Abstract
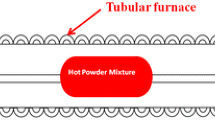
Phosphorous is treated as an impurity in conventional steels owing to segregation of phosphorous and formation of brittle phosphides along the grain boundaries. It is responsible for cold and hot shortness in wrought steels. In conventional powder metallurgy, involving compaction and sintering, high phosphorous content (up to 0·7%) in Fe-based alloys exhibit attractive set of mechanical and magnetic properties. These powder-processed alloys suffer from increasing volumetric shrinkage during sintering as phosphorous is increased beyond 0·6%. Thus both cast as well as conventional powder metallurgy routes have their own limitations in dealing with iron–phosphorous alloys. Hot-powder forging was used in the present investigation for the development of high-density soft magnetic materials containing 0·3–0·8% phosphorous to overcome these difficulties. It was observed that phosphorous addition improves the final density of the resulting product. It was further observed that hot-forged iron–phosphorous alloys have excellent hot/cold workability and could be easily shaped to thin strips (0·5–1·0 mm thick) and wires (0·5–1·0 mm diameter). The powder hot-forged alloys were characterized in terms of microstructure, porosity content/densification, hardness, soft magnetic properties and electrical resistivity. Magnetic properties such as coercivity 0·35–1·24 Oe, saturation magnetization 14145–17490 G and retentivity 6402–10836 G were observed. The obtained results were discussed based on the microstructures evolved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chandra K 2004 Design and development of Fe–P based powder metallurgical magnetic materials, PhD Thesis, IIT Roorkee
Das J 2006 To develop and characterize high density Fe–P based P/M alloys, MTech Dissertation, IIT Roorkee
Das J, Chandra K, Mishra P S and Sarma B 2008 J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 320 906
Hanejko F G, Rutz H G and Oliver C G 1992 Effects of processing and materials on soft magnetic performance of powder metallurgy parts, Presented at the 1992 Powder Metallurgy World Congress, San Francisco, CA (www.hoeganaes.com)
Hopkins H E and Tipler H R 1958 J. Iron Steel Institute 188 218
Lund 1985 Int. J. Powder Metall. Powder Technol. 21 47
Lindskog P, Tengzelius J and Kvist S A 1977 Powder Metall. 10 97
Moyer K H 1998 ASM Handbook Powder Metall. Appl. 7 1006
Panasyuk O A and Radomysel I D 1973 Institute of Material Science, Academy of Sciences of the Ukrainian SSR, Translated from Poroshkovaya Metallurgiya 4 124 29
Rutz H G and Hanejko F G 1994 High density processing of high performance ferrous materials, Presented at the international conference and exhibition on powder metallurgy and particulate materials, Toronto, Canada (www.hoeganaes.com) Technical publications library
Shimada Y, Matsunuma K, Nishioka T, Ikegaya A, Itou Y and Koiso T 2003 SEI Technical Review 56 46
Sudan A S and Misra P S 1991 Indian Patent No. 184576
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
CHAURASIA, S.K., PRAKASH, U., MISRA, P.S. et al. Development of P/M Fe–P soft magnetic materials. Bull Mater Sci 35, 191–196 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-012-0272-z
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12034-012-0272-z