao LM, Jin DZ, Wang JQ (2015) Regulation of synaptic MAPK/ERK phosphorylation in the rat striatum and medial prefrontal cortex by dopamine and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors. J Neurosci Res 93(10):1592–9
Edbauer D, Cheng D, Batterton MN, Wang CF, Duong DM, Yaffe MB, Peng J, Shang M (2009) Identification and characterization of neuronal mitogen-activated protein kinase substrates using a specific phosphomotif antibody. Mol Cell Proteomics 8:681–695
Sabio G, Reuver S, Feijoo C, Hasegawa M, Thomas GM, Centeno F, Kuhlendahl F, Leal-Ortiz S, Goedert M, Garner C, Cuenda A (2004) Stress- and mitogen-induced phosphorylation of the synapse-associated protein SAP90/PSD-95 by activation of SAPK3/p38gamma and ERK1/ERK2. Biochem J 380:19–30
Xu W (2011) PSD-95 like membrane associated guanylate kinases (PSD-MAGUKs) and synaptic plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 21:306–312
DeGiorgis JA, Jaffe H, Moreira JE, Carlotti CG Jr, Leite JP, Dosemeci A (2005) Phosphoproteomic analysis of synaptosomes from human cerebral cortex. J Proteome Res 4:306–315
Jaffe H, Vinade L, Dosemeci A (2004) Identification of novel phosphorylation sites on postsynaptic density proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 321:210–218
Nada S, Shima T, Yanai H, Husi H, Grant SGN, Okada M, Akiyama T (2003) Identification of PSD-93 as a substrate for the Src family tyrosine kinase Fyn. J Biol Chem 48:47610–47621
Guo ML, Xue B, Jin DZ, Mao LM, Wang JQ (2012) Interactions and phosphorylation of postsynaptic density 93 (PSD-93) by extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). Brain Res 1460:18–25
Israely I, Costa RM, Xie CW, Silva AJ, Kosik KS, Liu X (2004) Deletion of the neuron-specific protein delta-catenin leads to severe cognitive and synaptic dysfunction. Curr Biol 14:1657–1663
Martinez MC, Ochiishi T, Majewski M, Kosik KS (2003) Dual regulation of neuronal morphogenesis by a δ-catenin-cortactin complex and Rho. J Cell Biol 162:99–111
Kosik KS, Donahue CP, Israely I, Liu X, Ochiishi T (2005) δ-Catenin at the synaptic-adherens junction. Trends Cell Biol 15:172–178
Hoffman DA, Magee JC, Colbert CM, Johnston D (1997) K+ channel regulation of signal propagation in dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Nature 387:869–875
Sheng M, Tsaur ML, Jan YN, Jan LY (1992) Subcellular segregation of two A-type K+ channel proteins in rat central neurons. Neuron 9:271–284
Hu HJ, Glauner KS, Gereau RW 4th (2003) ERK integrates PKA and PKC signaling in superficial dorsal horn neurons. I. Modulation of A-type K+ currents. J Neurophysiol 90:1671–1679
Yuan LL, Adams JP, Swank M, Sweatt JD, Johnson D (2002) Protein kinase modulation of dendritic K+ channels in hippocampal involves a mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. J Neurosci 22:4860–4868
Adams JP, Anderson AE, Varga AW, Dineley KT, Cook RG, Pfaffinger PJ, Sweatt JD (2000) The A-type potassium channel Kv4.2 is a substrate for the mitogen-activated protein kinase ERK. J Neurochem 75:2277–2287
Schrader LA, Bimbaum SG, Nadin BM, Ren Y, Bui D, Anderson AE, Sweatt JD (2006) ERK/MAPK regulates the Kv4.2 potassium channel by direct phosphorylation of the pore-forming subunit. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290:C852–861
Niswender CM, Conn PJ (2010) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: physiology, pharmacology, and disease. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 50:295–322
Lujan R, Nusser Z, Roberts JD, Shigemoto R, Somogyi P (1996) Perisynaptic location of metabotropic glutamate receptors mGluR1 and mGluR5 on dendrites and dendritic spines in the rat hippocampus. Eur J Neurosci 8:1488–1500
Kuwajima M, Hall RA, Aiba A, Smith Y (2004) Subcellular and subsynaptic localization of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors in the monkey subthalamic nucleus. J Comp Neurol 474:589–602
Enz R (2007) The trick of the tail: protein-protein interactions of metabotropic glutamate receptors. Bioessays 29:60–73
Enz R (2012) Metabotropic glutamate receptors and interacting proteins: evolving drug targets. Curr Drug Targets 13:145–156
Fagni L (2012) Diversity of metabotropic glutamate receptor-interacting proteins and pathophysiological functions. Adv Exp Med Biol 970:63–79
Dhami GK, Ferguson SS (2006) Regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor signaling, desensitization and endocytosis. Pharmacol Ther 111:260–271
Jin DZ, Guo ML, Xue B, Fibuch EE, Choe ES, Mao LM, Wang JQ (2013) Phosphorylation and feedback regulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 by calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. J Neurosci 33:3402–3412
Kim CH, Lee J, Lee JY, Roche KW (2008) Metabotropic glutamate receptors: phosphorylation and receptor signaling. J Neurosci Res 86:1–10
Mao LM, Guo ML, Jin DZ, Fibuch EE, Choe ES, Wang JQ (2011) Posttranslational modification biology of glutamate receptors and drug addiction. Front Neuroanat 5:19
Orlando LR, Ayala R, Kett LR, Curley AA, Duffner J, Bragg DC, Tsai LH, Dunah AW, Young AB (2009) Phosphorylation of the homer-binding domain of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors by cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J Neurochem 110:557–569
Hu JH, Yang L, Kammermeier PJ, Moore CG, Brakeman PR, Tu J, Yu S, Petralia RS, Li Z, Zhang PW, Park JM, Dong X, Xiao B, Worley PF (2012) Preso1 dynamically regulates group I metabotropic glutamate receptors. Nat Neurosci 15:836–844
Park JM, Hu JH, Milshteyn A, Zhang PW, Moore CG, Park S, Datko MC, Domingo RD, Reyes CM, Wang XJ, Etzkorn FA, Xiao B, Szumlinski KK, Kern D, Linden DJ, Worley PF (2013) A prolyl-isomerase mediates dopamine-dependent plasticity and cocaine motor sensitization. Cell 154:637–650
Stornetta RL, Zhu JJ (2011) Ras and Rap signaling in synaptic plasticity and mental disorders. Neuroscientist 17:54–78
McCormack SG, Stornetta RL, Zhu JJ (2006) Synaptic AMPA receptors exchange maintains bidirectional plasticity. Neuron 50:75–88
Qin Y, Zhu Y, Baumqart JP, Stornetta RL, Seidenman K, Mack V, van Aelst L, Zhu JJ (2005) State-dependent Ras signaling and AMPA receptor trafficking. Genes Dev 19:2000–2015
Zhu JJ, Qin Y, Zhao M, Van Aelst L, Malinow R (2002) Ras and Rap control AMPA receptor trafficking during synaptic plasticity. Cell 110:443–455
Zhu JJ (2009) Activity level-dependent synapse-specific AMPA receptor trafficking regulates transmission kinetics. J Neurosci 29:6320–6335
Jovanovic JN, Benfenati F, Siow YL, Sihra TS, Sanghera JS, Pelech SL, Greengard P, Czernik AJ (1996) Neurotrophins stimulate phosphorylation of synapsin I by MAP kinase and regulate synapsin I-actin interactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:3679–3683
Vara H, Onofri F, Benfenati F, Sassoe-Pognetto M, Giustetto M (2009) ERK activation in axonal varicosities modulates presynaptic plasticity in the CA3 region of the hippocampus through synapsin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:9872–9877
Treisman R (1996) Regulation of transcription by MAP kinase cascades. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8:205–215
Kosako H, Yamaguchi N, Aranami C, Ushiyama M, Kose S, Imamoto N, Taniguchi H, Nishida E, Hattori S (2009) Phosphoproteomics reveals new ERK MAP kinase targets and links ERK to nucleoporin-mediated nuclear transport. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16:1026–1035
Sutton MA, Schuman EM (2006) Dendritic protein synthesis, synaptic plasticity, and memory. Cell 127:49–58
Gong R, Tang SJ (2006) Mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling is essential for activity-dependent dendritic protein synthesis. Neuroreport 17:1575–1578
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the NIH grants DA10355 (J.Q.W.) and MH61469 (J.Q.W.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mao, LM., Wang, J.Q. Synaptically Localized Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases: Local Substrates and Regulation. Mol Neurobiol 53, 6309–6315 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9535-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9535-1