Abstract
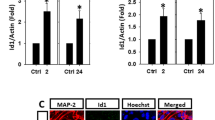
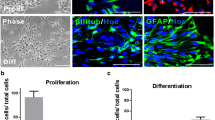
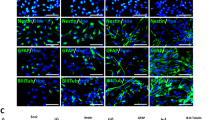
One major pathological hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the accumulation of senile plaques mainly composed of neurotoxic amyloid beta-peptide (Aβ) in the patients’ brains. Sonic hedgehog (SHH) is a morphogen critically involved in the embryonic development of the central nervous system (CNS). In the present study, we tested whether Aβ may induce SHH expression and explored its underlying mechanisms. We found that both Aβ25-35 and Aβ1-42 enhanced SHH expression in the primary cortical neurons derived from fetal rat brains. Immunohistochemistry revealed heightened expression of SHH in the cortex and hippocampus of aged (9 and 12 months old) AD transgenic mouse brains as compared to age-matched littermate controls. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assay demonstrated that Aβ25-35 enhanced binding of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) to the promoter of the Shh gene in primary cortical cultures; consistently, Aβ25-35 induction of SHH was abolished by HIF-1α small interfering RNA (siRNA). Aβ25-35 also time-dependently induced inhibitor of differentiation-1 (Id1) that has been shown to stabilize HIF-1α; further, Aβ25-35-mediated induction of HIF-1α and SHH was both suppressed by Id1 siRNA. Pharmacological induction of HIF-1α by cobalt chloride and application of the cell-permeable recombinant Id1 proteins were both sufficient to induce SHH expression. Finally, both the SHH pathway inhibitor cyclopamine and its neutralizing antibody attenuated Aβ cytotoxicity, albeit to a minor extent. These results thus established a signaling cascade of “Aβ → Id1 → HIF-1 → SHH” in primary rat cortical cultures; furthermore, SHH may in part contribute to Aβ neurotoxicity.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palop JJ, Mucke L (2010) Amyloid-beta-induced neuronal dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease: from synapses toward neural networks. Nat Neurosci 13(7):812–818
O’Brien RJ, Wong PC (2011) Amyloid precursor protein processing and Alzheimer’s disease. Annu Rev Neurosci 34:185–204
Soucek T, Cumming R, Dargusch R, Maher P, Schubert D (2003) The regulation of glucose metabolism by HIF-1 mediates a neuroprotective response to amyloid beta peptide. Neuron 39(1):43–56
Kawamoto EM, Lepsch LB, Boaventura MF, Munhoz CD, Lima LS, Yshii LM, Avellar MC, Curi R, Mattson MP, Scavone C (2008) Amyloid beta-peptide activates nuclear factor-kappaB through an N-methyl-D-aspartate signaling pathway in cultured cerebellar cells. J Neurosci Res 86(4):845–860
Akhter R, Sanphui P, Biswas SC (2014) The essential role of p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis and its regulation by FoxO3a transcription factor in beta-amyloid induced neuron death. J Biol Chem 289(15):10812–10822
Chen YS, Chen SD, Wu CL, Huang SS, Yang DI (2014) Induction of sestrin2 as an endogenous protective mechanism against amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity in primary cortical culture. Exp Neurol 253:63–71
Echelard Y, Epstein DJ, St-Jacques B, Shen L, Mohler J, McMahon JA, McMahon AP (1993) Sonic hedgehog, a member of a family of putative signaling molecules, is implicated in the regulation of CNS polarity. Cell 75(7):1417–1430
Fuccillo M, Joyner AL, Fishell G (2006) Morphogen to mitogen: the multiple roles of hedgehog signalling in vertebrate neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 7(10):772–783
Stone DM, Hynes M, Armanini M, Swanson TA, Gu Q, Johnson RL, Scott MP, Pennica D, Goddard A, Phillips H, Noll M, Hooper JE, de Sauvage F, Rosenthal A (1996) The tumour-suppressor gene patched encodes a candidate receptor for Sonic hedgehog. Nature 384(6605):129–134
Alcedo J, Ayzenzon M, Von Ohlen T, Noll M, Hooper JE (1996) The Drosophila smoothened gene encodes a seven-pass membrane protein, a putative receptor for the hedgehog signal. Cell 86(2):221–232
Riobo NA, Manning DR (2007) Pathways of signal transduction employed by vertebrate Hedgehogs. Biochem J 403(3):369–379
Kenney AM, Cole MD, Rowitch DH (2003) Nmyc upregulation by sonic hedgehog signaling promotes proliferation in developing cerebellar granule neuron precursors. Development 130(1):15–28
Regl G, Kasper M, Schnidar H, Eichberger T, Neill GW, Philpott MP, Esterbauer H, Hauser-Kronberger C, Frischauf AM, Aberger F (2004) Activation of the BCL2 promoter in response to Hedgehog/GLI signal transduction is predominantly mediated by GLI2. Cancer Res 64(21):7724–7731
Leung C, Lingbeek M, Shakhova O, Liu J, Tanger E, Saremaslani P, Van Lohuizen M, Marino S (2004) Bmi1 is essential for cerebellar development and is overexpressed in human medulloblastomas. Nature 428(6980):337–341
Zebedee Z, Hara E (2001) Id proteins in cell cycle control and cellular senescence. Oncogene 20(58):8317–8325
Benezra R, Davis RL, Lockshon D, Turner DL, Weintraub H (1990) The protein Id: a negative regulator of helix-loop-helix DNA binding proteins. Cell 61(1):49–59
Yokota Y, Mori S (2002) Role of Id family proteins in growth control. J Cell Physiol 190(1):21–28
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA, Semenza GL (1995) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92(12):5510–5514
Wang GL, Semenza GL (1995) Purification and characterization of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 270(3):1230–1237
Semenza GL, Jiang BH, Leung SW, Passantino R, Concordet JP, Maire P, Giallongo A (1996) Hypoxia response elements in the aldolase A, enolase 1, and lactate dehydrogenase A gene promoters contain essential binding sites for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 271(51):32529–32537
Semenza GL (2011) Oxygen sensing, homeostasis, and disease. N Engl J Med 365(6):537–547
Semenza GL (2013) HIF-1 mediates metabolic responses to intratumoral hypoxia and oncogenic mutations. J Clin Invest 123(9):3664–3671
Wang GL, Semenza GL (1993) General involvement of hypoxia-inducible factor 1 in transcriptional response to hypoxia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90(9):4304–4308
Chen SD, Wu CL, Lin TK, Chuang YC, Yang DI (2012) Renin inhibitor aliskiren exerts neuroprotection against amyloid beta-peptide toxicity in rat cortical neurons. Neurochem Int 61(3):369–377
Stine WB Jr, Dahlgren KN, Krafft GA, LaDu MJ (2003) In vitro characterization of conditions for amyloid-beta peptide oligomerization and fibrillogenesis. J Biol Chem 278(13):11612–11622
Ju TC, Yang YT, Yang DI (2004) Protective effects of S-nitrosoglutathione against neurotoxicity of 3-nitropropionic acid in rat. Neurosci Lett 362(3):226–231
Ju TC, Chen SD, Liu CC, Yang DI (2005) Protective effects of S-nitrosoglutathione against amyloid beta-peptide neurotoxicity. Free Radic Biol Med 38(7):938–949
Wu CL, Chen SD, Yin JH, Hwang CS, Yang DI (2010) Erythropoietin and sonic hedgehog mediate the neuroprotective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor against mitochondrial inhibition. Neurobiol Dis 40(1):146–154
Wu CL, Yin JH, Hwang CS, Chen SD, Yang DY, Yang DI (2012) c-Jun-dependent sulfiredoxin induction mediates BDNF protection against mitochondrial inhibition in rat cortical neurons. Neurobiol Dis 46(2):450–462
Wu CL, Hwang CS, Yang DI (2009) Protective effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor against neurotoxicity of 3-nitropropionic acid in rat cortical neurons. Neurotoxicology 30(4):718–726
Wu MF, Yin JH, Hwang CS, Tang CM, Yang DI (2014) NAD attenuates oxidative DNA damages induced by amyloid beta-peptide in primary rat cortical neurons. Free Radic Res 48(7):794–805
Jankowsky JL, Fadale DJ, Anderson J, Xu GM, Gonzales V, Jenkins NA, Copeland NG, Lee MK, Younkin LH, Wagner SL, Younkin SG, Borchelt DR (2004) Mutant presenilins specifically elevate the levels of the 42 residue beta-amyloid peptide in vivo: evidence for augmentation of a 42-specific gamma secretase. Hum Mol Genet 13(2):159–170
Volianskis A, Kostner R, Molgaard M, Hass S, Jensen MS (2010) Episodic memory deficits are not related to altered glutamatergic synaptic transmission and plasticity in the CA1 hippocampus of the APPswe/PS1deltaE9-deleted transgenic mice model of β-amyloidosis. Neurobiol Aging 31(7):1173–1187
Bijlsma MF, Groot AP, Oduro JP, Franken RJ, Schoenmakers SH, Peppelenbosch MP, Spek CA (2009) Hypoxia induces a hedgehog response mediated by HIF-1alpha. J Cell Mol Med 13(8B):2053–2060
Mabjeesh NJ, Escuin D, LaVallee TM, Pribluda VS, Swartz GM, Johnson MS, Willard MT, Zhong H, Simons JW, Giannakakou P (2003) 2ME2 inhibits tumor growth and angiogenesis by disrupting microtubules and dysregulating HIF. Cancer Cell 3(4):363–375
Perk J, Iavarone A, Benezra R (2005) Id family of helix-loop-helix proteins in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5(8):603–614
Jung S, Park RH, Kim S, Jeon YJ, Ham DS, Jung MY, Kim SS, Lee YD, Park CH, Suh-Kim H (2010) Id proteins facilitate self-renewal and proliferation of neural stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 19(6):831–841
Kim HJ, Chung H, Yoo YG, Kim H, Lee JY, Lee MO, Kong G (2007) Inhibitor of DNA binding 1 activates vascular endothelial growth factor through enhancing the stability and activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha. Mol Cancer Res 5(4):321–329
Lee TK, Poon RT, Yuen AP, Ling MT, Wang XH, Wong YC, Guan XY, Man K, Tang ZY, Fan ST (2006) Regulation of angiogenesis by Id-1 through hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha-mediated vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 12(23):6910–6919
Lofstedt T, Jogi A, Sigvardsson M, Gradin K, Poellinger L, Pahlman S, Axelson H (2004) Induction of ID2 expression by hypoxia-inducible factor-1: a role in dedifferentiation of hypoxic neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 279(38):39223–39231
Favaro R, Valotta M, Ferri AL, Latorre E, Mariani J, Giachino C, Lancini C, Tosetti V, Ottolenghi S, Taylor V, Nicolis SK (2009) Hippocampal development and neural stem cell maintenance require Sox2-dependent regulation of Shh. Nat Neurosci 12(10):1248–1256
Chen JK, Taipale J, Cooper MK, Beachy PA (2002) Inhibition of Hedgehog signaling by direct binding of cyclopamine to Smoothened. Genes Dev 16(21):2743–2748
Mille F, Thibert C, Fombonne J, Rama N, Guix C, Hayashi H, Corset V, Reed JC, Mehlen P (2009) The Patched dependence receptor triggers apoptosis through a DRAL-caspase-9 complex. Nat Cell Biol 11(6):739–746
He P, Staufenbiel M, Li R, Shen Y (2014) Deficiency of Patched 1-induced Gli1 signal transduction results in astrogenesis in Swedish mutated APP transgenic mice. Hum Mol Genet 23(24):6512–6527
Wu CL, Chen SD, Hwang CS, Yang DI (2009) Sonic hedgehog mediates BDNF-induced neuroprotection against mitochondrial inhibitor 3-nitropropionic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 385(1):112–117
Kusano KF, Pola R, Murayama T, Curry C, Kawamoto A, Iwakura A, Shintani S, Ii M, Asai J, Tkebuchava T, Thorne T, Takenaka H, Aikawa R, Goukassian D, von Samson P, Hamada H, Yoon YS, Silver M, Eaton E, Ma H, Heyd L, Kearney M, Munger W, Porter JA, Kishore R, Losordo DW (2005) Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: tissue repair through transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med 11(11):1197–1204
Ruiz i Altaba A, Palma V, Dahmane N (2002) Hedgehog-Gli signalling and the growth of the brain. Nat Rev Neurosci 3(1):24–33
Wang G, Zhang Z, Xu Z, Yin H, Bai L, Ma Z, Decoster MA, Qian G, Wu G (2010) Activation of the sonic hedgehog signaling controls human pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation in response to hypoxia. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803(12):1359–1367
Kasperczyk H, Baumann B, Debatin KM, Fulda S (2009) Characterization of sonic hedgehog as a novel NF-kappaB target gene that promotes NF-kappaB-mediated apoptosis resistance and tumor growth in vivo. FASEB J 23(1):21–33
Nakashima H, Nakamura M, Yamaguchi H, Yamanaka N, Akiyoshi T, Koga K, Yamaguchi K, Tsuneyoshi M, Tanaka M, Katano M (2006) Nuclear factor-kappaB contributes to hedgehog signaling pathway activation through sonic hedgehog induction in pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res 66(14):7041–7049
Guo S, Bragina O, Xu Y, Cao Z, Chen H, Zhou B, Morgan M, Lin Y, Jiang BH, Liu KJ, Shi H (2008) Glucose up-regulates HIF-1 alpha expression in primary cortical neurons in response to hypoxia through maintaining cellular redox status. J Neurochem 105(5):1849–1860
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Council/Ministry of Science and Technology in Taiwan (NSC 101-2314-B-010-042MY2 and MOST 103-2314-B-010-013MY3 to Ding-I Yang; NSC 102-2314-B-038-024 to Liang-Yo Yang), Ministry of Education in Taiwan Aim for the Top University Plan (103AC-B5 to Ding-I Yang), Department of Health in Taipei City Government (10201-62-067 and 10301-62-003 to Ding-I Yang and Chi-Shin Hwang), and Cheng Hsin General Hospital (102F218C12 and 103F003C16 to Ding-I Yang and Jiu-Haw Yin).
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no actual or potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yu-Hsing Hung and Shih-Hsin Chang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hung, YH., Chang, SH., Huang, CT. et al. Inhibitor of Differentiation-1 and Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-1 Mediate Sonic Hedgehog Induction by Amyloid Beta-Peptide in Rat Cortical Neurons. Mol Neurobiol 53, 793–809 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9046-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-9046-5