Abstract
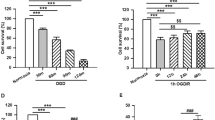
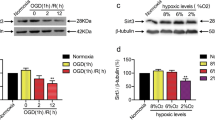
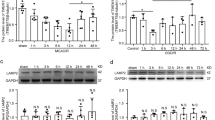
Disturbance of neuregulin-1β/ErbB4 signaling is considered to be associated with brain ischemia, but the mechanisms of this disruption are largely unknown. In the present study, we provide evidence that degradation of ErbB4 is involved in neuronal cell death in response to ischemia. Our data showed that the application of neuregulin-1β provided significant protection against oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD)-induced neuronal death as detected by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, annexin V/propidium iodide flow cytometry analysis and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining. Furthermore, neuregulin-1β treatment significantly reduced the infarct volume of ischemic mice, and this result was not seen in the ErbB4 knockout mice. We found that brain ischemia induced the breakdown of ErbB4 in a time-dependent manner in vivo, but not that of ErbB2. In vitro studies further indicated that recombinant calpain induced the cleavage of ErbB4 in a dose-dependent way, whereas the calpain inhibitor significantly reduced the OGD-induced ErbB4 breakdown. Additionally, OGD-induced apoptosis was partially abolished by transfection with the ErbB4E872K mutant. Taken together, neuregulin-1β elicits its neuroprotective effect in an ErbB4-dependent manner, and the cleavage of ErbB4 by calpain contributes to a neuronal cell death cascade during brain ischemia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moskowitz MA, Lo EH, Iadecola C (2010) The science of stroke: mechanisms in search of treatments. Neuron 67:181–198
Tymianski M (2011) Emerging mechanisms of disrupted cellular signaling in brain ischemia. Nat Neurosci 14:1369–1373
Lo EH, Moskowitz MA, Jacobs TP (2005) Exciting, radical, suicidal: how brain cells die after stroke. Stroke 36:189–192
Yarden Y, Sliwkowski MX (2001) Untangling the ErbB signalling network. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2:127–137
Shamir A, Kwon OB, Karavanova I, Vullhorst D, Leiva-Salcedo E, Janssen MJ, Buonanno A (2012) The importance of the NRG-1/ErbB4 pathway for synaptic plasticity and behaviors associated with psychiatric disorders. J Neurosci 32:2988–2997
Huang YZ, Won S, Ali DW, Wang Q, Tanowitz M, Du QS, Pelkey KA, Yang DJ et al (2000) Regulation of neuregulin signaling by PSD-95 interac1ting with ErbB4 at CNS synapses. Neuron 26:443–455
Ma L, Huang YZ, Pitcher GM, Valtschanoff JG, Ma YH, Feng LY, Lu B, Xiong WC et al (2003) Ligand-dependent recruitment of the ErbB4 signaling complex into neuronal lipid rafts. J Neurosci 23:3164–3175
Neddens J, Buonanno A (2010) Selective populations of hippocampal interneurons express ErbB4 and their number and distribution is altered in ErbB4 knockout mice. Hippocampus 20:724–744
Tan GH, Liu YY, Hu XL, Yin DM, Mei L, Xiong ZQ (2012) Neuregulin 1 represses limbic epileptogenesis through ErbB4 in parvalbumin-expressing interneurons. Nat Neurosci 15:258–266
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Yang HI, Thajeb P, Li H (2004) Neuregulin-1 reduces ischemia-induced brain damage in rats. Neurobiol Aging 25:935–944
Xu Y, Li X, Zhou M (2009) Neuregulin-1/ErbB signaling: a druggable target for treating heart failure. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:214–219
Li Y, Lein PJ, Liu C, Bruun DA, Giulivi C, Ford GD, Tewolde T, Ross-Inta C et al (2012) Neuregulin-1 is neuroprotective in a rat model of organophosphate-induced delayed neuronal injury. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 262:194–204
Chen YJ, Zhang M, Yin DM, Wen L, Ting A, Wang P, Lu YS, Zhu XH et al (2010) ErbB4 in parvalbumin-positive interneurons is critical for neuregulin 1 regulation of long-term potentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:21818–21823
Fisahn A, Neddens J, Yan L, Buonanno A (2009) Neuregulin-1 modulates hippocampal gamma oscillations: implications for schizophrenia. Cereb Cortex 19:612–618
Zhou W, Carpenter G (2000) Heregulin-dependent trafficking and cleavage of ErbB-4. J Biol Chem 275:34737–34743
Lee HJ, Jung KM, Huang YZ, Bennett LB, Lee JS, Mei L, Kim TW (2002) Presenilin-dependent gamma-secretase-like intramembrane cleavage of ErbB4. J Biol Chem 277:6318–6323
Higa-Nakamine S, Maeda N, Toku S, Yamamoto T, Yingyuenyong M, Kawahara M, Yamamoto H (2012) Selective cleavage of ErbB4 by G-protein-coupled gonadotropin-releasing hormone receptor in cultured hypothalamic neurons. J Cell Physiol 227:2492–2501
Gassmann M, Casagranda F, Orioli D, Simon H, Lai C, Klein R, Lemke G (1995) Aberrant neural and cardiac development in mice lacking the ErbB4 neuregulin receptor. Nature 378:390–394
Golding JP, Trainor P, Krumlauf R, Gassmann M (2000) Defects in pathfinding by cranial neural crest cells in mice lacking the neuregulin receptor ErbB4. Nat Cell Biol 2:103–109
Tidcombe H, Jackson-Fisher A, Mathers K, Stern DF, Gassmann M, Golding JP (2003) Neural and mammary gland defects in ErbB4 knockout mice genetically rescued from embryonic lethality. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(14):8281–8286
Tvorogov D, Sundvall M, Kurppa K, Hollmen M, Repo S, Johnson MS, Elenius K (2009) Somatic mutations of ErbB4: selective loss-of-function phenotype affecting signal transduction pathways in cancer. J Biol Chem 284:5582–5591
Neumar RW, Xu YA, Gada H, Guttmann RP, Siman R (2003) Cross-talk between calpain and caspase proteolytic systems during neuronal apoptosis. J Biol Chem 278:14162–14167
Yamashima T (2004) Ca2+-dependent proteases in ischemic neuronal death: a conserved ‘calpain-cathepsin cascade’ from nematodes to primates. Cell Calcium 36:285–293
Croall DE, Ersfeld K (2007) The calpains: modular designs and functional diversity. Genome Biol 8(6):218
Liu J, Liu MC, Wang KK (2008) Calpain in the CNS: from synaptic function to neurotoxicity. Sci Signal 1(14):re1
Tsubokawa T, Solaroglu I, Yatsushige H, Cahill J, Yata K, Zhang JH (2006) Cathepsin and calpain inhibitor E64d attenuates matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Stroke 37:1888–1894
Koumura A, Nonaka Y, Hyakkoku K, Oka T, Shimazawa M, Hozumi I, Inuzuka T, Hara H (2008) A novel calpain inhibitor, ((1S)-1((((1S)-1-benzyl-3-cyclopropylamino-2,3-di-oxopropyl)amino)carbonyl)-3-met hylbutyl) carbamic acid 5-methoxy-3-oxapentyl ester, protects neuronal cells from cerebral ischemia-induced damage in mice. Neuroscience 157:309–318
Li XM, Yang JM, Hu DH, Hou FQ, Zhao M, Zhu XH, Wang Y, Li JG et al (2007) Contribution of downregulation of L-type calcium currents to delayed neuronal death in rat hippocampus after global cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. J Neurosci 27:5249–5259
Liu QB, Liu LL, Lu YM, Tao RR, Huang JY, Han F (2010) Lou YJ (2010) The induction of reactive oxygen species and loss of mitochondrial Omi/HtrA2 is associated with S-nitrosoglutathione-induced apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Toxicol Appl Pharm 244:374–384
Han F, Tao RR, Zhang GS, Lu YM, Liu LL, Chen YX, Lou YJ, Fukunaga K et al (2011) Melatonin ameliorates ischemic-like injury-evoked nitrosative stress: Involvement of HtrA2/PED pathways in endothelial cells. J Pineal Res 50:281–291
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Fischer R, Torres-Badillo CC, Davies HA, Logan K, Pfizenmaier K, Male DK, Sharrack B et al (2012) Role of caspases in cytokine-induced barrier breakdown in human brain endothelial cells. J Immunol 189:3130–3139
Birukova AA, Zebda N, Fu P, Poroyko V, Cokic I, Birukov KG (2010) Association between adherens junctions and tight junctions via Rap1 promotes barrier protective effects of oxidized phospholipids. J Cell Physiol 226:2052–2062
Han F, Ali Raie A, Shioda N, Qin ZH, Fukunaga K (2008) Accumulation of beta-amyloid in the brain microvessels accompanies increased hyperphosphorylated tau proteins following microsphere embolism in aged rats. Neuroscience 153:414–427
Li KX, Lu YM, Xu ZH, Zhang J, Zhu JM, Zhang JM, Cao SX, Chen XJ et al (2012) Neuregulin 1 regulates excitability of fast-spiking neurons through Kv1.1 and acts in epilepsy. Nat Neurosci 15:267–273
Shioda N, Han F, Moriguchi S, Fukunaga K (2007) Constitutively active calcineurin mediates delayed neuronal death through Fas-ligand expression via activation of NFAT and FKHR transcriptional activities in mouse brain ischemia. J Neurochem 102:1506–1517
Han F, Chen YX, Lu YM, Huang JY, Zhang GS, Tao RR, Ji YL, Liao MH et al (2011) Regulation of the ischemia-induced autophagy-lysosome processes by nitrosative stress in endothelial cells. J Pineal Res 51:124–135
Shioda N, Ishigami T, Han F, Moriguchi S, Shibuya M, Iwabuchi Y, Fukunaga K (2007) Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B pathway by a vanadyl compound mediates its neuroprotective effect in mouse brain ischemia. Neuroscience 148:221–229
Roysommuti S, Carroll SL, Wyss JM (2003) Neuregulin-1beta modulates in vivo entorhinal-hippocampal synaptic transmission in adult rats. Neuroscience 121:779–785
Fleisig H, El-Din El-Husseini A, Vincent SR (2004) Regulation of ErbB4 phosphorylation and cleavage by a novel histidine acid phosphatase. Neuroscience 127:91–100
Neumar RW, Meng FH, Mills AM, Xu YA, Zhang C, Welsh FA, Siman R (2001) Calpain activity in the rat brain after transient forebrain ischemia. Exp Neurol 170:27–35
Shioda N, Moriguchi S, Shirasaki Y, Fukunaga K (2006) Generation of constitutively active calcineurin by calpain contributes to delayed neuronal death following mouse brain ischemia. J Neurochem 98:310–320
Xu Z, Ford BD (2005) Upregulation of erbB receptors in rat brain after middle cerebral arterial occlusion. Neurosci Lett 375:181–186
Woo RS, Lee JH, Yu HN, Song DY, Baik TK (2010) Expression of ErbB4 in the apoptotic neurons of Alzheimer’s disease brain. Anat Cell Biol 43:332–339
Xu Z, Jiang J, Ford G, Ford BD (2004) Neuregulin-1 is neuroprotective and attenuates inflammatory responses induced by ischemic stroke. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 322:440–446
Xu Z, Ford GD, Croslan DR, Jiang J, Gates A, Allen R, Ford BD (2005) Neuroprotection by neuregulin-1 following focal stroke is associated with the attenuation of ischemia-induced pro-inflammatory and stress gene expression. Neurobiol Dis 19:461–470
Barros CS, Calabrese B, Chamero P, Roberts AJ, Korzus E, Lloyd K, Stowers L, Mayford M et al (2009) Impaired maturation of dendritic spines without disorganization of cortical cell layers in mice lacking NRG1/ErbB signaling in the central nervous system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4507–4512
Liu Y, Tao YM, Woo RS, Xiong WC, Mei L (2007) Stimulated ErbB4 internalization is necessary for neuregulin signaling in neurons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:505–510
Zhang GS, Tian Y, Huang JY, Tao RR, Liao MH, Lu YM, Ye WF, Wang R et al (2013) The gamma-secretase blocker DAPT reduces the permeability of the blood–brain barrier by decreasing the ubiquitination and degradation of occludin during permanent brain ischemia. CNS Neurosci Ther 19:53–60
Sardi SP, Murtie J, Koirala S, Patten BA, Corfas G (2006) Presenilin-dependent ErbB4 nuclear signaling regulates the timing of astrogenesis in the developing brain. Cell 127:185–197
Golub MS, Germann SL, Lloyd KC (2004) Behavioral characteristics of a nervous system-specific erbB4 knock-out mouse. Behav Brain Res 153:159–170
Law AJ, Kleinman JE, Weinberger DR, Weickert CS (2007) Disease-associated intronic variants in the ErbB4 gene are related to altered ErbB4 splice-variant expression in the brain in schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 16:129–141
Backx L, Ceulemans B, Vermeesch JR, Devriendt K, Van Esch H (2009) Early myoclonic encephalopathy caused by a disruption of the neuregulin-1 receptor ErbB4. Eur J Hum Genet 17:378–382
Veikkolainen V, Vaparanta K, Halkilahti K, Iljin K, Sundvall M, Elenius K (2011) Function of ERBB4 is determined by alternative splicing. Cell Cycle 10:2647–2657
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Josh Huang (CSH, USA) and Dr. X.H. Zhang (ION, China) for kindly providing the PV-Cre miceline. This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81225007, 81202533, 20130633B32). State Key Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (31430034), the Funds for Creative Research Groups of China (81221003), the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20120101110003) , PCSIRT, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, the Zhejiang Province Program for Cultivation of High-level Health talents, New Century 151 Talent Project of Zhejiang Province.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, Ym., Gao, Yp., Tao, Rr. et al. Calpain-Dependent ErbB4 Cleavage Is Involved in Brain Ischemia-Induced Neuronal Death. Mol Neurobiol 53, 2600–2609 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9275-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-015-9275-2