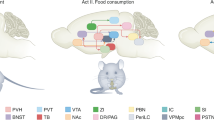
Abstract
The prevalence of obesity and its associated medical complications, including type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease, continues to rise globally. Lifestyle changes in the last decades have greatly contributed to the current obesity trends. However, inheritable biological factors that disrupt the tightly regulated equilibrium between caloric intake and energy expenditure also appear to play a critical part. Mounting evidence obtained from human and rodent studies suggests that perturbed brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) signaling in appetite-regulating centers in the brain might be a culprit. Here, we review findings that inform the critical roles of BDNF and its receptor TrkB in energy balance and reward centers of the brain impacting feeding behavior and body weight.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Patapoutian A, Reichardt LF (2001) Trk receptors: mediators of neurotrophin action. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:272–280
Reichardt LF (2006) Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 361:1545–1564
Donovan MJ, Lin MI, Wiegn P, Ringstedt T, Kraemer R, Hahn R, Wang S, Ibanez CF, Rafii S, Hempstead BL (2000) Brain derived neurotrophic factor is an endothelial cell survival factor required for intramyocardial vessel stabilization. Development 127:4531–4540
Ernfors P, Lee KF, Jaenisch R (1994) Mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor develop with sensory deficits. Nature 368:147–150
Carter AR, Chen C, Schwartz PM, Segal RA (2002) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor modulates cerebellar plasticity and synaptic ultrastructure. J Neurosci 22:1316–1327
Korte M, Carroll P, Wolf E, Brem G, Thoenen H, Bonhoeffer T (1995) Hippocampal long-term potentiation is impaired in mice lacking brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:8856–8860
McAllister AK, Katz LC, Lo DC (1997) Opposing roles for endogenous BDNF and NT-3 in regulating cortical dendritic growth. Neuron 18:767–778
Lapchak PA, Hefti F (1992) BDNF and NGF treatment in lesioned rats: effects on cholinergic function and weight gain. Neuroreport 3:405–408
Martin-Iverson MT, Todd KG, Altar CA (1994) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 activate striatal dopamine and serotonin metabolism and related behaviors: interactions with amphetamine. J Neurosci 14:1262–1270
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Wellman CL (1995) Characteristics of BDNF-induced weight loss. Exp Neurol 131:229–238
Kernie SG, Liebl DJ, Parada LF (2000) BDNF regulates eating behavior and locomotor activity in mice. EMBO J 19:1290–1300
Lyons WE, Mamounas LA, Ricaurte GA, Coppola V, Reid SW, Bora SH, Wihler C, Koliatsos VE, Tessarollo L (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor-deficient mice develop aggressiveness and hyperphagia in conjunction with brain serotonergic abnormalities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:15239–15244
Xu B, Goulding EH, Zang K, Cepoi D, Cone RD, Jones KR, Tecott LH, Reichardt LF (2003) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy balance downstream of melanocortin-4 receptor. Nat Neurosci 6:736–742
Fox EA, Byerly MS (2004) A mechanism underlying mature-onset obesity: evidence from the hyperphagic phenotype of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mutants. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 286:R994–R1004
Rios M, Fan G, Fekete C, Kelly J, Bates B, Kuehn R, Lechan RM, Jaenisch R (2001) Conditional deletion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the postnatal brain leads to obesity and hyperactivity. Mol Endocrinol 15:1748–1757
Coppola V, Tessarollo L (2004) Control of hyperphagia prevents obesity in BDNF heterozygous mice. Neuroreport 15:2665–2668
Unger TJ, Calderon GA, Bradley LC, Sena-Esteves M, Rios M (2007) Selective deletion of Bdnf in the ventromedial and dorsomedial hypothalamus of adult mice results in hyperphagic behavior and obesity. J Neurosci 27:14265–14274
Yeo GS, Connie Hung CC, Rochford J, Keogh J, Gray J, Sivaramakrishnan S, O’Rahilly S, Farooqi IS (2004) A de novo mutation affecting human TrkB associated with severe obesity and developmental delay. Nat Neurosci 7:1187–1189
Gray J, Yeo GS, Cox JJ, Morton J, Adlam AL, Keogh JM, Yanovski JA, El Gharbawy A, Han JC, Tung YC, Hodges JR, Raymond FL, O’Rahilly S, Farooqi IS (2006) Hyperphagia, severe obesity, impaired cognitive function, and hyperactivity associated with functional loss of one copy of the brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) gene. Diabetes 55:3366–3371
Han JC, Liu QR, Jones M, Levinn RL, Menzie CM, Jefferson-George KS, Adler-Wailes DC, Sanford EL, Lacbawan FL, Uhl GR, Rennert OM, Yanovski JA (2008) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and obesity in the WAGR syndrome. N Engl J Med 359:918–927
Monteleone P, Tortorella A, Martiadis V, Serritella C, Fuschino A, Maj M (2004) Opposite changes in the serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in anorexia nervosa and obesity. Psychosom Med 66:744–748
Suwa M, Kishimoto H, Nofuji Y, Nakano H, Sasaki H, Radak Z, Kumagai S (2006) Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor level is increased and associated with obesity in newly diagnosed female patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 55:852–857
Beckers S, Peeters A, Zegers D, Mertens I, Van Gaal L, Van Hul W (2008) Association of the BDNF Val66Met variation with obesity in women. Mol Genet Metab 95:110–112
Skledar M, Nikolac M, Dodig-Curkovic K, Curkovic M, Borovecki F, Pivac N (2011) Association between brain-derived neurotrophic factor Val66Met and obesity in children and adolescents. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry [Epub ahead of print].
Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, Allen HL, Lindgren CM, Luan J, Magi R, Randall JC, Vedantam S, Winkler TW, Qi L, Workalemahu T, Heid IM, Steinthorsdottir V, Stringham HM, Weedon MN, Wheeler E, Wood AR, Ferreira T, Weyant RJ, Segre AV, Estrada K, Liang L, Nemesh J, Park JH, Gustafsson S, Kilpelainen TO, Yang J, Bouatia-Naji N, Esko T, Feitosa MF, Kutalik Z, Mangino M, Raychaudhuri S, Scherag A, Smith AV, Welch R, Zhao JH, Aben KK, Absher DM, Amin N, Dixon AL, Fisher E, Glazer NL, Goddard ME, Heard-Costa NL, Hoesel V, Hottenga JJ, Johansson A, Johnson T, Ketkar S, Lamina C, Li S, Moffatt MF, Myers RH, Narisu N, Perry JR, Peters MJ, Preuss M, Ripatti S, Rivadeneira F, Sandholt C, Scott LJ, Timpson NJ, Tyrer JP, van Wingerden S, Watanabe RM, White CC, Wiklund F, Barlassina C, Chasman DI, Cooper MN, Jansson JO, Lawrence RW, Pellikka N, Prokopenko I, Shi J, Thiering E, Alavere H, Alibrandi MT, Almgren P, Arnold AM, Aspelund T, Atwood LD, Balkau B, Balmforth AJ, Bennett AJ, Ben-Shlomo Y, Bergman RN, Bergmann S, Biebermann H, Blakemore AI, Boes T, Bonnycastle LL, Bornstein SR, Brown MJ, Buchanan TA et al (2010) Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet 42:937–948
Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Gudbjartsson DF, Steinthorsdottir V, Sulem P, Helgadottir A, Styrkarsdottir U, Gretarsdottir S, Thorlacius S, Jonsdottir I, Jonsdottir T, Olafsdottir EJ, Olafsdottir GH, Jonsson T, Jonsson F, Borch-Johnsen K, Hansen T, Andersen G, Jorgensen T, Lauritzen T, Aben KK, Verbeek AL, Roeleveld N, Kampman E, Yanek LR, Becker LC, Tryggvadottir L, Rafnar T, Becker DM, Gulcher J, Kiemeney LA, Pedersen O, Kong A, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2009) Genome-wide association yields new sequence variants at seven loci that associate with measures of obesity. Nat Genet 41:18–24
Shimizu E, Hashimoto K, Iyo M (2004) Ethnic difference of the BDNF 196 G/A (val66met) polymorphism frequencies: the possibility to explain ethnic mental traits. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 126:122–123
Chen ZY, Jing D, Bath KG, Ieraci A, Khan T, Siao CJ, Herrera DG, Toth M, Yang C, McEwen BS, Hempstead BL, Lee FS (2006) Genetic variant BDNF (Val66Met) polymorphism alters anxiety-related behavior. Science 314:140–143
Noble EE, Billington CJ, Kotz CM, Wang C (2011) The lighter side of BDNF. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 300:R1053–R1069
Dietrich MO, Horvath TL (2009) Feeding signals and brain circuitry. Eur J Neurosci 30:1688–1696
Simpson KA, Martin NM, Bloom SR (2009) Hypothalamic regulation of food intake and clinical therapeutic applications. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 53:120–128
Yan Q, Radeke MJ, Matheson CR, Talvenheimo J, Welcher AA, Feinstein SC (1997) Immunocytochemical localization of TrkB in the central nervous system of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 378:135–157
Wang C, Bomberg E, Billington C, Levine A, Kotz CM (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus reduces energy intake. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1003–R1012
Pinto S, Roseberry AG, Liu H, Diano S, Shanabrough M, Cai X, Friedman JM, Horvath TL (2004) Rapid rewiring of arcuate nucleus feeding circuits by leptin. Science 304:110–115
Sternson SM, Shepherd GM, Friedman JM (2005) Topographic mapping of VMH --> arcuate nucleus microcircuits and their reorganization by fasting. Nat Neurosci 8:1356–1363
Antoni FA, Palkovits M, Makara GB, Linton EA, Lowry PJ, Kiss JZ (1983) Immunoreactive corticotropin-releasing hormone in the hypothalamoinfundibular tract. Neuroendocrinology 36:415–423
Koylu EO, Couceyro PR, Lambert PD, Ling NC, DeSouza EB, Kuhar MJ (1997) Immunohistochemical localization of novel CART peptides in rat hypothalamus, pituitary and adrenal gland. J Neuroendocrinol 9:823–833
Toni R, Lechan RM (1993) Neuroendocrine regulation of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in the tuberoinfundibular system. J Endocrinol Invest 16:715–753
Toriya M, Maekawa F, Maejima Y, Onaka T, Fujiwara K, Nakagawa T, Nakata M, Yada T (2010) Long-term infusion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor reduces food intake and body weight via a corticotrophin-releasing hormone pathway in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus. J Neuroendocrinol 22:987–995
Wang C, Godar RJ, Billington CJ, Kotz CM (2010) Chronic administration of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus reverses obesity induced by high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 298:R1320–R1332
Anand BK, Brobeck JR (1951) Localization of a “feeding center” in the hypothalamus of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 77:323–324
Penicaud L, Larue-Achagiotis C, Le Magnen J (1983) Endocrine basis for weight gain after fasting or VMH lesion in rats. Am J Physiol 245:E246–E252
Valenstein ES, Cox VC, Kakolewski JW (1968) Modification of motivated behavior elicited by electrical stimulation of the hypothalamus. Science 159:1119–1121
King BM (2006) The rise, fall, and resurrection of the ventromedial hypothalamus in the regulation of feeding behavior and body weight. Physiol Behav 87:221–244
Komori T, Morikawa Y, Nanjo K, Senba E (2006) Induction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor by leptin in the ventromedial hypothalamus. Neuroscience 139:1107–1115
Tran PV, Akana SF, Malkovska I, Dallman MF, Parada LF, Ingraham HA (2006) Diminished hypothalamic bdnf expression and impaired VMH function are associated with reduced SF-1 gene dosage. J Comp Neurol 498:637–648
Aid T, Kazantseva A, Piirsoo M, Palm K, Timmusk T (2007) Mouse and rat BDNF gene structure and expression revisited. J Neurosci Res 85:525–535
Tran PV, Lee MB, Marin O, Xu B, Jones KR, Reichardt LF, Rubenstein JR, Ingraham HA (2003) Requirement of the orphan nuclear receptor SF-1 in terminal differentiation of ventromedial hypothalamic neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 22:441–453
Sugiyama N, Kanba S, Arita J (2003) Temporal changes in the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus of the developing rat brain. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 115:69–77
Wang C, Bomberg E, Levine A, Billington C, Kotz CM (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the ventromedial nucleus of the hypothalamus reduces energy intake. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R1037–R1045
Nakagawa T, Tsuchida A, Itakura Y, Nonomura T, Ono M, Hirota F, Inoue T, Nakayama C, Taiji M, Noguchi H (2000) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates glucose metabolism by modulating energy balance in diabetic mice. Diabetes 49:436–444
Tonra JR, Ono M, Liu X, Garcia K, Jackson C, Yancopoulos GD, Wiegand SJ, Wong V (1999) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor improves blood glucose control and alleviates fasting hyperglycemia in C57BLKS-Lepr(db)/lepr(db) mice. Diabetes 48:588–594
Date Y, Ueta Y, Yamashita H, Yamaguchi H, Matsukura S, Kangawa K, Sakurai T, Yanagisawa M, Nakazato M (1999) Orexins, orexigenic hypothalamic peptides, interact with autonomic, neuroendocrine and neuroregulatory systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:748–753
Zamir N, Skofitsch G, Jacobowitz DM (1986) Distribution of immunoreactive melanin-concentrating hormone in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res 373:240–245
Bray GA, Inoue S, Nishizawa Y (1981) Hypothalamic obesity. The autonomic hypothesis and the lateral hypothalamus. Diabetologia 20(Suppl):366–377
Satoh N, Ogawa Y, Katsuura G, Numata Y, Tsuji T, Hayase M, Ebihara K, Masuzaki H, Hosoda K, Yoshimasa Y, Nakao K (1999) Sympathetic activation of leptin via the ventromedial hypothalamus: leptin-induced increase in catecholamine secretion. Diabetes 48:1787–1793
Wang C, Bomberg E, Billington C, Levine A, Kotz CM (2007) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus increases energy expenditure by elevating metabolic rate. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 293:R992–R1002
Wang C, Bomberg E, Billington CJ, Levine AS, Kotz CM (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus increases energy expenditure. Brain Res 1336:66–77
Nonomura T, Tsuchida A, Ono-Kishino M, Nakagawa T, Taiji M, Noguchi H (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates energy expenditure through the central nervous system in obese diabetic mice. Int J Exp Diabetes Res 2:201–209
Tsuchida A, Nonomura T, Ono-Kishino M, Nakagawa T, Taiji M, Noguchi H (2001) Acute effects of brain-derived neurotrophic factor on energy expenditure in obese diabetic mice. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 25:1286–1293
Fan W, Ellacott KL, Halatchev IG, Takahashi K, Yu P, Cone RD (2004) Cholecystokininmediated suppression of feeding involves the brainstem melanocortin system. Nat Neurosci 7(4):335–336
Conner JM, Lauterborn JC, Yan Q, Gall CM, Varon S (1997) Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: evidence for anterograde axonal transport. J Neurosci 17:2295–2313
Bariohay B, Lebrun B, Moyse E, Jean A (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor plays a role as an anorexigenic factor in the dorsal vagal complex. Endocrinology 146:5612–5620
Bariohay B, Roux J, Tardivel C, Trouslard J, Jean A, Lebrun B (2009) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor/tropomyosin-related kinase receptor type B signaling is a downstream effector of the brainstem melanocortin system in food intake control. Endocrinology 150:2646–2653
Bassareo V, De Luca MA, Di Chiara G (2002) Differential expression of motivational stimulus properties by dopamine in nucleus accumbens shell versus core and prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 22:4709–4719
Hernandez L, Hoebel BG (1988) Food reward and cocaine increase extracellular dopamine in the nucleus accumbens as measured by microdialysis. Life Sci 42:1705–1712
Rada P, Avena NM, Hoebel BG (2005) Daily bingeing on sugar repeatedly releases dopamine in the accumbens shell. Neuroscience 134:737–744
Numan S, Lane-Ladd SB, Zhang L, Lundgren KH, Russell DS, Seroogy KB, Nestler EJ (1998) Differential regulation of neurotrophin and trk receptor mRNAs in catecholaminergic nuclei during chronic opiate treatment and withdrawal. J Neurosci 18:10700–10708
Numan S, Seroogy KB (1999) Expression of trkB and trkC mRNAs by adult midbrain dopamine neurons: a double-label in situ hybridization study. J Comp Neurol 403:295–308
Okazawa H, Murata M, Watanabe M, Kamei M, Kanazawa I (1992) Dopaminergic stimulation up-regulates the in vivo expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in the striatum. FEBS Lett 313:138–142
Freeman AY, Soghomonian JJ, Pierce RC (2003) Tyrosine kinase B and C receptors in the neostriatum and nucleus accumbens are co-localized in enkephalin-positive and enkephalin-negative neuronal profiles and their expression is influenced by cocaine. Neuroscience 117:147–156
Cordeira JW, Frank L, Sena-Esteves M, Pothos EN, Rios M (2010) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor regulates hedonic feeding by acting on the mesolimbic dopamine system. J Neurosci 30:2533–2541
Baquet ZC, Bickford PC, Jones KR (2005) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for the establishment of the proper number of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. J Neurosci 25:6251–6259
Pu L, Liu QS, Poo MM (2006) BDNF-dependent synaptic sensitization in midbrain dopamine neurons after cocaine withdrawal. Nat Neurosci 9:605–607
Bina KG, Cincotta AH (2000) Dopaminergic agonists normalize elevated hypothalamic neuropeptide Y and corticotropin-releasing hormone, body weight gain, and hyperglycemia in ob/ob mice. Neuroendocrinology 71:68–78
Fulton S, Pissios P, Manchon RP, Stiles L, Frank L, Pothos EN, Maratos-Flier E, Flier JS (2006) Leptin regulation of the mesoaccumbens dopamine pathway. Neuron 51:811–822
Teegarden SL, Nestler EJ, Bale TL (2008) Delta FosB-mediated alterations in dopamine signaling are normalized by a palatable high-fat diet. Biol Psychiatry 64:941–950
Stice E, Spoor S, Bohon C, Veldhuizen MG, Small DM (2008) Relation of reward from food intake and anticipated food intake to obesity: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Abnorm Psychol 117:924–935
Bello NT, Lucas LR, Hajnal A (2002) Repeated sucrose access influences dopamine D2 receptor density in the striatum. NeuroReport 13:1575–1578
Monteleone P, Zanardini R, Tortorella A, Gennarelli M, Castaldo E, Canestrelli B, Maj M (2006) The 196 G/A (val66met) polymorphism of the BDNF gene is significantly associated with binge eating behavior in women with bulimia nervosa or binge eating disorder. Neurosci Lett 406:133–137
Koizumi H, Hashimoto K, Itoh K, Nakazato M, Shimizu E, Ohgake S, Koike K, Okamura N, Matsushita S, Suzuki K, Murayama M, Higuchi S, Iyo M (2004) Association between the brain-derived neurotrophic factor 196 G/A polymorphism and eating disorders. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 127:125–127
Nakazato M, Hashimoto K, Shimizu E, Kumakiri C, Koizumi H, Okamura N, Mitsumori M, Komatsu N, Iyo M (2003) Decreased levels of serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor in female patients with eating disorders. Biol Psychiatry 54:485–490
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by NIH grant DK073311 to MR.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cordeira, J., Rios, M. Weighing in the Role of BDNF in the Central Control of Eating Behavior. Mol Neurobiol 44, 441–448 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8212-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8212-2