Abstract
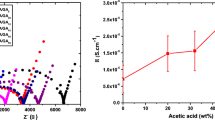
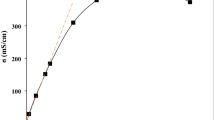
Ionic drift velocity (v d) measurements of a new Ag+ ion conducting glass-polymer electrolytes (GPEs): (1−x) PEO : x [0.8(0.75AgI : 0.25AgCl) : 0.2(Ag 2O : V2O5)], where 0 < x < 50 wt%, were reported. GPEs were casted using the hot-press techniques developed in recent times. The composition: 70PEO : 30[0.8(0.75AgI : 0.25AgCl) : 0.2(Ag2O : V2O5)] with conductivity (σ) ∼ 7.7 × 10−7 S cm−1 was identified as highest conducting composition from the compositional-dependent conductivity studies. The ionic mobility (μ), mobile ion concentration (n), ionic transference number (t ion) and ionic drift velocity (v d) of GPEs were determined at different temperatures with the help of the d.c. polarization technique and other well-known important relations.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fenton D E, Parker J M and Wrigth P V 1973 Polymer 14 589
Chandra S 1981 Superionic solids—principle and applications (Amsterdam: North Holland Publisher)
Scrosati B 1993 Applications of electroactive polymers (London: Chapman & Hall)
Choudhary S and Sengwa R J 2012 Indian J. Phys. 86 335
Sharma J P and Sekhon S S 2013 Bull. Mater. Sci. 36 629
Armand M B 1987 Polymer electrolyte reviews (London: Elsevier Publisher)
Cho J and Liu M 1977 Electrochim. Acta 42 1481
Kumar B, Schaffer J D, Nookala M and Scanlon L G 1994 J. Power Sources 47 63
Zhang X W, Wang C, Appleby A J and Little F E 2002 J. Power Sources 112 209
Appetecchi G B, Croce F, Persi L, Ronci F and Srosati B 2000 Electrochim. Acta 45 1481
Appetecchi G B, Croce F, Hasson J, Scrosati B, Salomon M and Cassel F 2003 J. Power Sources 114 105
Chandra A, Agrawal R C and Mahipal Y K 2009 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 42 135107
Chandra A 2010 Eur. Phys. J. Appl. Phys. 50 21103
Chandra A and Chandra A 2010 Hot-pressed polymer electrolytes: synthesis and characterization (Germany: Lambert Academic Publisher)
Choudhary S and Sengwa R J 2011 Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 49 204
Chandra A, Chandra A, Bhatt A and Thakur K 2012 Int. J. Chem. 1 209
Chandra A 2013 Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 51 788
Chandra A 2013 Indian J. Phys. 87 643
Chandra S, Tolpadi S K and Hashmi S A 1988 Solid State Ion. 28–30 651
Gray F M 1991 Polymer electrolytes: fundamentals and technological applications (New York: VCH Publisher)
Agrawal R C and Pandey G P 2008 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 41 223001
Cohen M H and Turnbull D 1959 J. Chem. Phys. 31 1164
Chandra A, Chandra A, Thakur S S and Chakrawarti V 2011 AIP Conf. Proc. 1372 238
Agrawal R C and Chandra A 2007 J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys. 40 7024
Acknowledgement
I gratefully acknowledge SERB DST, New Delhi, for providing financial assistance through the ‘Fast Track Young Scientist Research Project’ (No. SR/FTP/PS-23/2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHANDRA, A. Ionic drift velocity measurement on hot-pressed Ag+ ion conducting glass-polymer electrolytes. Bull Mater Sci 38, 1743–1747 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-1107-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-1107-5