Abstract
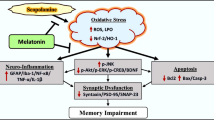
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is the most prevalent type of dementia in elderly people. There are decreased melatonin levels in the serum of AD patients, and melatonin supplements are able to reverse AD pathology and memory deficits in many animal experiments and clinical trials. However, the underlying mechanism regarding how melatonin rescues the AD-like memory/synaptic disorder remains unknown. Here, we use the Morris water maze, step-down inhibitory avoidance task, in vivo long-term potentiation recording, and Golgi staining and report that intraperitoneal injection of melatonin (1 mg/kg/day) for 14 days in rats effectively reverses the memory and synaptic impairment in scopolamine-induced amnesia, a well-recognized dementia animal model. Using real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting experiments, we further determined that melatonin rescues the EPACs/miR-124/Egr1 signal pathway, which is important in learning and memory, as reported recently. Our studies provide a novel underlying epigenetic mechanism for melatonin to attenuate the synaptic disorder and could benefit drug discovery in neurodegenerative diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chang CF, Huang HJ, Lee HC, Hung KC, Wu RT, Lin AM (2012) Melatonin attenuates kainic acid-induced neurotoxicity in mouse hippocampus via inhibition of autophagy and alpha-synuclein aggregation. J Pineal Res 52:312–321. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00945.x
Zhu LQ, Wang SH, Ling ZQ, Wang DL, Wang JZ (2004) Effect of inhibiting melatonin biosynthesis on spatial memory retention and tau phosphorylation in rat. J Pineal Res 37:71–77. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00136.xJPI136 [pii]
Zhou JN, Liu RY, Kamphorst W, Hofman MA, Swaab DF (2003) Early neuropathological Alzheimer's changes in aged individuals are accompanied by decreased cerebrospinal fluid melatonin levels. J Pineal Res 35:125–130
Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Ortiz-Lopez L, Dominguez-Alonso A, Benitez-King GA, Kempermann G (2010) Chronic treatment with melatonin stimulates dendrite maturation and complexity in adult hippocampal neurogenesis of mice. J Pineal Res 50:29–37. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2010.00802.x
Dominguez-Alonso A, Ramirez-Rodriguez G, Benitez-King G (2012) Melatonin increases dendritogenesis in the hilus of hippocampal organotypic cultures. J Pineal Res 52:427–436. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00957.x
Gonzalez-Burgos I, Letechipia-Vallejo G, Lopez-Loeza E, Morali G, Cervantes M (2007) Long-term study of dendritic spines from hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cells, after neuroprotective melatonin treatment following global cerebral ischemia in rats. Neurosci Lett 423:162–166. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.06.050
Pascual R, Bustamante C (2010) Melatonin promotes distal dendritic ramifications in layer II/III cortical pyramidal cells of rats exposed to toluene vapors. Brain Res 1355:214–220. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.07.086
Saxena G, Bharti S, Kamat PK, Sharma S, Nath C (2009) Melatonin alleviates memory deficits and neuronal degeneration induced by intracerebroventricular administration of streptozotocin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 94:397–403. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2009.09.022
Shen YX, Wei W, Yang J, Liu C, Dong C, Xu SY (2001) Improvement of melatonin to the learning and memory impairment induced by amyloid beta-peptide 25–35 in elder rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin 22:797–803
Yang X et al (2010) Melatonin ameliorates Alzheimer-like pathological changes and spatial memory retention impairment induced by calyculin A. J Psychopharmacol 25:1118–1125. doi:10.1177/0269881110367723
Agrawal R, Tyagi E, Shukla R, Nath C (2008) Effect of insulin and melatonin on acetylcholinesterase activity in the brain of amnesic mice. Behav Brain Res 189:381–386. doi:10.1016/j.bbr.2008.01.015
Schratt G (2009) microRNAs at the synapse. Nat Rev Neurosci 10:842–849. doi:10.1038/nrn2763
Lee SE, Kim SJ, Youn JP, Hwang SY, Park CS, Park YS (2011) MicroRNA and gene expression analysis of melatonin-exposed human breast cancer cell lines indicating involvement of the anticancer effect. J Pineal Res 51:345–352. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2011.00896.x
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Yin YY et al (2010) Acetyl-l-carnitine attenuates okadaic acid induced tau hyperphosphorylation and spatial memory impairment in rats. J Alzheimers Dis 19:735–746. doi:10.3233/JAD-2010-1272
Zhu LQ et al (2007) Activation of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibits long-term potentiation with synapse-associated impairments. J Neurosci 27:12211–12220. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3321-07.2007
Segal M (2005) Dendritic spines and long-term plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:277–284. doi:10.1038/nrn1649
Hsieh MT, Hsieh CL, Lin LW, Wu CR, Huang GS (2003) Differential gene expression of scopolamine-treated rat hippocampus-application of cDNA microarray technology. Life Sci 73:1007–1016
Roy D, Belsham DD (2002) Melatonin receptor activation regulates GnRH gene expression and secretion in GT1-7 GnRH neurons. Signal transduction mechanisms. J Biol Chem 277:251–258. doi:10.1074/jbc.M108890200 M108890200 [pii]
Yang Y et al (2012) EPAC null mutation impairs learning and social interactions via aberrant regulation of miR-124 and Zif268 translation. Neuron 73:774–788. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2012.02.003
Verloes R, Scotto AM, Gobert J, Wulfert E (1988) Effects of nootropic drugs in a scopolamine-induced amnesia model in mice. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 95:226–230
Brouillette J, Young D, During MJ, Quirion R (2007) Hippocampal gene expression profiling reveals the possible involvement of Homer1 and GABA(B) receptors in scopolamine-induced amnesia. J Neurochem 102:1978–1989. doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04666.x
Laurent AC, Breckler M, Berthouze M, Lezoualc'h F (2012) Role of Epac in brain and heart. Biochem Soc Trans 40:51–57. doi:10.1042/BST20110642
Ostroveanu A, van der Zee EA, Eisel UL, Schmidt M, Nijholt IM (2009) Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP 2 (Epac2) plays a specific and time-limited role in memory retrieval. Hippocampus 20:1018–1026. doi:10.1002/hipo.20700
Ouyang M, Zhang L, Zhu JJ, Schwede F, SA T (2008) Epac signaling is required for hippocampus-dependent memory retrieval. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:11993–11997
Ma N, Abel T, Hernandez PJ (2009) Exchange protein activated by cAMP enhances long-term memory formation independent of protein kinase A. Learn Mem 16:367–370. doi:10.1101/lm.1231009
Gelinas JN, Banko JL, Peters MM, Klann E, Weeber EJ, Nguyen PV (2008) Activation of exchange protein activated by cyclic-AMP enhances long-lasting synaptic potentiation in the hippocampus. Learn Mem 15:403–411. doi:10.1101/lm.830008
Ster J et al (2009) Epac mediates PACAP-dependent long-term depression in the hippocampus. J Physiol 587:101–113. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2008.157461
Gekel I, Neher E (2008) Application of an Epac activator enhances neurotransmitter release at excitatory central synapses. J Neurosci 28:7991–8002. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0268-08.2008
Woolfrey KM et al (2009) Epac2 induces synapse remodeling and depression and its disease-associated forms alter spines. Nat Neurosci 12:1275–1284. doi:10.1038/nn.2386
Enserink JM et al (2004) The cAMP-Epac-Rap1 pathway regulates cell spreading and cell adhesion to laminin-5 through the alpha3beta1 integrin but not the alpha6beta4 integrin. J Biol Chem 279:44889–44896. doi:10.1074/jbc.M404599200 M404599200 [pii]
Lopez De Jesus M et al (2006) Cyclic AMP-dependent and Epac-mediated activation of R-Ras by G protein-coupled receptors leads to phospholipase D stimulation. J Biol Chem 281:21837–21847. doi:10.1074/jbc.M604156200
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T (2007) The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 27:435–448. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2007.07.015
Clokie SJ, Lau P, Kim HH, Coon SL, Klein D (2012) Micro RNAs in the pineal gland: mir-483 regulates melatonin synthesis by targeting arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.356733
Masilamoni JG et al (2008) The neuroprotective role of melatonin against amyloid beta peptide injected mice. Free Radic Res 42:661–673. doi:10.1080/10715760802277388
Jeong JK, Moon MH, Lee YJ, Seol JW, Park SY (2012) Melatonin-induced autophagy protects against human prion protein-mediated neurotoxicity. J Pineal Res. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2012.00980.x
Lee EJ et al (2005) Melatonin attenuates gray and white matter damage in a mouse model of transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Pineal Res 38:42–52. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2004.00173.x
Asayama K, Yamadera H, Ito T, Suzuki H, Kudo Y, Endo S (2003) Double blind study of melatonin effects on the sleep-wake rhythm, cognitive and non-cognitive functions in Alzheimer type dementia. J Nihon Med Sch 70:334–341
Uchida K, Okamoto N, Ohara K, Morita Y (1996) Daily rhythm of serum melatonin in patients with dementia of the degenerate type. Brain Res 717:154–159
Crozier RA, Bi C, Han YR, Plummer MR (2008) BDNF modulation of NMDA receptors is activity dependent. J Neurophysiol 100:3264–3274. doi:10.1152/jn.90418.2008
Evans GJ, Cousin MA (2007) Activity-dependent control of slow synaptic vesicle endocytosis by cyclin-dependent kinase 5. J Neurosci 27:401–411. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3809-06.2007
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30971478, 91132725, 31201011), the New Century Excellent Talent of Education Ministry (NCET-10-0421), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2011DFG33250), the New Investigator Research Grant of Alzheimer’s Association (NIRG-11-205737), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities, HUST, (nos. 0118510011 and 0118510019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Xiong Wang and Zhi-Hao Wang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, ZH., Wu, YY. et al. Melatonin Attenuates Scopolamine-Induced Memory/Synaptic Disorder by Rescuing EPACs/miR-124/Egr1 Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 47, 373–381 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8355-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8355-9