Abstract
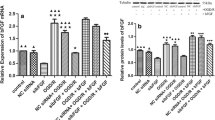
Sonic hedgehog (Shh) has been found to regulate the angiogenic growth factor such as VEGF, Ang-1, and Ang-2 during ischemic insults, but the underlying mechanism is not fully understood. In this study, we employed oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD) in astrocytes to mimic the ischemia in vitro. We found that OGD could induce the expressions of VEGF, Ang-1, and Ang-2, with the expression of Shh signaling components increased. Moreover, inhibiting the Shh signaling pathway with 5EI, a specific antibody, could decrease the expressions of VEGF, Ang-1, and Ang-2. Furthermore, the administration of exogenous Shh could induce the expressions of VEGF, Ang-1, and Ang-2 in astrocytes. The results of silencing Gli-1, or NR2F2, exhibited that exogenous Shh could regulate the expressions of VEGF, Ang-1, and Ang-2 in astrocytes by activating the NR2F2, but not the Gli-1. These results suggested that Shh could regulate the angiogenic growth factor after ischemic insults in astrocytes, and the regulation was partially mediated by the NR2F2.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pola R, Ling LE et al (2001) The morphogen Sonic hedgehog is an indirect angiogenic agent upregulating two families of angiogenic growth factors. Nat Med 7(6):706–711
Kusano KF, Pola R et al (2005) Sonic hedgehog myocardial gene therapy: tissue repair through transient reconstitution of embryonic signaling. Nat Med 11(11):1197–1204
Lee SW, Moskowitz MA et al (2007) Sonic hedgehog inversely regulates the expression of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 in fibroblasts. Int J of Mol Med 19(3):445
Sims JR, Lee SW et al (2009) Sonic hedgehog regulates ischemia/hypoxia-induced neural progenitor proliferation. Stroke; A J of Cerebral Circ 40(11):3618
Wallace VA, Raff MC (1999) A role for Sonic hedgehog in axon-to-astrocyte signalling in the rodent optic nerve. Development 126(13):2901–2909
Amankulor NM, Hambardzumyan D et al (2009) Sonic hedgehog pathway activation is induced by acute brain injury and regulated by injury-related inflammation. J Neurosci 29(33):10299–10308
Atkinson PJ, Dellovade T et al (2009) Sonic hedgehog signaling in astrocytes is dependent on p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and G-protein receptor kinase 2. J Neurochem 108(6):1539–1549
Chen Y, Swanson RA (2003) Astrocytes and brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23(2):137–149
Takano T, Oberheim NA et al (2009) Astrocytes and ischemic injury. Stroke; A J of Cerebral Circ 40(3 Suppl):S8
Hermann DM, Chopp M (2012) Promoting brain remodelling and plasticity for stroke recovery: therapeutic promise and potential pitfalls of clinical translation. Lancet Neurol 11(4):369–380
Xia YP, Dai RL et al (2012) The protective effect of sonic hedgehog is mediated by the propidium iodide 3-kinase/AKT/BCL-2 pathway in cultured rat astrocytes under oxidative stress. Neuroscience 209:1–11
He H, Zhang H et al (2010) Blockade of the sonic hedgehog signalling pathway inhibits choroidal neovascularization in a laser-induced rat model. J of Huazhong Univ of Sci and Technol–Med Sci 30(5):659–665
Zhou Y, Dai R et al (2010) Activation of sonic hedgehog signaling pathway in S-type neuroblastoma cell lines. J of Huazhong Univ of Sc and Technol–Med Sc 30(3):271–277
Pola R, Ling LE et al (2003) Postnatal recapitulation of embryonic hedgehog pathway in response to skeletal muscle ischemia. Circulation 108(4):479–485
Krishnan V, Pereira F et al (1997) Mediation of Sonic hedgehog-induced expression of COUP-TFII by a protein phosphatase. Sci (New York, NY) 278(5345):1947
Gauchat D, Escriva H et al (2004) The orphan COUP-TF nuclear receptors are markers for neurogenesis from cnidarians to vertebrates. Dev Biol 275(1):104–123
Qin J, Chen X et al (2010) COUP-TFII regulates tumor growth and metastasis by modulating tumor angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(8):3687–3692
Pereira FA, Qiu Y et al (1999) The orphan nuclear receptor COUP-TFII is required for angiogenesis and heart development. Genes Dev 13(8):1037–1049
Naka H, Nakamura S et al (2008) Requirement for COUP-TFI and II in the temporal specification of neural stem cells in CNS development. Nat Neurosci 11(9):1014–1023
Du H, Li P et al (2010) Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling implicated in neuroprotective effects of placental growth factor in an in vitro ischemic model. Brain research 1357:1–8
Straface G, Aprahamian T et al (2009) Sonic hedgehog regulates angiogenesis and myogenesis during post–natal skeletal muscle regeneration. J of Cell and Mol Med 13(8b):2424–2435
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grant 81070938 from the Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (to BH), grant 81101905 from the Program of National Natural Science Foundation of China (to LM), New Century Excellent Talents in University NCET-10-0406 (to BH), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST no.2010JC028 (to BH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Yanan Li and Yuanpeng Xia contributed equally to this project.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Xia, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Sonic Hedgehog (Shh) Regulates the Expression of Angiogenic Growth Factors in Oxygen–Glucose-Deprived Astrocytes by Mediating the Nuclear Receptor NR2F2. Mol Neurobiol 47, 967–975 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8395-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8395-9