Abstract
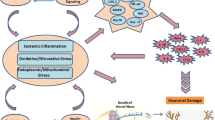
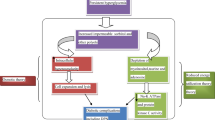
There are still no approved treatments for the prevention or of cure of diabetic neuropathy, and only symptomatic pain therapies of variable efficacy are available. Inflammation is a cardinal pathogenic mechanism of diabetic neuropathy. The relationships between inflammation and the development of diabetic neuropathy involve complex molecular networks and processes. Herein, we review the key inflammatory molecules (inflammatory cytokines, adhesion molecules, chemokines) and pathways (nuclear factor kappa B, JUN N-terminal kinase) implicated in the development and progression of diabetic neuropathy. Advances in the understanding of the roles of these key inflammatory molecules and pathways in diabetic neuropathy will facilitate the discovery of the potential of anti-inflammatory approaches for the inhibition of the development of neuropathy. Specifically, many anti-inflammatory drugs significantly inhibit the development of different aspects of diabetic neuropathy in animal models and clinical trials.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edwards JL, Vincent AM, Cheng HT, Feldman EL (2008) Diabetic neuropathy: mechanisms to management. Pharmacol Ther 120(1):1–34
Nowicki M, Kosacka J, Serke H, Bluher M, Spanel-Borowski K (2012) Altered sciatic nerve fiber morphology and endoneural microvessels in mouse models relevant for obesity, peripheral diabetic polyneuropathy, and the metabolic syndrome. J Neurosci Res 90(1):122–131
Pop-Busui R, Herman WH, Feldman EL, Low PA, Martin CL, Cleary PA, Waberski BH, Lachin JM, Albers JW, Group DER (2010) DCCT and EDIC studies in type 1 diabetes: lessons for diabetic neuropathy regarding metabolic memory and natural history. Curr Diab Rep 10(4):276–282
Vincent AM, Callaghan BC, Smith AL, Feldman EL (2011) Diabetic neuropathy: cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Neurol 7(10):573–583
Obrosova IG, Ilnytska O, Lyzogubov VV, Pavlov IA, Mashtalir N, Nadler JL, Drel VR (2007) High-fat diet induced neuropathy of pre-diabetes and obesity: effects of "healthy" diet and aldose reductase inhibition. Diabetes 56(10):2598–2608
Brownlee M (2001) Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 414(6865):813–820
Tecilazich F, Dinh T, Lyons TE, Guest J, Villafuerte RA, Sampanis C, Gnardellis C, Zuo CS, Veves A (2013) Postexercise phosphocreatine recovery, an index of mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, is reduced in diabetic patients with lower extremity complications. J Vasc Surg 57(4):997–1005
Toyooka K, Fujimura H (2009) Iatrogenic neuropathies. Curr Opin Neurol 22(5):475–479
Kaley TJ, Deangelis LM (2009) Therapy of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. Br J Haematol 145(1):3–14
Freehill MT, Shi LL, Tompson JD, Warner JJ (2012) Suprascapular neuropathy: diagnosis and management. Phys Sportsmed 40(1):72–83
Boykin RE, Friedman DJ, Higgins LD, Warner JJ (2010) Suprascapular neuropathy. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(13):2348–2364
Tang CY, Fung B (2011) The last defence? Surgical aspects of gouty arthritis of hand and wrist. Hong Kong Med J 17(6):480–486
Douglas EW (2011) Inflammatory mediators in diabetic neuropathy. J Diabetes Metab S5–004
Bluher M, Unger R, Rassoul F, Richter V, Paschke R (2002) Relation between glycaemic control, hyperinsulinaemia and plasma concentrations of soluble adhesion molecules in patients with impaired glucose tolerance or Type II diabetes. Diabetologia 45(2):210–216
Burke B, Giannoudis A, Corke KP, Gill D, Wells M, Ziegler-Heitbrock L, Lewis CE (2003) Hypoxia-induced gene expression in human macrophages: implications for ischemic tissues and hypoxia-regulated gene therapy. Am J Pathol 163(4):1233–1243
Zent R, Pozzi A (2007) Angiogenesis in diabetic nephropathy. Semin Nephrol 27(2):161–171
Chavez JC, Almhanna K, Berti-Mattera LN (2005) Transient expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha and target genes in peripheral nerves from diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 374(3):179–182
Doss DJ, Kuruvilla R, Bianchi R, Peterson RG, Eichberg J (1997) Effects of hypoxia and severity of diabetes on Na, K-ATPase activity and arachidonoyl-containing glycerophospholipid molecular species in nerve from streptozotocin diabetic rats. J Peripher Nerv Syst 2(2):155–163
Grafe P, Bostock H, Schneider U (1994) The effects of hyperglycaemic hypoxia on rectification in rat dorsal root axons. J Physiol 480(Pt 2):297–307
Honma H, Gross L, Windebank AJ (2004) Hypoxia-induced apoptosis of dorsal root ganglion neurons is associated with DNA damage recognition and cell cycle disruption in rats. Neurosci Lett 354(2):95–98
Veves A, Donaghue VM, Sarnow MR, Giurini JM, Campbell DR, LoGerfo FW (1996) The impact of reversal of hypoxia by revascularization on the peripheral nerve function of diabetic patients. Diabetologia 39(3):344–348
Juranek JK, Geddis MS, Song F, Zhang J, Garcia J, Rosario R, Yan SF, Brannagan TH, Schmidt AM (2013) RAGE deficiency improves postinjury sciatic nerve regeneration in type 1 diabetic mice. Diabetes 62(3):931–943
Empl M, Renaud S, Erne B, Fuhr P, Straube A, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Steck AJ (2001) TNF-alpha expression in painful and nonpainful neuropathies. Neurology 56(10):1371–1377
Yamakawa I, Kojima H, Terashima T, Katagi M, Oi J, Urabe H, Sanada M, Kawai H, Chan L, Yasuda H, Maegawa H, Kimura H (2011) Inactivation of TNF-alpha ameliorates diabetic neuropathy in mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 301(5):E844–852
Leung L, Cahill CM (2010) TNF-alpha and neuropathic pain—a review. J Neuroinflammation 7:27
Liao YH, Zhang GH, Jia D, Wang P, Qian NS, He F, Zeng XT, He Y, Yang YL, Cao DY, Zhang Y, Wang DS, Tao KS, Gao CJ, Dou KF (2011) Spinal astrocytic activation contributes to mechanical allodynia in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Brain Res 1368:324–335
Ren PC, Zhang Y, Zhang XD, An LJ, Lv HG, He J, Gao CJ, Sun XD (2012) High-mobility group box 1 contributes to mechanical allodynia and spinal astrocytic activation in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Brain Res Bull 88(4):332–337
Talbot S, Chahmi E, Dias JP, Couture R (2010) Key role for spinal dorsal horn microglial kinin B1 receptor in early diabetic pain neuropathy. J Neuroinflammation 7(1):36
Wen YR, Tan PH, Cheng JK, Liu YC, Ji RR (2011) Microglia: a promising target for treating neuropathic and postoperative pain, and morphine tolerance. J Formos Med Assoc 110(8):487–494
Zhou R, Tardivel A, Thorens B, Choi I, Tschopp J (2010) Thioredoxin-interacting protein links oxidative stress to inflammasome activation. Nat Immunol 11(2):136–140
Shelbaya S, Amer H, Seddik S, Allah AA, Sabry IM, Mohamed T, El Mosely M (2012) Study of the role of interleukin-6 and highly sensitive C-reactive protein in diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetic patients. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 16(2):176–182
Cotter MA, Gibson TM, Nangle MR, Cameron NE (2010) Effects of interleukin-6 treatment on neurovascular function, nerve perfusion and vascular endothelium in diabetic rats. Diabetes Obes Metab 12(8):689–699
Doupis J, Lyons TE, Wu S, Gnardellis C, Dinh T, Veves A (2009) Microvascular reactivity and inflammatory cytokines in painful and painless peripheral diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94(6):2157–2163
Yu LN, Yang XS, Hua Z, Xie W (2009) Serum levels of pro-inflammatory cytokines in diabetic patients with peripheral neuropathic pain and the correlation among them. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi 89(7):469–471
Kolla VK, Madhavi G, Pulla Reddy B, Srikanth Babu BM, Yashovanthi J, Valluri VL, Ramesh J, Akka J (2009) Association of tumor necrosis factor alpha, interferon gamma and interleukin 10 gene polymorphisms with peripheral neuropathy in South Indian patients with type 2 diabetes. Cytokine 47(3):173–177
Bour-Jordan H, Thompson HL, Bluestone JA (2005) Distinct effector mechanisms in the development of autoimmune neuropathy versus diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. J Immunol 175(9):5649–5655
Press R, Deretzi G, Zou LP, Zhu J, Fredman P, Lycke J, Link H (2001) IL-10 and IFN-gamma in Guillain–Barre syndrome. Network Members of the Swedish Epidemiological Study Group. J Neuroimmunol 112(1–2):129–138
Herder C, Lankisch M, Ziegler D, Rathmann W, Koenig W, Illig T, Doring A, Thorand B, Holle R, Giani G, Martin S, Meisinger C (2009) Subclinical inflammation and diabetic polyneuropathy: MONICA/KORA Survey F3 (Augsburg, Germany). Diabetes Care 32(4):680–682
Papanas N, Katsiki N, Papatheodorou K, Demetriou M, Papazoglou D, Gioka T, Maltezos E (2011) Peripheral neuropathy is associated with increased serum levels of uric acid in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Angiology 62(4):291–295
Azenabor A, Ogbera AO, Adejumo NE, Adejare AO (2011) Acute phase reactant dynamics and incidence of microvascular dysfunctions in type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Res Med Sci 16(10):1298–1305
Zubair M, Malik A, Ahmad J (2012) Plasma adiponectin, IL-6, hsCRP, and TNF-alpha levels in subject with diabetic foot and their correlation with clinical variables in a North Indian tertiary care hospital. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 16(5):769–776
Lin CW, Hsu LA, Chen CC, Yeh JT, Sun JH, Lin CH, Chen ST, Hsu BR, Huang YY (2010) C-reactive protein as an outcome predictor for percutaneous transluminal angioplasty in diabetic patients with peripheral arterial disease and infected foot ulcers. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 90(2):167–172
Jeandrot A, Richard JL, Combescure C, Jourdan N, Finge S, Rodier M, Corbeau P, Sotto A, Lavigne JP (2008) Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein concentrations to distinguish mildly infected from non-infected diabetic foot ulcers: a pilot study. Diabetologia 51(2):347–352
Jude EB, Abbott CA, Young MJ, Anderson SG, Douglas JT, Boulton AJ (1998) The potential role of cell adhesion molecules in the pathogenesis of diabetic neuropathy. Diabetologia 41(3):330–336
Zakareia FA (2008) Electrophysiological changes, plasma vascular endothelial growth factor, fatty acid synthase, and adhesion molecules in diabetic neuropathy. Neurosciences 13(4):374–379
Albertini JP, Valensi P, Lormeau B, Aurousseau MH, Ferriere F, Attali JR, Gattegno L (1998) Elevated concentrations of soluble E-selectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 in NIDDM. Effect of intensive insulin treatment. Diabetes Care 21(6):1008–1013
Hussain MJ, Peakman M, Gallati H, Lo SS, Hawa M, Viberti GC, Watkins PJ, Leslie RD, Vergani D (1996) Elevated serum levels of macrophage-derived cytokines precede and accompany the onset of IDDM. Diabetologia 39(1):60–69
Vargas R, Rincon J, Pedreanez A, Viera N, Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Pena C, Mosquera J (2012) Role of angiotensin II in the brain inflammatory events during experimental diabetes in rats. Brain Res 1453:64–76
Michalowska-Wender G, Adamcewicz G, Wender M (2007) Impact of cytokines on the pathomechanism of diabetic and alcoholic neuropathies. Folia Neuropathol 45(2):78–81
Kim HJ, Jung CG, Jensen MA, Dukala D, Soliven B (2008) Targeting of myelin protein zero in a spontaneous autoimmune polyneuropathy. J Immunol 181(12):8753–8760
Galloway C, Chattopadhyay M (2013) Increases in inflammatory mediators in DRG implicate in the pathogenesis of painful neuropathy in type 2 diabetes. Cytokine 63(1):1–5
Bhangoo S, Ren D, Miller RJ, Henry KJ, Lineswala J, Hamdouchi C, Li B, Monahan PE, Chan DM, Ripsch MS, White FA (2007) Delayed functional expression of neuronal chemokine receptors following focal nerve demyelination in the rat: a mechanism for the development of chronic sensitization of peripheral nociceptors. Mol Pain 3:38
Rothman SM, Ma LH, Whiteside GT, Winkelstein BA (2011) Inflammatory cytokine and chemokine expression is differentially modulated acutely in the dorsal root ganglion in response to different nerve root compressions. Spine 36(3):197–202
Matsuda M, Kawasaki F, Inoue H, Kanda Y, Yamada K, Harada Y, Saito M, Eto M, Matsuki M, Kaku K (2004) Possible contribution of adipocytokines on diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 66(Suppl 1):S121–123
Tuttolomondo A, La Placa S, Di Raimondo D, Bellia C, Caruso A, Lo Sasso B, Guercio G, Diana G, Ciaccio M, Licata G, Pinto A (2010) Adiponectin, resistin and IL-6 plasma levels in subjects with diabetic foot and possible correlations with clinical variables and cardiovascular co-morbidity. Cardiovasc Diabetol 9:50
Gottsater A, Ahren B, Sundkvist G (1999) The relationship between leptin and the insulin resistance syndrome is disturbed in type 2 diabetic subjects with parasympathetic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 22(11):1913–1914
Drel VR, Mashtalir N, Ilnytska O, Shin J, Li F, Lyzogubov VV, Obrosova IG (2006) The leptin-deficient (ob/ob) mouse: a new animal model of peripheral neuropathy of type 2 diabetes and obesity. Diabetes 55(12):3335–3343
Negi G, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2011) Melatonin modulates neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy: effects on NF-kappaB and Nrf2 cascades. J Pineal Res 50(2):124–131
Kumar A, Negi G, Sharma SS (2011) JSH-23 targets nuclear factor-kappa B and reverses various deficits in experimental diabetic neuropathy: effect on neuroinflammation and antioxidant defence. Diabetes Obes Metab 13(8):750–758
Donath MY, Shoelson SE (2011) Type 2 diabetes as an inflammatory disease. Nat Rev Immunol 11(2):98–107
Martin CL, Albers J, Herman WH, Cleary P, Waberski B, Greene DA, Stevens MJ, Feldman EL, Group DER (2006) Neuropathy among the diabetes control and complications trial cohort 8 years after trial completion. Diabetes Care 29(2):340–344
NA (1998) Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 352 (9131):837–853
Jensen TS, Backonja MM, Hernandez Jimenez S, Tesfaye S, Valensi P, Ziegler D (2006) New perspectives on the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain. Diab Vasc Dis Res 3(2):108–119
Tesfaye S, Tandan R, Bastyr EJ 3rd, Kles KA, Skljarevski V, Price KL, Ruboxistaurin Study G (2007) Factors that impact symptomatic diabetic peripheral neuropathy in placebo-administered patients from two 1-year clinical trials. Diabetes Care 30(10):2626–2632
Loesch A, Tang H, Cotter MA, Cameron NE (2010) Sciatic nerve of diabetic rat treated with epoetin delta: effects on C-fibers and blood vessels including pericytes. Angiology 61(7):651–668
Bierhaus A, Nawroth PP (2009) Multiple levels of regulation determine the role of the receptor for AGE (RAGE) as common soil in inflammation, immune responses and diabetes mellitus and its complications. Diabetologia 52(11):2251–2263
Negi G, Kumar A, Kaundal RK, Gulati A, Sharma SS (2010) Functional and biochemical evidence indicating beneficial effect of melatonin and nicotinamide alone and in combination in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Neuropharmacology 58(3):585–592
Anand P, Shenoy R, Palmer JE, Baines AJ, Lai RY, Robertson J, Bird N, Ostenfeld T, Chizh BA (2011) Clinical trial of the p38 MAP kinase inhibitor dilmapimod in neuropathic pain following nerve injury. Eur J Pain 15(10):1040–1048
Genovese MC, Cohen SB, Wofsy D, Weinblatt ME, Firestein GS, Brahn E, Strand V, Baker DG, Tong SE (2011) A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel group study of the efficacy of oral SCIO-469, a p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor, in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 38(5):846–854
Kellogg AP, Converso K, Wiggin T, Stevens M, Pop-Busui R (2009) Effects of cyclooxygenase-2 gene inactivation on cardiac autonomic and left ventricular function in experimental diabetes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 296(2):H453–461
Kellogg AP, Wiggin TD, Larkin DD, Hayes JM, Stevens MJ, Pop-Busui R (2007) Protective effects of cyclooxygenase-2 gene inactivation against peripheral nerve dysfunction and intraepidermal nerve fiber loss in experimental diabetes. Diabetes 56(12):2997–3005
Bishnoi M, Bosgraaf CA, Abooj M, Zhong L, Premkumar LS (2011) Streptozotocin-induced early thermal hyperalgesia is independent of glycemic state of rats: role of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1(TRPV1) and inflammatory mediators. Mol Pain 7:52
Waterman RS, Morgenweck J, Nossaman BD, Scandurro AE, Scandurro SA, Betancourt AM (2012) Anti-inflammatory mesenchymal stem cells (MSC2) attenuate symptoms of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Stem Cells Transl Med 1(7):557–565
Nirogi R, Jabaris SL, Jayarajan P, Abraham R, Shanmuganathan D, Rasheed MA, Royapalley PK, Goura V (2011) Antinociceptive activity of alpha4beta2* neuronal nicotinic receptor agonist A-366833 in experimental models of neuropathic and inflammatory pain. Eur J Pharmacol 668(1–2):155–162
Pabreja K, Dua K, Sharma S, Padi SS, Kulkarni SK (2011) Minocycline attenuates the development of diabetic neuropathic pain: possible anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 661(1–3):15–21
Padi SS, Kulkarni SK (2008) Minocycline prevents the development of neuropathic pain, but not acute pain: possible anti-inflammatory and antioxidant mechanisms. Eur J Pharmacol 601(1–3):79–87
Kosacka J, Nowicki M, Kloting N, Kern M, Stumvoll M, Bechmann I, Serke H, Bluher M (2012) COMP-angiopoietin-1 recovers molecular biomarkers of neuropathy and improves vascularisation in sciatic nerve of ob/ob mice. PLoS One 7(3):e32881
Bianchi R, Cervellini I, Porretta-Serapiglia C, Oggioni N, Burkey B, Ghezzi P, Cavaletti G, Lauria G (2012) Beneficial effects of PKF275-055, a novel, selective, orally bioavailable, long-acting dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor in streptozotocin-induced diabetic peripheral neuropathy. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 340(1):64–72
Cohen KL, Harris S (1987) Efficacy and safety of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the therapy of diabetic neuropathy. Arch Intern Med 147(8):1442–1444
Valsecchi AE, Franchi S, Panerai AE, Sacerdote P, Trovato AE, Colleoni M (2008) Genistein, a natural phytoestrogen from soy, relieves neuropathic pain following chronic constriction sciatic nerve injury in mice: anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activity. J Neurochem 107(1):230–240
Valsecchi AE, Franchi S, Panerai AE, Rossi A, Sacerdote P, Colleoni M (2011) The soy isoflavone genistein reverses oxidative and inflammatory state, neuropathic pain, neurotrophic and vasculature deficits in diabetes mouse model. Eur J Pharmacol 650(2–3):694–702
Kandhare AD, Raygude KS, Ghosh P, Ghule AE, Bodhankar SL (2012) Neuroprotective effect of naringin by modulation of endogenous biomarkers in streptozotocin induced painful diabetic neuropathy. Fitoterapia 83(4):650–659
Stavniichuk R, Drel VR, Shevalye H, Maksimchyk Y, Kuchmerovska TM, Nadler JL, Obrosova IG (2011) Baicalein alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy through inhibition of oxidative-nitrosative stress and p38 MAPK activation. Exp Neurol 230(1):106–113
Zhang YP, Eber A, Yuan Y, Yang Z, Rodriguez Y, Levitt RC, Takacs P, Candiotti KA (2013) Prophylactic and antinociceptive effects of coenzyme Q10 on diabetic neuropathic pain in a mouse model of type 1 diabetes. Anesthesiology 118(4):945–954
Tiwari V, Kuhad A, Chopra K (2011) Emblica officinalis corrects functional, biochemical and molecular deficits in experimental diabetic neuropathy by targeting the oxido-nitrosative stress mediated inflammatory cascade. Phytother Res 25(10):1527–1536
Shevalye H, Watcho P, Stavniichuk R, Dyukova E, Lupachyk S, Obrosova IG (2012) Metanx alleviates multiple manifestations of peripheral neuropathy and increases intraepidermal nerve fiber density in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Diabetes 61(8):2126–2133
Acknowledgments
The work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81100597), the Natural Science Foundation Project of the Chongqing Science and Technology Commission (CSTC 2009BA5012), and the Natural Science Foundation of the Third Military Medical University (2012XJQ17, 2009XQN34).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, J., Zhou, S. Inflammation: Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Neuropathy. Mol Neurobiol 49, 536–546 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8537-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8537-0