Abstract
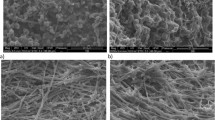
In this study, the rheology, morphology and mechanical properties of microfibrillar composites based on polypropylene reinforced with polyamide 6 (PA6) fibres have been investigated. Influence of different factors such as the PA6 composition and drawing ratio on the output of the extruder, and the compatibilizer composition on the properties of these composites, were investigated. The results of rheometric mechanical spectrometer rheological measurements and melt flow index (MFI) showed that the storage modulus, loss modulus and complex viscosity of the microfibrillar composites are directly related to the composition of PA6. It was also shown that the presence of compatibilizer was the main factor that led to decrease of some properties including the storage modulus, loss modulus and complex viscosity and increase in the MFI. The results of mechanical tests on samples prepared with different drawing ratios showed that by increasing the drawing ratio from 3 to 5, the mechanical properties increase, while increasing draw ratio from 5 to 8 reduces the mechanical properties. With the increase in the composition of the polyamide phase, the tensile strength of microfibrillar composite compatible with polypropylene-grafted-maleic anhydride initially increased; however, the tensile strength decreased with a high composition of polyamide phase. Scanning electron microscope images also revealed that the presence of the compatibilizer in the microfibrillar composites leads to decrease in the number of undeformed drops, while it reduces the micro-fibres diameter, which greatly improved the final properties of the composites.














Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharyya D and Fakirov S 2012 Synthetic polymer–polymer composites (Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG)
Fakirov S and Bhattacharyya D 2015 Engineering biopolymers: homopolymers, blends, and composites (Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH Co KG)
Yi X et al 2010 Eur. Polym. J. 46 719
Bigdeli A et al 2012 J. Polym. Res. 19 1
Chomat D et al 2015 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 10 1002
Huang W Y et al 2003 Polym. Int. 52 1131
Jayanarayanan K et al 2009 Eur. Polym. J. 45 1738
Li X et al 1997 Polym. J. 29 975
Naficy S and Garmabi H 2007 Compos. Sci. Technol. 67 3233
Pesneau I et al 2002 Polym. Eng. Sci. 42 1990
Shen J et al 2011 Polym. Adv. Technol. 22 237
Tavanaie M, Shoushtari A and Goharpey F 2010 J. Macromol. Sci. B: Phys. 49 163
Xu H S et al 2004 Macromol. Mater. Eng. 289 1087
Zoldan J, Siegmann A and Narkis M 2005 J. Macromol. Sci. B: Phys. 44 495
Li Z et al 2002 Polym.-Plast. Technol. Eng. 41 19
Houshyar S, Shanks R and Hodzic A 2005 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 96 2260
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Safaei, A., Masoomi, M. & Razavi, S.M.R. In-situ microfibrillar PP–PA6 composites: rheological, morphological and mechanical properties. Bull Mater Sci 40, 971–982 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1469-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-017-1469-y