Abstract
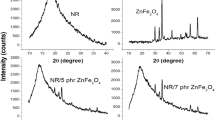
ZnO nanoparticles were synthesized by a precipitation method in aqueous media from zinc nitrate hexahydrate and sodium hydroxide. The synthesized ZnO nanoparticles exhibited a crystalline structure with hexagonal structure of the wurtzite. The morphology of the synthesized ZnO nanoparticles presented a spherical shape with the average primary size of 54.53 nm and the specific surface area of 20.28 m2 g−1. The effect of the synthesized ZnO nanoparticles by the precipitation method as a crosslinking agent for chloroprene rubber foam (CR foam ) on cure characteristics, mechanical properties and morphologies was investigated. The aim of this study is to vary the synthesized ZnO nanoparticles’ level in the range of 0.5–5 parts per hundred parts of rubber (phr) compared with the conventional ZnO at 5 phr. The rheological characterization showed that the maximum torque (M H ), the minimum torque (M L ), the differential torque (M H– M L ) and Mooney viscosity increased with the increase in synthesized ZnO nanoparticles’ content, whereas the optimum cure time (t 90 ) and scorch time (T5) decreased. On the other hand, the mechanical properties such as hardness, tensile strength and specific gravity were improved. For CR foam, the results compared to the amount of conventional ZnO, only 60 wt% (3 phr ) nano-ZnO was enough to obtain similar cure characteristics and mechanical properties. The synthesized ZnO nanoparticles showed the mechanical properties higher than conventional ZnO because of small particle size and large specific surface area which led to the increase in the degree of crosslinking.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Suntako R 2014 Adv. Mater. Res. 1025–1026 525
Aimable A, Buscaglia M T, Buscaglia V and Bowen P 2010 J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 30 591
Faure B, Alvarez G S, Ahniyaz A, Villaluenga I, Berriozabal G, Miguel Y D and Bergstrom L 2013 Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 14 1
Baskoutas S, Giabouranis P, Yannopoulos S N, Dracopoulos V, Toth L, Chrissanthopoulos A and Bouropoulos N 2007 Thin Solid Films 515 8461
Rani S, Suri P, Shishodia P K and Mehra R M 2008 Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. C 92 1639
Suntako R 2014 Adv. Mater. Res. 1044–1045 23
Sangari N U and Devi S C 2013 J. Solid State Chem. 197 483
Sharma D, Rajput J, Kaith B S, Kaur M and Sharma S 2010 Thin Solid Films 519 1224
Suntako R 2014 Appl. Mech. Mater. 481 60
Raoufi D 2013 Renew. Energy 50 932
Nejati K, Rezvani Z and Pakizevand R 2011 Int. Nano Lett. 1 75
Skapin S D, Drazic G and Orel Z C 2007 Mater. Lett. 61 2783
Kumar S S, Venkateswarlu P, Rao V R and Rao G N 2013 Int. Nano Lett. 3 30
Sahoo S, Maiti M, Ganguly A, George J J and Bhowmick A K 2007 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 105 2407
Kim I J, Kim W S, Lee D H, Kim W and Bae J W 2010 J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 117 1535
Wang H, Li C, Zhao H, Li R and Liu J 2013 Powder Technol. 239 266
Akhlaghi S, Kalaee M, Mazinani S, Jowdar E, Nouri A, Sharif A and Sedaghat N 2012 Thermochim. Acta 527 91
Przybyszewska M, Zaborski M, Jakubowski B and Zawadiak J 2009 Express Polym. Lett. 3 256
Tang M Z, Xing W, Wu J R, Huang G S, Li H and Wu S D 2014 Chin. J. Polym. Sci. 32 658
Scott J C, White G D F, Thom D J, Whitny R A and Hopkins W 2003 J. Polym. Sci. Part A 41 1915
Kim J H, Choi K C and Yoon J M 2006 J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 12 795
Zhang B S, Lv X F, Zhang Z X, Liu Y, Kim J K and Xin Z X 2010 Mater. Des. 31 3106
Acknowledgements
I gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the Research Promotion and Technology Transfer Center (RPTTC), Faculty of Liberal Arts and Science, Kasetsart University Kamphaeng Saen Campus and the Kasetsart University Research and Development Institute (KURDI).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
SUNTAKO, R. Effect of zinc oxide nanoparticles synthesized by a precipitation method on mechanical and morphological properties of the CR foam. Bull Mater Sci 38, 1033–1038 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0921-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-015-0921-0